Table Of Contents
What Is Materials Management?
Materials management refers to a more efficient administration of materials or firms' input. It will invariably result in a rise in the effectiveness of the company as a whole. Therefore, it is necessary for every industry that deals with distributing and delivering a significant number of raw materials and is a part of their supply chain management.
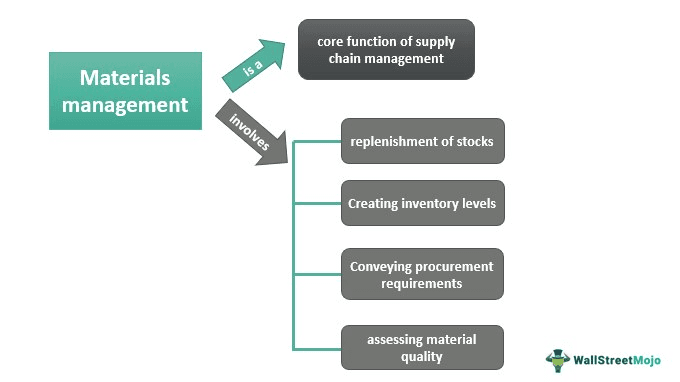
Materials management focuses on the right supplier, the right amount, the right pricing, the right quality, and the right timing. In addition, it entails the planning and control of materials, the procurement of raw materials, the planning, and control of inventories, production planning, and waste management.
Key Takeaways
- In materials management, controlling the flow of materials is one of the primary focuses.
- It ensures that producers have access to the specific resources they require precisely when needed.
- Material management ensures that the materials are of good quality and purchased from reliable vendors.
- It involves techniques like MRP - Material Requirement Planning and ERP - Enterprise Resource Planning.
Materials Management Explained
Materials management is responsible for successfully satisfying production demand. It requires a significant amount of coordination, particularly with the operations of material flow, coordination, sequencing, and the return of transport goods.
The materials handling task group is comprised of experienced members of the industry who are responsible for the design of material racks, as well as the enhancement of density and quality characteristics, to facilitate the efficient transit of goods into assembly facilities. The "life cycle" study of racks and the best practices around the recycling and life-maximization of shelves, including safety issues, exhaustion, and load management, is the current topic among the organization's members.
The management and planning of the supply chain include a component called materials management. The basic objective of materials management is to supply manufacturers with all the raw materials required to complete their wares' production.
In addition, the management of materials emphasizes preventing the loss of any individual components and achieving the highest possible efficiency in the maintenance and administration of stock. Therefore, in addition to being significantly involved in inventory management and storage, materials management needs a grasp of what materials are required and where they can be obtained to function properly.
Functions of Materials Management
#1 - Production And The Management Of Materials
The production manager is responsible for preparing production schedules that will be carried out in the future. The production schedules are the basis for determining the requirements for the various components and materials. Orders that have been placed or estimates of future demand for a product are considered when developing production schedules. To ensure that manufacturing runs without a hitch, every category or component of the raw materials is made available.
#2 - Purchasing
The purchasing department can create purchase agreements based on other departments' requisitions. This section maintains contracts with the various suppliers and regularly gathers quotations and other relevant information. This division will make every attempt to make purchases of appropriate items of appropriate quality at affordable costs.
Purchasing is a management action that extends beyond the basic act of buying and involves the planning and policy activities spanning a wide variety of activities that are connected to and complementary to one another. This means that purchasing is more than just an act of buying something.
Stores not used in producing non-production items such as office supplies, perishable tools, maintenance, repair, and operational supplies are kept in stock according to the company's requirements. One may not need these retailers daily, but having them available is necessary. Furthermore, labor can halt if these kinds of businesses are unavailable.
#3 - Transportation
One of the most significant functions of materials management is transporting materials from various suppliers. The responsibility for coordinating transportation service falls on the shoulders of the traffic department. Either the company will have to buy the cars themselves or find a third party to provide them on a rental basis. Everything relies on the amount and the frequency of the material purchases. The goal is to secure economic and practical transport facilities for the commodities.
It concerns the flow of materials inside a production organization, and the cost of handling materials is controlled. It is also observed that no material losses or wastages occur while the materials are being moved. For material handling, specialized apparatus may be purchased.
#4 - Receiving
The receiving department is in charge of unloading commodities, counting the units, verifying the quality of the items, and sending them to retailers, among other responsibilities. In addition, the purchasing department is kept apprised of the arrival of various materials.
Techniques
1. Material Requirement Planning
MRP stands for material requirement planning. A business must conduct accurate resource planning to guarantee that its manufacturing processes and activities are carried out correctly. Without such planning, the businesses risk being confronted with issues associated with the supply chain, such as production, output, etc.
MRP is a scheduling, project planning, and inventory planning methodology. It gives managers the ability to anticipate the number of raw materials that will be required for manufacturing. As a result, it makes it simpler for the managers to oversee, arrange, and put together the components.
2. Enterprise Resource Planning
ERP is an updated version of MRP, whereas MRP was exclusively used for material planning. ERP stands for "Enterprise Resource Planning." It encompasses the planning of all company-related operations. It refers to the business software essential to managing an organization's resources effectively. ERP gives the materials manager access to several useful and important tools that assist in administrating production resources, including materials and other resources.
In addition, the ERP has a consolidated database that streamlines procedures while cutting down on manual labor. It came about as a result of companies' subsequent realization that managing their office operations and MRP systems was important.
Importance
- The proportion of the overall cost devoted to materials is maintained at an acceptable level. The application of scientific purchasing assists in procuring resources at more affordable costs. The efficient storage of resources also contributes to the reduction of the wastage of such items. These aspects contribute to the overall cost-effectiveness of the items.
- The price of indirect materials is closely monitored to ensure accuracy. However, because there is not always enough control over indirect inputs, the cost of those items might sometimes contribute to an increase in the overall cost of manufacturing.
- There are no equipment breakdowns because of the late delivery of materials since there is no delay in the materials supply.
- There is no reduction in the amount of direct labor.
- The transportation of the materials and the stage of storage where they are maintained are monitored closely to prevent any unnecessary material waste.
- The delivery of the products is on time. There are just a few cases where they were late.
- Both under and over-stocking are prevented, which helps to keep the expenses related to the supplies under control.
- As a result, there is less crowding in retail establishments and the various production phases.
Best practices
#1 - Use Explicit Rules For Material Quality
Maintaining control over the material quality is helpful by ensuring that the person responsible for buying is extremely careful while making their selections. However, having a predetermined list of criteria that must be satisfied before purchasing or utilizing an item is a foolproof method for staying on top of this situation.
Having these company-wide rules eliminate any misunderstanding. It also ensures that standards can be maintained even in the absence of particular individuals.
#2 - Make Smart Selections Of Providers
Firms will want to select vendors with a history of earning a reputation for offering high-quality materials. On the other hand, various additional traits may be investigated, which may prove useful from a strategic standpoint. For example, when a last-minute order comes in, the geographic location of any given source may affect how soon one can get their hands on things.
The potential partner's degree of adaptability, level of transparency, and proficiency in communicating are all qualities that should be taken into consideration throughout the selection process. In the long term, firms will want to work with a provider that comprehends their requirements and is compatible with their business's values.
#3 - Employ A Specialist As Materials Manager
It is essential to have a person in a position of authority who is in charge of monitoring all aspects covered up to this point. Accountability is established when a specific worker is assigned to perform a task. As a result, there is a greater likelihood of meeting the duties.
Having a focal point also ensures that other employees always have someone to go to if they face significant obstacles. This key individual will be able to organize and execute strategies and implement plans. The strategies that they have developed will also act as a model for others to follow.
#4 - Use The "Just-In-Time" Inventory Control Approach
Many approaches to stock control may be utilized to increase the productivity of resources. Just-in-time manufacturing is one idea that illustrates this type of scenario. This strategy adheres to the thinking that one should not begin sourcing materials until after a client has already placed an order with the company.
This strategy can include risk, but if carried out correctly, it will lower the quantity of material inside the supply chain at any given time. It is possible to apply several different techniques, such as lean manufacturing or six sigma; nevertheless, the most important thing is to pick the successful one.
#5 - Maintain A Well-Organized Warehouse
The area where the goods are stored must have some organization in the architecture of the space. This will make it simpler to locate products at the precise moment they are required. Also, it will reduce the likelihood of anything going wrong because there will be less confusion.
