Table Of Contents
What Is Mobile Money?
Mobile money refers to a mobile-based system offering technique to store and manage money in an account connected to a mobile phone. Financial institutions and telecom operators offer it for purposes such as remittances, microloans, managing business finances, shopping, emergency funds, and personal savings.
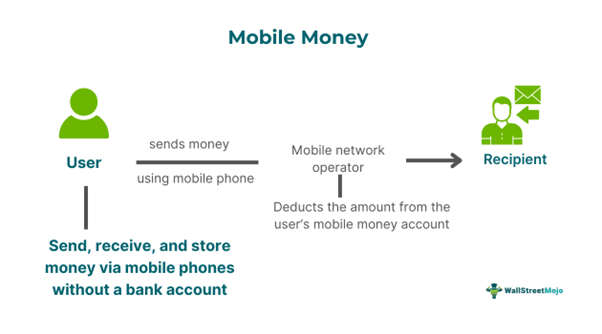
People can store, request, and transfer money through their mobile phones without the help of a traditional bank accounts. It has been beneficial in increasing financial inclusion, developing regions and countries with low banking penetration due to its convenient and secure access to financial services.
Key Takeaways
- Mobile money focuses on specialized mobile-based payment methods for financial services and transactions through accounts with mobile operators.
- It facilitates personal savings, emergency funds, remittances, microloans, business financial management, and shopping via financial institutions and telecom providers.
- Advantages include easy online payments, seamless checkout, financial inclusion, convenience, security for businesses, and extending services to underserved populations.
- Mobile money requires only a mobile number for transactions, while mobile banking necessitates a registered bank account number.
Mobile Money Explained
Mobile money is a system enabling simple way for making payment and transferring money using a mobile device. It involves directing financial transactions and managing money through mobile devices, including savings, transfers, and payments. It operates through a network of agents rather than banks, using only mobile phones with money accounts. This system mainly benefit unbanked individuals who have minimal or no access to traditional banking infrastructure by providing access to access to financial services outside of conventional banks.
Users must register to create an account linked to their mobile numbers, which act as account identifiers, similar to how T-Mobile Money functions. Transactions use security features like PINs, and money can be transferred or accessed through SMS commands, making it user-friendly for those without internet access.
Mobile money has empowered small businesses and low-income individuals by providing access to a range of low-cost financial services. It has also included people in areas with limited banking services in the scope of financial inclusion. It stimulates local economies by increasing transaction efficiency and reducing cash handling costs.
Globally, mobile money has been widely adopted, with over 1 billion accounts registered. It has become the preferred choice for many in developing nations due to its speed, security, and lower costs. Studies have shown that it positively impacts GDP and contributes significantly to economic development.
Additionally, it has enhanced government monetary policies in underbanked regions. Although mobile money has become a strong alternative to traditional banking, it currently does not offer mobile money order deposits.
Examples
Let us use a few good examples to understand the topic.
Example #1
The company that operates the largest cryptocurrency exchange, Binance, has launched its One Click Buy and Sell (OCBS) feature in Africa, allowing users in Ghana, Tanzania, Uganda, and Zambia to buy and sell cryptocurrencies via mobile money accounts. This eases the financial inclusion of the unbanked and underbanked populations by integrating mobile money facility into its crypto trading platform. In other words, this integration simplifies access to digital assets. The system also follows the security commitment with stringent Know Your Customer (KYC) protocols to protect user assets and ensure regulatory compliance.
Example #2
Another example is M-Pesa, it’s a popular mobile money service in Africa. M-Pesa has more than 60 million customers in the financial year ending 31 March 2024. Its broad range of services, strategy of serving micro-payments and positive social impact such as aiding small businesses and reducing poverty, attributed to its success.
Advantages
Mobile money offers several benefits, including:
- Promoting financial inclusion for populations with limited or no banking infrastructure.
- Allowing businesses to receive payments conveniently and securely without expensive equipment.
- Enabling merchants to accept payments online through card transactions, bank transfers, and digital methods.
- Providing a seamless checkout experience with integrated payment options for apps and websites.
- Simplifying payment collection with automated systems using payment links across various channels.
- Eliminating the need for an app or website to collect payments directly.
- Extending financial services across borders, reaching underserved and underbanked populations.
Mobile Money Vs. Mobile Banking
Mobile Money
- Requires only a mobile number for transactions.
- Provided by private entities, mainly telecom operators.
- Focuses on merchant payments and peer-to-peer transfers.
- Functions primarily as a digital wallet.
- Operates independently of the traditional banking sector.
- Provides access to banking in remote and rural areas.
- Aims to include the unbanked population in financial services.
Mobile Banking
- Requires a registered bank account number.
- Offered by traditional banks.
- Covers all types of banking services, including account management.
- Part of a broader digital banking system.
- Integrated with the banking sector.
- Serves urban and semi-urban banked populations.
- Offers a wide range of services to banked individuals.
