Table Of Contents
Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) Definition
A memorandum of understanding (MOU) is an initial level of consent shown by the involved parties in a document to proceed with certain mutually agreed objectives. For example, two countries signing an MOU to outline the terms of their upcoming trade partnership.
Key Takeaways
- A memorandum of understanding (MOU) is a written set of roles, responsibilities, terms, conditions, restrictions, and expectations of the parties involved in a collaboration.
- It is a bilateral or multilateral document where the MOU parties are private companies, public sector units, international organizations, non-profit organizations, or even countries.
- A memorandum of understanding is not a legally binding contract. However, it could contain clauses to treat certain terms with a legal agreement during the course of the collaboration.
- It reveals the intention of the collaborating parties and also assures of an upcoming legally backed agreement. Thus, an MOU lays the foundation for a memorandum of agreement (MOA).
How does Memorandum of Understanding Work?
- You must have heard of the numerous MOUs signed between the nations. For example, recently, China and Russia agreed to build a lunar research station, reportedly on the moon's surface, for which a memorandum of understanding was signed. So, what purpose does an MOU serve?
- As the name suggests, the term "memorandum" refers to a letter, while "understanding" is a process of knowing someone's intentions. An MOU is a written bilateral or multilateral declaration of certain mutually accepted goals directed to help the parties involved. MOU essentially specifies the purpose, goals, and a rough roadmap of the collaboration to the parties involved. MOUs can be commonly found in business deals, mergers, takeovers, government tenders, international trades, etc.
- In an MOU, the parties mention a detailed description of the conditions, expectations, roles, responsibilities, obligations, compensation, and restrictions for each other. Both the parties show a willingness to move ahead with the collaboration towards fulfilling the terms mentioned in the MOU.
Steps Involved while Drafting an MOU
An MOU is usually a five-step process that involves planning, drafting, negotiating, timeline negotiation, and restrictions. For example, in this MOU between WHO and UNODC -
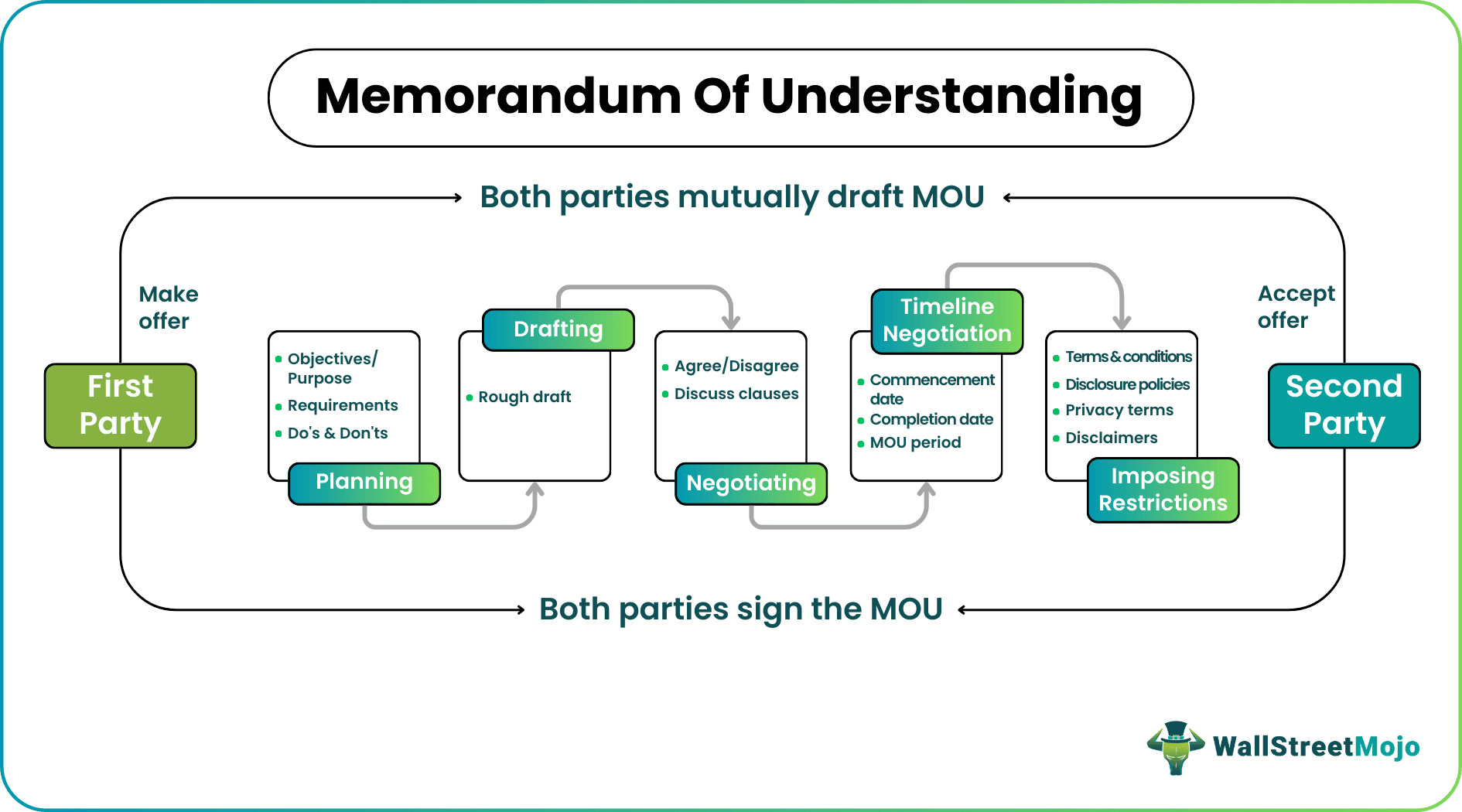
- For MOU planning, both parties have put forward their objectives, requirements, dos, and don'ts to reduce drug abuse and ensure the treatment of such disorders globally.
- In the next step, the parties make a rough layout of the memorandum. They then go through the various listed points in the draft to reach a consensus.
- Then, the involved parties decide a time frame for the commencement and completion of the MOU, i.e., five years in this case. Also, they ascertain the specific conditions, including those around non-fulfilment, that could result in the termination of the MOU.
- The parties then state all the mutually agreed disclosure policies, privacy terms, disclaimers, and confidential information.
- Finally, the MOU is duly signed and accepted by both parties.
Examples
Given below is a sample or a template of the memorandum of understanding between two educational institutions collaborating for the admission/recruitment process.

Now that we know how an MOU looks like, let's have a look at the essential components included in the above memorandum of understanding sample/template -
- Introduction of Parties/Partners: This section of MOU consists of a brief on the parties, i.e., the entity names and kinds of business activities they perform.
- Purpose: When we say objective, it reflects that both the parties' reason and intention are to work together.
- Roles and Responsibilities: An MOU lists the duties, roles, functions, and responsibilities of each partner.
- Funding: The amount or share each partner readily agrees to invest in the project appears in the funding section.
- Period: The MOU should state the duration for which such collaboration lasts. This part of an MOU consists of the commencement date, the end date, and the conditions that may result in these dates' alteration.
- Confidentiality: Since any dealing involves the exchange of confidential facts between the partners, they have to agree with the non-disclosure policies of this MOU.
- Dispute Resolution: While the MOU is not legally binding, it has a simple clause of settling disputes through mutual discussion and negotiation between the partners.
- Disclaimer: In this MOU clause, the partners promise to adhere to all the federal and state laws.
- Conditions of Alteration or Termination: This clause of an MOU reflects all those situations/events responsible for discontinuing an MOU.
- Contact Person: Each company assigns a representative to proceed with the dealing; this part includes their names, contact numbers, and addresses.
- Signature: The document should be duly signed by the authorized persons or representatives of both organizations.
- Date of Signing the MOU: This is when both the partners' representatives duly sign the MOU document.
Is Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) Legally Binding?
- In case of non-adherence by one party, the other cannot challenge an MOU in a court of law. Therefore, we can say that it isn't a legally binding document.
- Non-legality has been a contentious issue for many countries. This special story talks about how it is not considered good to walk away from an MOU in Chinese civil law. As such, in some countries, MOUs hold some form of ethical responsibility.
- Besides, in some instances, MOU contains a legal clause added with the parties' consent. In such a case, the MOU can be considered a legally binding document. In India, any MOU fulfilling the criteria for a contract as prescribed by Section 10 of the Indian Contracts Act 1872 can be juridical. The four major elements of a legally binding MOU are offer, acceptance, the intention of legal binding, and consideration.
- Despite not being legally binding in many cases, an MOU jots down an initial roadmap for collaboration, making it popular. Moreover, when two parties enter into a collaboration, over its course, a legal contract usually comes into the picture. MOUs normally serve as an easy base for such proceedings.
Memorandum of Understanding vs Memorandum of Agreement
- An MOU is a formal document signed by the collaborating parties before going for a memorandum of agreement (MOA). That means an MOU gives an overview of the terms and conditions or acts as the foundation point for an MOA.
- Many of us use these terms interchangeably; however, these documents are way different from each other in the real world. While an MOU is not always legally enforceable, an MOA can be challenged by any aggrieved parties in the court of law. Also, an MOU that involves a financial transaction often becomes legally binding to the collaborating parties.
- An MOU doesn't provide any rights to the involved parties; however, an MOA offers collateral rights.
- Many colossal business entities, non-profit organizations, government organizations, and countries seek for business, resource, scientific and infrastructure collaborations to ensure rapid development in the respective fields. But they prefer signing an MOU with their partners before entering into a final agreement or contract.
