Table Of Contents
What Is Material Flow?
The material flow is a sequence of processes which describes the journey of raw materials starting from their extraction, processing, conversion to end products and final delivery to consumers. Thus products are created from materials, making them an important factor in a production company.
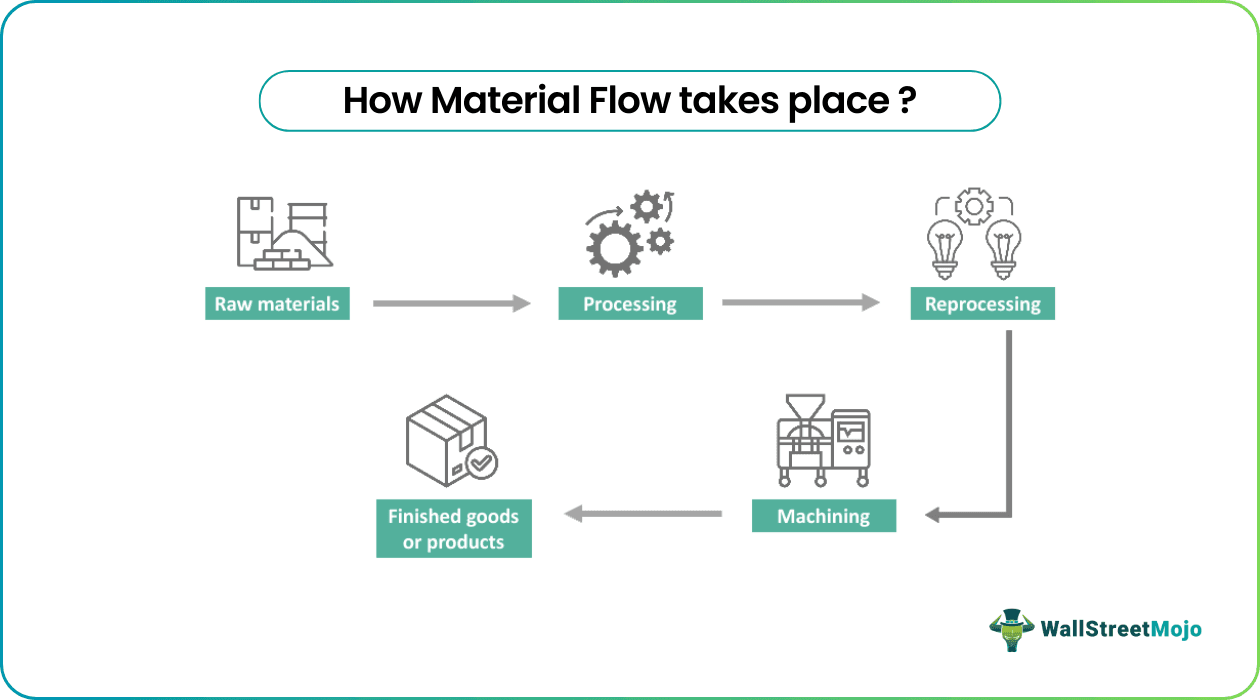
The modeled flows are often designed in a way that meets customer expectations. The flow helps in accurately tracking the process's progress, locating products and parts quickly, and bringing stability to the production cycle. This helps deliver the end product to the customers within the stipulated time with the expected quality.
Key Takeaways
- Material flow is a systematic approach to understanding materials from the extraction of raw materials, processing, and manufacturing to their final disposition.
- Good material flow systems reduce the costs involved, speed up the process, decrease movement time, eliminate waste, and clear congestion.
- When a business has a "good" material flow, materials move consistently and predictably at each stage of the process.
- A "poor" flow involves frequent stops and starts, ultimately leading to an ineffective system.
- The flow of materials can be divided into two categories: internal and external.
Material Flow Process Explained
Material flow is a supply chain management model that displays how work moves through a system. It represents the movement of raw materials and components for work-in-progress inventory, and finished goods inventory as a directional process.
When a business has a "good" flow, goods move consistently and predictably at each stage of the process. A "poor" flow involves frequent stops and starts, ultimately leading to an ineffective system. The flow is a wonderful place to start when a business wants to adopt lean practices. Lean manufacturing advocates using a pull system and necessary technologies to ensure supplies move across the facility efficiently.
The company loses time, money, and resources when production stops in the middle of a process, and items are left in storage. A lack of proper material flow systems can make it challenging for managers to place timely reorders of materials. Too much inventory could cause lengthy lead times (the delay between the start and finish of a procedure) and defective issues.
A facility's movement of materials should be examined from all angles, including warehousing, production, shipping, and acceptance. The objective is to have a level flow and complete departmental alignment. The next step for leaders is locating the flow points that do not benefit the business or the client. These areas can then be upgraded or optimized to maximize production and efficiency.
Types
Material flow can be divided into two categories - internal and external.
#1 - External Flow
The logistics of external material flow is transporting raw materials and finished goods.
#2 - Internal Flow
The internal flow begins with the supply of raw materials, parts, or subassemblies to the arrival of goods to the warehouse. It concludes with the transfer of finished or semi-finished goods to the departing goods department. Therefore, the in-house material flow includes all transportation operations between warehouses for arriving and exiting commodities.
Examples
Check out these examples to get a better idea:
Example #1
Suppose Matthew is the manager of a small manufacturing company. He was concerned about the low-profit rates his company was making due to delays in the delivery of products. Matthew decided to look into the flow of the business by creating a material flow diagram. He discovered there was a delay in collecting the product components from one stage to another. This was due to improper "information flow," where communication was not promptly happening. After realizing this, he took steps toward recovery and significantly improved his profit.
Example #2
AGCO, an agricultural equipment manufacturer, stayed afloat during the COVID-19 pandemic due to its supply chain management application. When there was an issue, the application showed a graphical view of the company's supply chains across various supplier tiers. If any suppliers' continued flow was in trouble, it illustrated the components' flow to various other factories and nodes in the supply chain.
Later, their commodity managers were notified to ease the situation. The final delivery of a product relies heavily on how well the flow has been followed to get the products to the supply chain. Management of this supply chain helped them in delivering the products. Therefore, material flow management is a vital part of the process.
Importance
The flow symbolizes the logistics chain from the supplier to the client, which can be efficiently and sustainably optimized based on routine material flow assessments. These analyses help find the weak spots in the flow. In addition to that, these assessments document the processing, storage, and transport operations. The optimal design of the flow ensures a reduction in costs, speeds up throughput, and eliminates waste.
The flow's importance can be expressed through the following points:
- It minimizes travel time by rerouting supplies.
- Orders can be filled more quickly and accurately by removing superfluous procedures and automating operations that are still done by hand. This will result in better-satisfied clients. Additionally, happy consumers are more likely to return, increasing long-term revenue.
- It ensures streamlined processes via flow analysis, through which redundancies can be eliminated, turnaround times can be shortened, and operational expenses can be decreased.
- Manufacturing companies can save money on capital expenditures. By conducting a material flow analysis, they drastically cut the costs associated with processing, storing, and transporting commodities.
- Manufacturers can discover waste in production and learn how to manage labor and resources effectively by doing a flow analysis.
- The required number of workers and equipment reduces by optimizing the movement of a component through the manufacturing process.
- Manufacturers can use material flow analysis to reduce travel time and clear congestion by rerouting materials.
Material Flow And Information Flow
Here is a comparison between the two:
| Key points | Material Flow | Information Flow |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Material flow is the process of moving materials within an organization. | Information flow is a model of how information is disseminated within an organization. |
| Process | The flow facilitates the movement of goods from the start until the process is completed and reaches the consumers. | Information flow in logistics facilitates cooperation between a supplier and a recipient of goods as it connects the many nodes in the supply chain. |
| Direction | This low is unidirectional. | Information can move in both directions (up and down), unlike the movement of products. |
