Table Of Contents
What Are Manufacturing Operations?
Manufacturing operations refer to the processes and activities involved in the large-scale production of goods and products using raw materials, machines, and human labor. It encompasses the entire production process, from design and development to production, assembly, testing, and delivery of the final product. Its goal is to produce high-quality products efficiently and cost-effectively.
It also aims at continuous improvement, quality control, cost reduction, scalability, and flexibility of operations. These goals are interdependent and must be balanced to achieve optimal results in the manufacturing process. Manufacturing operations jobs require careful planning, diligent implementation, and ongoing evaluation. This is to ensure success and meet the needs of customers and stakeholders.
Key Takeaways
- Manufacturing Operations are a critical part of the production process, transforming raw materials or components into finished products.
- Its primary focus is to produce uniform, reliable, and high quality while optimizing production efficiency and cost.
- Manufacturing operations excellence requires careful planning, management, and control to ensure that production runs smoothly and that the quality of the finished product meets customer expectations.
- Managing manufacturing operations and production methods can significantly impact the efficiency and cost of production, and manufacturers must choose carefully to achieve the desired outcomes.
Manufacturing Operations Explained
Manufacturing operations refer to the processes and activities involved in transforming raw materials into finished products. Therefore, effective manufacturing operations management is essential for success in the modern business environment.
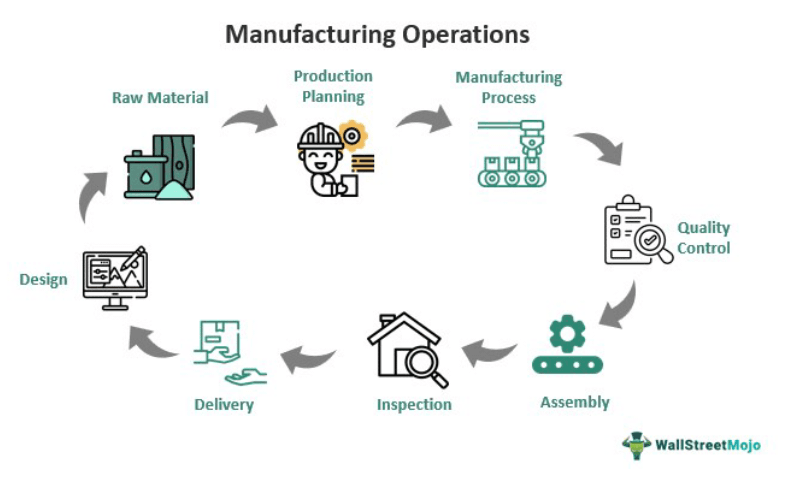
Its working mechanism includes the following steps:
- Design and Development: The first step in the manufacturing process is to create a design and product specification. It involves defining the product, identifying the materials and components needed, and determining the manufacturing processes required to produce the product.
- Raw Material Procurement: The next step is to acquire the raw materials needed for production. It can involve sourcing materials from suppliers, negotiating prices, and establishing delivery schedules.
- Production Planning: It includes scheduling production runs, determining the order of operations, and allocating resources such as labor and machines. To manage labor at scale, manufacturers often rely on an industrial workforce payroll solution, which helps streamline wage calculation, shift tracking, compliance, and labor cost management, ensuring the workforce is aligned with production demands efficiently.
- Manufacturing Process: The manufacturing process begins with preparing raw materials and includes cutting, shaping, and assembling components. Depending on the product, this can involve several stages, such as machining, welding, and painting.
- Quality Control: Quality control ensures that products meet the required specifications and standards. It can involve conducting tests and inspections, adjusting the production process, and correcting any issues.
- Assembly: Once the individual components have been manufactured, they are assembled into the final product. It can involve manual groups or the use of automated assembly equipment.
- Testing and Inspection: It ensures that it meets the required specifications and standards. It also ensures necessary adjustments or repairs before the packaging and shipment of the product.
- Delivery: The final step in the manufacturing process is to deliver the product to the customer. It can involve shipping the product directly to the customer or a distribution center for further distribution.
Types
There are several types of manufacturing operations, including:
- Mass Production: This manufacturing involves producing large quantities of identical products in a highly efficient and automated manner. It is often for consumer goods such as automobiles, electronics, and appliances.
- Batch Production: This type of manufacturing involves producing several units of a product simultaneously before switching to making a different outcome. It is apt for products with moderate demands.
- Job Production: This type of manufacturing involves producing a single unit of a product tailored to the specific needs and requirements of the customer. It is for custom products such as bespoke furniture, specialized machinery, and one-of-a-kind products.
- Process Production: This type of manufacturing involves transforming raw materials into finished products using a series of chemical or physical processes. It applies to food and beverage production, pharmaceuticals, and petrochemicals.
- Lean Manufacturing: This manufacturing involves optimizing production processes to reduce waste and improve efficiency. It can include techniques such as just-in-time production, continuous improvement, and visual management.
- Six Sigma: This is a data-driven approach to manufacturing that aims to improve the quality of products and processes by reducing defects and improving efficiency. It involves using statistical analysis and process improvement techniques to eliminate waste and improve performance.
- Agile Manufacturing: This type of manufacturing involves adapting to changing markets and buyers' needs by being flexible and responsive. It can include modular design, quick response manufacturing, and product and process diversity.
Examples
Let us understand it through the following examples.
Example #1
Suppose a smartphone manufacturer Amacon Ltd. creates a design and product specification, defining the features, materials, and components needed. The manufacturer sources the raw materials, such as electronics components, battery cells, and casing materials, from suppliers.
A production plan is developed, including scheduling production runs, determining the order of operations, and allocating resources such as labor and machines. Next, the electronic components are assembled, and the casing is molded and finished. Quality control measures are implemented throughout manufacturing, including testing and inspection of individual members and finished products. Finally, the unique pieces are assembled into the smartphone's outcome.
The smartphone is tested and inspected to meet the required specifications and standards. Then, necessary adjustments or repairs are made before the product is packaged and shipped. Finally, the smartphone is delivered to the customer directly or to a distribution center for further distribution.
Example #2
As per a survey by Bloomberg conducted in May 2020, the US manufacturing slowdown grew worse due to a decline in orders and industrial production. The Institute for Supply Management's indicator of manufacturing activity dropped for a fifth consecutive month in January to 47.4, the lowest level since May 2020 and below the consensus prediction.
Manufacturing Operations vs Service Operations
Manufacturing operations excellence focuses on producing uniform, reliable, and high-quality products. Service Operations, on the other hand, refer to the provision of intangible services to customers. The focus of service operations is on delivering personalized and customized experiences to customers while ensuring quality and consistency of service delivery.
Some critical differences between Manufacturing Operations and Service Operations include:
- Tangibility: It produces tangible goods that can be seen, touched, and physically possessed, while Service Operations deliver intangible services that cannot be physically connected.
- Process: It follows a well-defined and repeatable process, while Service Operations are often more flexible and adaptable, with a greater emphasis on personalization.
- Inputs And Outputs: It starts with raw materials or components and ends with finished goods, while Service Operations start with customer needs and a personalized service experience.
- Quality Control: Quality control often focuses more on producing uniform and reliable goods. In contrast, quality control in Service Operations is more focused on delivering consistent and personalized customer experiences.
- Cost Structure: The cost structure is often driven by production efficiency and material costs, while labor costs and the need for personalization often go against the cost structure of service operations.
