Table Of Contents
What Is Margin Account?
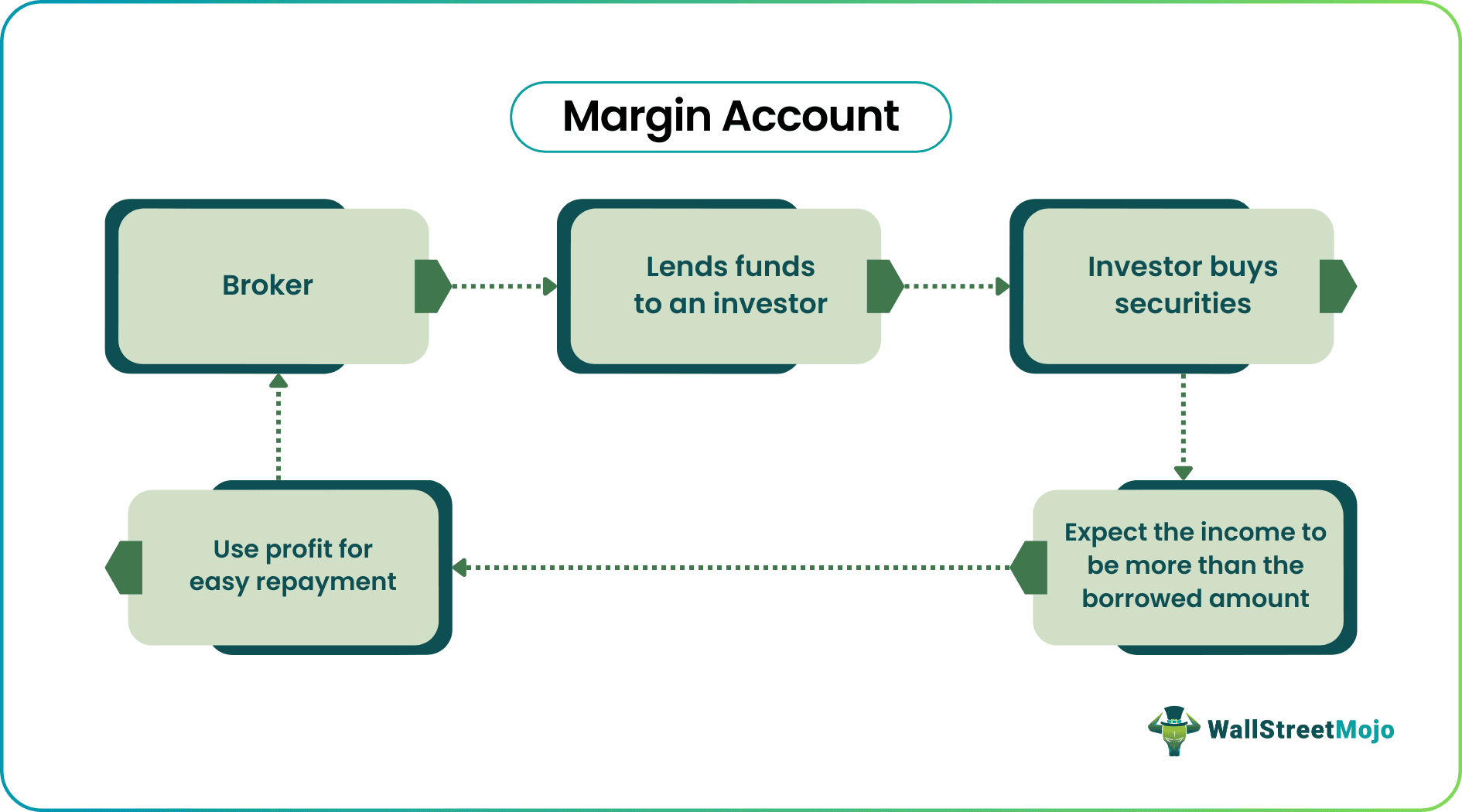
Margin accounts are loans offered by a broker to an investor. The broker uses the margin account as collateral. Therefore, the investor's purchasing power increases. Characteristically, buying on margin is a high-risk strategy.
It is also referred to as a loan account. The loan account facilitates purchasing financial instruments—bonds, futures, and options—the investor signs a separate margin account agreement to open a loan account.
Table of contents
- What Is Margin Account?
- Margin accounts refer to loans that allow investors to borrow cash from brokerage firms. Using the extra funds, investors trade in securities. Therefore, it is also referred to as a loan account.
- Since the amount borrowed can be used to acquire assets and generate capital, it is also known as financial leverage. Furthermore, investors use this borrowing approach to earn more and profit.
- For the loan, the brokerage charges an interest rate from the investor. If the investor accrues losses, they can repay a substantial amount quickly. Therefore, this investment strategy is only recommended for experienced investors.
How Does Margin Account Work?
Margin accounts are loans offered by a broker to an investor. Therefore, It is also referred to as a loan account. Buying on margin helps investors buy financial products—bonds, futures, and options.
Simply put, investors borrow funds and use the borrowed amount for investing. A brokerage offers the loan. Naturally, the brokerage charges interest from the investor. If the investor accrues losses, they can repay a substantial amount quickly. High risk is the characteristic feature of buying on margin. Therefore, it is recommended only for experienced investors.
This method of investment is known as leveraging. Financial leverage is using borrowed amounts to purchase assets, build capital, and expand a business. This method helps investors maximize profits by earning more than the cost of borrowing
A loan account can be opened with a broker or firm with certain requirements. But, again, due to the strategy's high-risk nature, investors must thoroughly research the particular investment's pros and cons. In addition, they need to monitor the investment closely and compare it with their risk tolerance.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
Requirements
The margin account requirements are as follows:
- An investor interested in opening a loan account must first deposit $2000 or 100% cash equivalents of the stock they wish to purchase.
- A brokerage loan account has a 50% borrowing limit—50% of the stock value—known as the initial margin requirement or restriction.
- When an investor buys on margin, the brokerage attaches a maintenance margin to the account—typically 25%. But this maintenance margin varies from firm to firm; it can even go up to 40% of the security's value.
- A margin call is issued if an investor falls below the minimum margin. Similarly, lack of funds and interest repayment defaults also raise margin calls.
- A brokerage firm charges a yearly interest rate on a loan offered to the investor. Typically interests on margin loans range between 2% and 4%. But it may vary depending on the particular firm. Interests on these loans are called margin interest rates.
Examples
Let us look at some margin account examples to understand the concept better.
Example #1
Phil buys a stock for $90. Soon, the stock price rises to $135. If Phil sells the stock, he will earn a 50% return and receive the full payment.
Now, let us assume that Phil bought the stock on margin. In this case, Phil only paid $45 in cash, he borrowed the remaining $45 from a broker. In such a scenario, Phil will make a 100% return when he sells the stock.
To be precise, Phil also owes the broker an interest, so his actual returns are a little less than 100%.
Let us assume that the same stock’s price declines from $90 to $45. If Phil had bought the stock with cash, he would lose only 50% of his money. But Phil bought the stock on margin, so he loses more than 100% of his money. On top of the investment, Phil also owes interest to the broker.
Example #2
Bybit is a Chinese derivatives brokerage firm in Singapore. In July 2022, Bybit announced the launch of a unified margin account—for eligible investors.
Bybit claimed to unveil a new structure. This new feature allows investors to use all their assets as collateral to procure investment loans.
This loan account will offer calculations in terms of USD terms. In addition, it will allow traders to trade USDT perpetual, USDC perpetual, and USDC option contracts without transferring assets back and forth.
Pros And Cons
Margin account pros are as follows.
- It offers to leverage financial opportunities.
- For advanced investors, it acts as a line of credit.
- Loan accounts facilitate repayment flexibility—low-interest rate options.
- It allows investors to make profits from stock price declines.
The cons are as follows:
- It is a high-risk strategy. Investors can lose 100% of what they invested and more.
- Buying on margin agreement allows the investor's firm to sell securities to cover the loan borrowed from the broker without consent.
- There is no time extension on a margin call.
- The broker or firm can raise a margin call without informing the investor.
- When an investor encounters a loss, they might end up repaying substantial amounts within a short period.
Margin Account vs Cash Account
Now, let us look at the margin account vs cash account comparison to distinguish between the two.
- Loan accounts offer additional leverage facilities. In contrast, a cash account only offers standard trading facilities.
- To buy on margin, investors require a separate agreement signed by both parties. In contrast, a cash account is a brokerage account with typical terms and conditions.
- Margin trading can potentially end up in huge losses. That is not the case with a cash account.
- To buy on margin, investors must fulfill specific requirements. In comparison, a cash brokerage account has standard rules common to everyone.
- When an investor buys on margin, they repay an additional interest. That is not the case with a cash brokerage account.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
An investor can buy on margin by procuring a loan from a dealer, broker, or investment firm. Both parties sign a specific agreement. When an investor connects with a broker, they sign a general agreement. This document must contain the buying-on-margin clause.
Buying on margin is risky because markets are dynamic; one wrong decision can result in huge losses. Therefore, it is recommended only for experienced investors. Nonetheless, it offers the benefits of financial leveraging.
Most brokerage firms require investors to have at least $2000 cash to open a loan account. But this amount varies from firm to firm. Typically, an investor must possess 50% of trade on margin beforehand.

