Table Of Contents
What Is Manufacturing System?
A manufacturing system is a collection of resources and processes that transform raw materials into finished goods. It aims to produce goods efficiently with high quality. Additionally, it can improve production processes by increasing regulations, reducing waste, and improving product quality and consistency.
Its prime motive is to reduce costs while meeting customers' demands and staying profitable. This is primarily done by including equipment, labor, and materials, while the processes can include assembly, fabrication, and inspection. It can assist businesses in adjusting to shifts in consumer demand. Systems for manufacturing can expand or contract depending on the volume of production.
Key Takeaways
- A manufacturing system is a collection of resources and processes that transform raw materials into finished goods.
- It aims to produce goods efficiently and with high quality while meeting customers' demands and staying profitable.
- Manufacturing systems require skilled labor to operate and maintain the equipment, which can be challenging to find and retain.
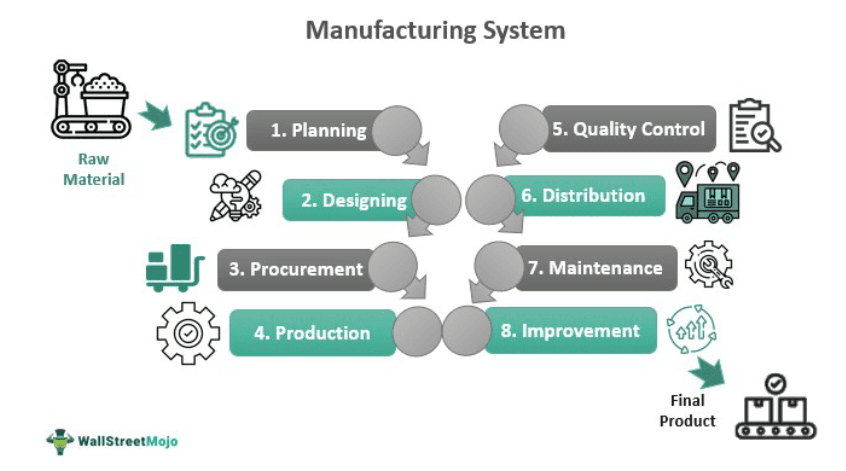
- Such a system typically involves several stages: planning, design, procurement, production, quality control, distribution, maintenance, and continuous improvement.
Manufacturing System Explained
A manufacturing system is a combination of tools and procedures used to turn raw materials into completed products. Its objective is to create products and services profitably, effectively, and by client requests.
The process of such a system typically involves several stages, including:
- Planning involves determining the type of products, resources, and production process.
- Design involves designing the products, tools, and equipment used in manufacturing. It may include creating detailed drawings, specifications, and blueprints.
- Procurement involves obtaining the raw materials and components to create the finished products. It may include purchasing materials from suppliers or sourcing them from internal inventory.
- Production: Transformation of raw materials into finished goods through various manufacturing processes such as assembly, fabrication, and inspection. It may involve the use of multiple types of machinery and equipment, as well as manual labor.
- Quality Control involves inspecting and testing the finished products to ensure they meet the required quality standards.
- Distribution involves delivering the finished products to customers or storing them in inventory for future use.
- Maintenance involves maintaining the manufacturing equipment and tools to ensure they are in good working condition and can operate at optimal performance.
- Continuous improvement involves continuous monitoring, which will increase efficiency, reduce waste, improve quality and reduce costs.
Components
Components of a manufacturing system can include:
- Equipment and machinery can constitute the tools and machines used to transform raw materials into finished goods. It can consist of everything from essential hand tools to highly automated and computer-controlled machinery.
- Raw materials and components are used to create the finished goods. It can include raw materials, such as metal and plastics, to purchased ingredients, such as motors and sensors.
- Labor includes the human resources needed to operate the equipment and perform tasks such as assembly and inspection.
- Methods and procedures include the systems that transform raw materials into finished goods. It includes assembly instructions, fabrication techniques, and quality control procedures.
- Software and control systems include the software and control systems used to manage and control the manufacturing process. It can have everything from simple manual controls to sophisticated computer-controlled systems that monitor and adjust production in real-time.
- Workflow and production planning include the manufacturing process layout, the flow of materials and information, and the production schedule.
- Maintenance and repair include the maintenance and repair of the equipment and facilities to ensure that the manufacturing process runs efficiently.
- Quality Control includes inspecting and testing the finished products to ensure they meet the required quality standards.
Types
There are several automated manufacturing systems, each with unique characteristics and applications. However, some common types of manufacturing systems include:
- Job Shop Manufacturing: It produces a wide variety of products in small quantities. It characterizes a high degree of flexibility and customization and is a one-of-a-kind or custom product.
- Batch Production: It produces small quantities of products. It is the ability to create various products using the same equipment with moderate complexity.
- Flow Production: It produces large quantities of products. It is a high degree of automation and a continuous flow of materials and information.
- Lean Manufacturing: It minimizes waste, maximizes efficiency, and increases overall quality. The use of pull systems, continuous improvement, and waste elimination in the production process characterizes it.
- Just-in-time (JIT) Manufacturing: It is characterized by producing goods only when needed rather than producing goods in advance and storing them in inventory. It helps to reduce waste and costs and improve overall efficiency.
- Mass Customization is characterized by the ability to produce large quantities of customized products with high flexibility and efficiency. It helps meet customers' specific needs by leveraging advanced technologies such as automation and robotics.
- Agile manufacturing is characterized by the ability to adapt quickly to changes in demand, technology, and other factors. It helps increase responsiveness and flexibility in the production process to meet the dynamic needs of the market.
Examples
Let us understand it through the following examples.
Example #1
Suppose a company specializing in eco-friendly cleaning products wants to set up a new manufacturing system software. The company aims to produce its cleaning products efficiently and cost-effectively while maintaining high-quality standards.
The first step would be to conduct a thorough planning process. Once the planning takes place, the company would then proceed to the design stage. But, first, it would involve designing the products, tools, and equipment used in manufacturing.
Next, the company would move on to procurement, including obtaining the raw materials and components used to create the finished products. The production stage would then begin involving processes such as mixing, filling, and packaging.
Quality control is a crucial part of the manufacturing process. Therefore, the company would establish a strict quality control system to inspect and test the finished products to ensure they meet the required quality standards.
Finally, the company would continuously monitor and improve the integrated manufacturing system to increase efficiency, reduce waste, improve quality, and reduce costs. It could involve implementing new technologies, optimizing production processes, and training employees.
Example #2
In January 2023, Worksport Ltd. announced the installation of a custom manufacturing line inspection. A custom-made manufacturing line is crucial for Worksport to launch and scale up automated production of its American-made rigid folding truck covers. Additionally, Its production line will produce parts for Worksport's much-awaited Solar Truck Bed Cover System.
Advantages And Disadvantages
Manufacturing systems can provide many benefits, such as increased efficiency, improved quality, and flexibility. Still, they also come with challenges, such as high initial costs and dependence on technology.
Advantages
- Increased Efficiency: Manufacturing systems can increase efficiency by automating specific processes and reducing the amount of manual labor required. It can lead to faster production times and lower costs.
- Improved Quality: Manufacturing systems can improve product quality by implementing strict quality control procedures and using advanced technologies such as sensors and automation.
- Increased Flexibility: Manufacturing systems are flexible and adaptable to changing production needs. It can help organizations respond quickly to changes in demand or market conditions.
- Increased Scalability: Manufacturing systems scale up or down depending on the production volume. It can help organizations adjust to market demand.
- Improved Safety: Manufacturing systems can improve security by automating dangerous tasks, implementing safety procedures, and providing better working conditions for employees.
Disadvantages
- High Initial Cost: Setting up it can be expensive, especially if it involves purchasing new equipment and technologies.
- Dependence On Technology: It relies heavily on technology, which can be vulnerable to technical failures and cyber-attacks.
- Lack Of Flexibility: Flexible manufacturing system makes them inflexible to changes in production needs.
- Limited To Specific Products: It designs to produce particular products, so it can be difficult to change over to make different effects.
- Skilled Labor Needed: It requires professional work to operate and maintain the equipment, which can be challenging to find and retain.
