Table Of Contents
What is Macaulay Duration?
Macaulay Duration is the time the investor takes to recover his invested money in the bond through coupons and principal repayment. This length of time is the weighted average of the period the investor should remain invested in the security to have the present value of the cash flows from the investment match the amount paid for the bond.
Macaulay Duration is very important to consider before buying a debt instrument. It can greatly help investors choose from varied sets of available fixed-income securities in the market. As we all know, bond prices are inversely related to interest rates. Investors get a good sense of idea in terms of which bond to buy, longer-term or shorter term if they know the Duration the various coupon bonds are offering along with the projected interest rate structure.
Key Takeaways
- Macaulay Duration is the time it takes to recover investment in a bond through interest and principal payments.
- It is calculated by taking the weighted average of the time an investor holds the bond until the present value of cash inflows equals the amount paid.
- Consider Macaulay's Duration when buying bonds to determine whether a longer or shorter-term option is best based on projected interest rates.
- It is essential in calculating the risk level of fixed-income assets. It is used to gauge risk like equity risk is quantified by deviation from the mean or by calculating beta
Macaulay Duration Formula
It can be calculated using the below formula,
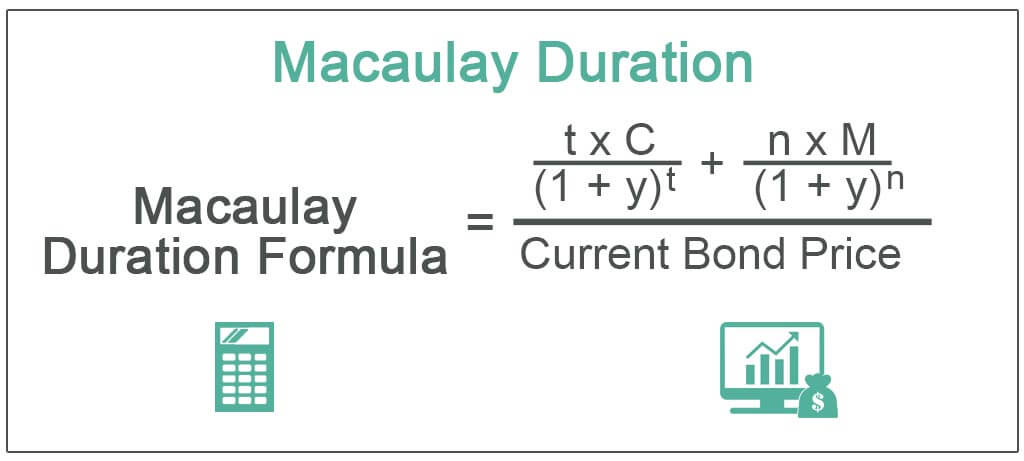
Where,
- t = time period
- C = coupon payment
- y = yield
- n = number of periods
- M = maturity
- Current Bond Price = present value of cash flows
Calculation of Macaulay Duration with Example
Let’s see an example of Macaulay’s duration to understand it better.
A $1,000 value bond pays an 8% coupon rate and matures in four years. The coupon rate is 8% p.a. With semi-annual payment. We can expect the following cash flows to occur.
- Six months: $40
- One year: $40
- 1.5 years: $40
- Two years: $40
- years: $40
- Three years: $40
- 3.5 years: $40
- 4 years: $1,040
Calculate Macaulay Duration
Solution:
With the above information, we can calculate the discount factor. We can use the following semi-annual interest formula to derive the discount factor. 1 / (1 + r)n, where r is the coupon rate, and n is the number of periods compounded.
Discount Factor
Calculation of discount factors for six months will be –

Discount factors for 6 months = 1 / (1 + 8%/2)
Discount Factors = 0.9615
Similarly, we can calculate the discount factor for years 1 to 4.

Present Value of Cash Flow
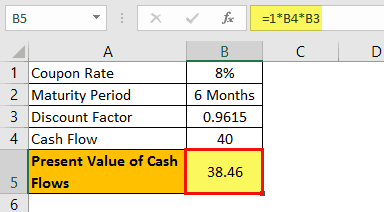
The present value of cash flow for six months will be –

Now, to get the present value of the cash flows, we must multiply each period's cash flow with its respective discount factor.
Present value of cash flow for 6 months : 1 x $40 x 0.9615
Present Value of Cash Flow = $38.46
Similarly, we can calculate the present cash flow value for years 1 to 4.

Macaulay Duration
Calculation of Macaulay Duration will be –

- Current Bond Price = PV of all the cash flows 6,079.34
- Macaulay Duration = $ 6,079.34/ $1,000 = 6.07934
You can refer to the given excel template above for the detailed calculation of Macaulay duration.
Merits of Using Duration
Duration plays an important role in helping investors understand the risk factor for the available fixed-income security. Just as how the risk in equities is measured by deviation from the mean or by deriving the security's beta, the risk in fixed-income instruments is strictly estimated by Macaulay's duration of the instrument.
Understanding and comparing Macaulay's Duration of the instruments can go a long way in choosing the right fit for your fixed-income portfolio.
Setbacks of Using Duration
Duration is a good approximation of price changes for an option-free bond, but it’s only good for small changes in interest rates. As rate changes become larger, the curvature of the bond price-yield relationship becomes more important. In other words, a linear estimate of price changes, such as duration, will contain errors.
The relationship between bond price and yield is not linear but convex. This convexity shows that the difference between actual and estimated prices widens as the yields go up. That is, the widening error in the estimated price is due to the curvature of the actual price path. This is known as the degree of convexity.
Bottom Line
Macaulay Duration knowledge is paramount in ascertaining the future returns from fixed income instruments. As such, it is highly advisable for investors, especially risk-averse investors, to assess and compare the duration offered by the various bonds to reach a minimum variance mix and draw maximum returns with the least risk possible. Also, the interest rate factor should be considered before buying.