Table Of Contents
What Is Management Information System (MIS)?
Management information systems facilitate a firm’s daily operations. It is present in every organization. Record keeping is significantly easier with information systems. The primary role of an information system is to simplify workflow; it saves the time and energy of employees.
Data is crucial for every business. In the internet era, firms are bombarded with too much data, not just relevant data. Firms collect data in files, documents, cloud storage, hard copies, and soft copy formats. Primarily the MIS stores data in a secure manner. For example, a bank maintains records of account deposits, withdrawals, and customer details.
Key Takeaways
- A management information system is a database that facilitates day-to-day business activities. Primarily, information systems increase efficiency by reducing employee effort.
- An MIS is present in every organization to collect, record, and track information.
- The biggest hurdle with an information system is employee training. In addition, the system needs maintenance.
- Despite the benefits, not all firms can afford an advanced information system. Sometimes, due to MIS, work becomes too easy for the employees, and their growth stagnates.
Management Information System (MIS) Explained
A management information system (MIS) is used for processing data. In an institution, employees, managers, and staff access MIS. Employees use MIS for day-to-day operations, to print invoices, bill payments, or performance reviews. In addition, they use MIS to compare, analyze, and store data—a database for information. Thus, MIS helps firms in taking decisions rapidly and accurately.
Initially, employees are given MIS training—MIS interface, usage, and importance. Then, in some firms, training is given to customers and clients who use the system instead of employees.
The term ‘information system’ is often misunderstood. There is a misconception that MIS is all about coding and computer technology. Practically though, MIS is more than a code. In many scenarios, information systems do not require any code. MIS is more to do with data analysis. Fundamentally, an information system is a common framework that increases the productivity of all firm employees.
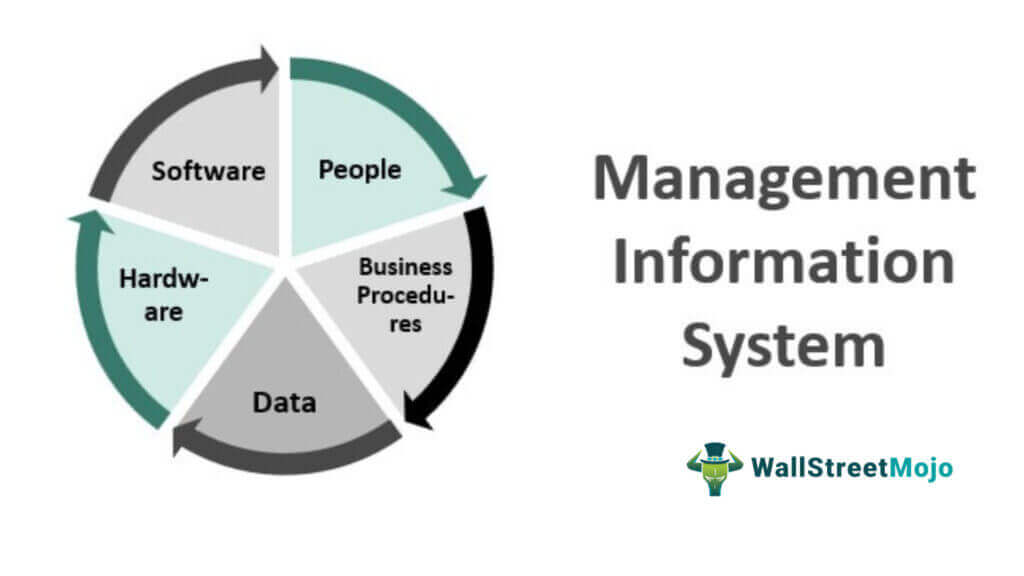
Management Information System Components
The management information system comprises the following components.
#1 - Data
Data is crucial for every business. Unfortunately, in the internet era, firms are bombarded with too much data, not just relevant data. Firms collect data in files, documents, cloud storage, hard copies, and soft copy formats.
Primarily the MIS stores data in a secure manner. For example, a bank maintains records of account deposits, withdrawals, and customer details.
#2 - People
An MIS is designed to be used by firm employees. managers, accountants, executives, and staff for day-to-day operations. Ideally, the MIS should be customized based on the firm needs. The MIS features should suit common usage.
#3 - Business Processes
Information systems simplify complex processes—the centralization of operations achieves this.
#4 - Hardware
Hardware is an indispensable component of MIS. Every system runs on a device, but the processing capabilities vary.
#5 - Software
MIS software is categorized into two—system software and application software. The term system software refers to operating systems like windows and iOS. Application software is more specific—banking systems, accounting applications, payroll applications, etc.
Requirements
The requirements of MIS are as follows.
- Every MIS requires a database that stores information, documents, files, and reports. This could be employee details, performance reviews, records, old presentations, and new projects.
- For installing an information system, firms need to make an Initial expenditure. Further, the MIS requires timely maintenance and employee training.
- Information systems are useful when employees use them regularly. For that, employees need access, and the system should be maintained.
- Business operations and firms evolve, and the MIS needs to keep up. Therefore, information systems need updating. In some cases, firms may need additional hardware and new software applications.
Role
The MIS plays the following roles.
- MIS stores data and records vital information.
- Firm employees use MIS software to complete daily operations and administrative tasks. Therefore, MIS should increase employee efficiency.
- Larger firms use automation and data generation to conserve employees’ time and energy. But those systems can be expensive.
- Again. The success of a system depends more on users than the software or hardware. Unfortunately, MIS training is often overlooked.
- An information system is beneficial in strategizing, analysis, and performance comparison.
Types
Management information systems are classified into 12 different types.
#1 - Process Control
Process control creates continuous reports and allows managers to observe real-time productivity and progress. For example, in manufacturing, product managers use it to analyze products’ quality and consistency.
#2 - Management Reporting System
A management reporting system is the most common MIS. It records labor information—efficiency, attendance, and financial documents. Firms use management reporting systems to track employee records and growth. The MIS generates quantitative reports; managers compare laborers based on data.
#3 - Inventory Management
Factories use MIS to track raw materials and inventory items. This way, managers make sure every small item is secure. If inventory management is efficient, firms need smaller warehouses and encounter fewer production delays.
#4 - Sales and Marketing Systems
Top-level management uses MIS to ascertain the firm’s sales figures. MIS also tracks firms’ marketing expenditures, customer reviews, customer feedback, and product availability. Also, MIS is used to track the usefulness of an advertising model.
#5 - HR MIS
In large firms or multinational companies, HR managers circulate information through MIS. This way, everyone is kept in the loop. In human resources, MIS is used to ensure that all employees are complying with firm guidelines.
#6 - Accounting and finance MIS
MIS tracks a company's assets and investments. In addition, managers, CA, and the accounting department use information systems for computing taxes, funds, and compliance.
#7 - Decision Support Systems
A decision support system collects both internal data and raw external data. Further, MIS streamlines raw data into relevant data. Thus, managers can access relevant data for efficient decision-making. For example, this could be avoiding risk, stratification, or introducing a new policy.
#8 - Expert MIS
Expert systems are algorithms-based MIS—they assist new employees design concepts—for a specific subject. Some expert MISs also employ AI to improve models and concepts.
#9 - Executive Information System
It compiles easy-to-read reports and summaries. In addition, organizational systems optimize data presentation—the system reorients data into charts, graphs, spreadsheets, and statistical tables. As a result, managers can process graphical data at a faster pace.
#10 - Transaction MIS
Transaction MIS automates business operations that involve complex processes—monetary transactions and calculations. It replaces processes that are time-consuming (when done manually).
#11 - School MIS
Information systems are used in schools, colleges, and universities to create schedules. In addition, educational institutions use MIS for storing files (record keeping). As a result, MIS databases save considerable time over manual record keeping.
#12 - Local Database
A local database is a community-managed MIS; typically, a database is used for public information and infrastructure. It is a source of information for citizens; if required, citizens can also request formal documentation (about precise public information). Social surveys also local databases.
Examples
Now, let us look at some examples of management information systems to understand their application.
Example #1
Let us assume that a multinational company owns multiple domestic and foreign offices. The total number of employees is 900. Maintaining a manual record of all the employees is not feasible.
Therefore, firms' human resource department uses a human resource information system to collect, record, and classify employee information. The firm also uses MIS to track attendance and leaves. In addition, the firm opts for a centralized database to store large amounts of data.
Example #2
Consider a large hospital—a plethora of patients and staff hustling around. The hospital has multiple departments, each employing nurses, surgeons, and physicians. Some are permeant employees, and others work for a few hours. The hospital's administration needs to record everything.
The hospital installs a health information system to record every minute detail. The MIS also tracks every single expense. As a result, the doctors get easy access to patient information; there is minimal chaos.
Advantages And Disadvantages
MIS has the following advantages and disadvantages.
- MIS drafts real-time reports—organizations become more dynamic—performance is enhanced.
- With a firm, MIS enables easy information sharing—everyone is kept in the loop. For example, information could be regarding ongoing projects or updates.
- Information systems transform raw data into relevant data, graphical representation, and analytical reports. Proper presentation of data speeds up decision-making.
- An MIS compares performances and reviews projects. This is used for projecting the future requirements of a firm.
The disadvantages are as follows.
- MIS can be expensive. The benefits may not justify the expenditure.
- MIS requires constant monitoring.
- Over time employee becomes dependent on it. Sometimes, when work is easy, employee growth stagnates.
- MIS outputs are primarily based on inputs, which means output is quantitative and qualitative. Therefore, MIS is only effective for empirical data.
- The system does not update itself and therefore requires manual support.
- An MIS can fail. Firms that heavily depend on MIS struggle during emergencies.
Management Information System vs Computer Science vs Decision Support System
Now, let us look at MIS vs computer science vs decision support system comparison to distinguish between them.
- An MIS identifies data and converts it into useful information. In contrast, computer science is a branch of science that develops technology benchmarks for computing. On the other hand, a Decision support system (DSS) is a decision-making tool.
- MIS can work on corporate databases, but DSS requires a specialized database. Computer science creates an infrastructure for MIS and DSS.
- MIS focuses on speed and efficiency. DSS prioritizes effectiveness; it is used for complex functions.
- MIS is designed for mass usage—a large number of employees. On the other hand, DSS is explicitly designed for managers, analysts, and top-level management.
- Primarily MIS store data. In contrast, DSS is more inclined toward data manipulation.
