Table Of Contents
What Is Market Model?
A market model is a numerical representation of the interaction between market forces and economic situations. It helps to forecast the outcomes of a business or plan activities like production, sales, prices, or improvement strategies in an organization to understand global markets and identify opportunities in them.
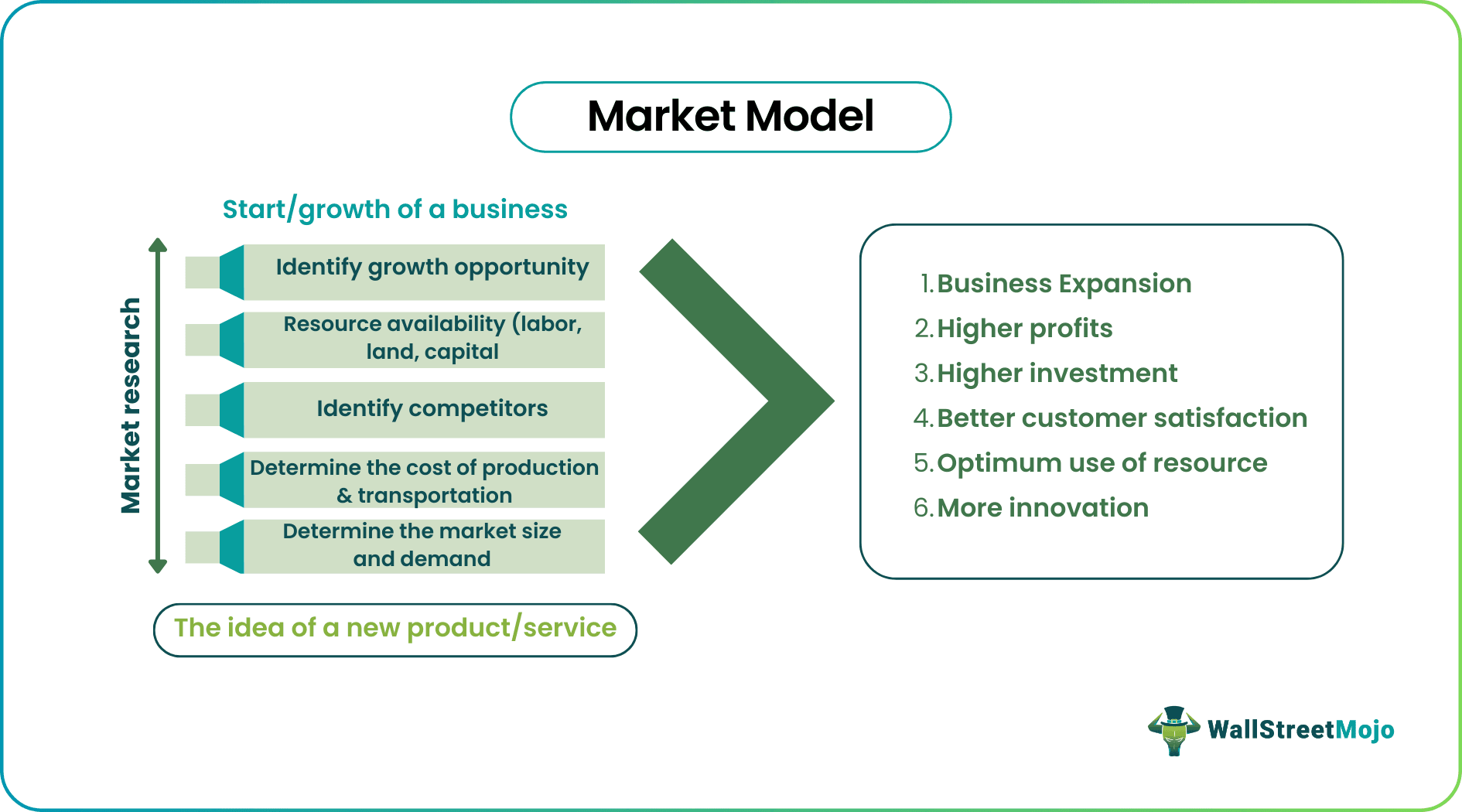
It helps evaluate a business based on its historical and current financial data, product competition, market size, types of target customers, and industry trends. This information predicts the business's earning potential and future investment and expansion opportunity, considering various risk factors and deviations due to changing economic and political scenarios.
Table of contents
- What Is Market Model?
- A market model represents the interaction of market forces and economic conditions in numerical terms.
- It helps a business predict future performance and plan activities like marketing and sales, pricing, production, or implementing improvement ideas.
- It identifies growth and investment opportunities in the market for expansion with optimum use of resources and at minimum cost.
- Through these models, it is possible to identify the correct target customers and reduce underperformance risk, which is otherwise difficult to analyze or control.
Market Model Explained
Market models in economics refer to the interaction of market forces of demand and supply and the economic trends in a country. It helps to plan and manage business activities like production, sales, marketing, finance, etc., through maximum use of resources with minimum cost, which is extremely important in an economy because many other models are derived from it. Companies use them to launch new products and services, expand a business, make innovations, and identify key competitors and functions that have an essential role to play.
A financial market model uses past and current financial data, revenue drivers, cost drivers, ratios, leverage, liquidity levels, and trend analysis to plan an entry into a new market or expand in the existing areas. In addition, the business can identify unexplored areas or target customers through a market assessment, which helps focus on growth and expansion.
There are various types of competitive market model that an organization can use in its framework. Understanding which model will fit best in the business environment is essential. In addition, they help compare a company with its peers and the sector as a whole. The financial market model also shows profitability, solvency, and efficiency, indicating whether the business is running well or needs improvement.
A stock market model elaborates on the fact that the return earned on stock will depend on the portfolio return that the investor holds and the stock's volatility, which is measured by beta.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
Types
There are four basic types of market models in economics:
1. Pure Competition
In this type of market, a large number of firms are there that manufacture standardized products. The interaction of supply and demand determines the prices of products. Thus, it is a competitive market model where the suppliers or manufacturers do not have any influence over the prices, which implies that they are the price takers. In pure competition, firms can enter or leave the market at any time. We can refer to the market for agricultural goods as an example of this model.
2. Monopolistic Competition
This model is very close to pure competition because it has a low entry barrier and many suppliers. But each supplier tries to make their product different in some respects so that it is possible to get a better price than the competitors.
Products like clothes, cosmetics, restaurants, hotels, etc., fall into this category. In addition, firms often use interesting advertising techniques or innovative designs and attributes in their product to make them different from others and convince consumers to buy them, which is called product differentiation.
3. Oligopoly
In Oligopoly, only a few firms operate in the market. The product prices are fixed. The firms try to come together to minimize competition and, in the process, negotiate the prices of goods and services. The firms determine how much money should be invested in marketing and advertising, sales promotion, etc.
The businesses depend on each other because a firm will fix prices depending on the reaction of its competitor. In this market model, firms either have a vast reserve of natural resources or sell any patented product and are financially robust, due to which there is a high entry barrier. Thus, each firm influences the price of its development. Companies in the steel industry, media, telephone, etc., fall into this category.
4. Monopoly
There is just one firm operating in the market which controls the supply, demand, and prices. There is no close substitute for that product, and the entry barrier is very high. In a monopoly model, the supplier can charge different prices for the same product at different quantity levels. It can also set different prices for the same quantity from other consumers. They do this keeping in mind their customers' income and demand level. The electricity supplier is a perfect example of the same.
The above are the broad categories of market models. There are many models created using the above, like the stock market model, the labor market model, the loanable fund market or the model for the money market, and the market for foreign exchange.
Examples
Some market model examples will help in analyzing the topic better:
Example #1
Waterworks Company, a specialist in plumbing services and manufacturing of plumbing products, is located in Boston, Massachusetts. The products and services offered by the company are the best in the market. Due to continuous infrastructure development for commercial and residential purposes, the demand for its products and services is rising.
However, Waterworks Company has recently noticed a demand for water pipes that are heat-resistant and clogging-free, especially in residential projects far away from the city, and people need access to plumbers immediately. They need to clean the clogged pipes or replace them with entirely new lines, which is both time-consuming and expensive.
The company decided to use this opportunity to enter into the new segment of heat-resistant and clogging-free pipes. It analyzed the following:
- Market size to determine the current demand.
- The manufacturing cost.
- Competitors who might enter the future market.
- Growth opportunities within and outside the country.
- Transport cost of bringing the various raw materials for manufacturing.
- The availability of skilled labor in the market to handle the process.
Based on the above study and other assumptions, the company developed a model to capture the market quickly that helped increase the market presence and cater to customers in a new segment.
Example #2
According to the study by McKinsey & Company, the new payment models entering the US market are a threat to the credit card lending business. As per the data, 37% of US consumers use credit cards to purchase. But slowly, the growing point-of-sale (POS) financing process is replacing credit cards. This market model is a combination of credit card and installment lending.
However, credit card issuers already have an established market. A huge chunk of customers uses the credit card facility regularly. Moreover, credit cards offer facilities like short-term loans, deposits, etc., which are its strength. Thus, whether the credit card facility can sustain itself in the competitive market is yet to be seen.
Market Model vs CAPM
A market model is used to identify the demand and supply levels of a product in the market, which can be used for market expansion, planning production and investment, or forecasting the future profitability of a business. In contrast, the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) shows the relationship between risk and return on investment. Now, let us analyze the difference between them.
| Market Model | CAPM |
| It is a model to predict a business’s future and expansion or investment plans. | It is a model used to calculate an investment’s expected return. |
| It is the primary model from which various other business models are designed. | It is a market model used in corporate finance, also called the financial model. |
| It helps companies modify production, sales, or marketing plans to earn more profit. | It helps companies choose between many options to finance the business. |
| In this model, the main factors are demand and supply. | In this model, the main factors are a risk-free rate of a treasury bill, the beta (risk of investment), and the market risk premium. |
| It helps to understand whether a business can meet the required target. | It helps to understand whether an investment is worth it or not. |
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A variable dependent on another variable is called an endogenous variable. For example, in the goods market, factors like income, quantity, price equilibrium, interest rate, etc., are endogenous because of changes in other factors like consumer preference, income, economic growth, and availability of substitutes.
In this model, the laborers or workers try to secure the best job that satisfies both money and work. Employers also try to hire the best talent available in the market. The labor market works under the demand and supply forces of labor. A supply and demand gap is created because of both skilled and unskilled labor in the market.
A unique product exists only in the case of a monopoly. Monopoly firms control the market because they produce a product that has no substitutes. Thus, the product is unique, which helps the firm to control the market demand, supply, and price. They charge prices based on the income level or demand of customers.

