Table Of Contents
What Is A Licensing Agreement?
A licensing agreement is a legal contract between two parties that outlines the terms and conditions under which one party (the licensor) grants the other party (the licensee) the right to use or access a certain intellectual property or product. The intellectual property can be anything from a patent, trademark, copyright, or even software.
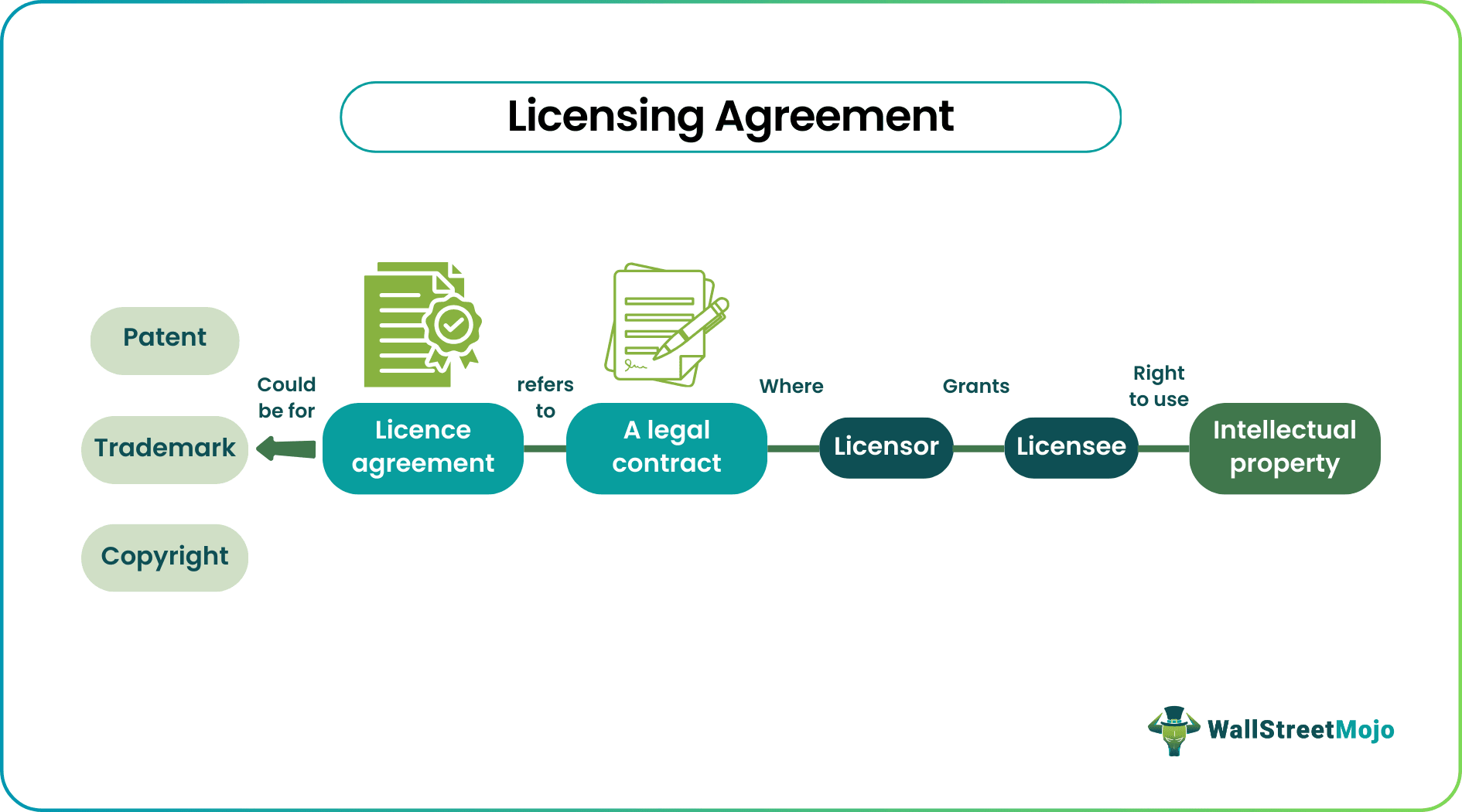
Licensing agreements are commonly used in business and commerce, allowing companies to monetize their intellectual property without investing in production or marketing. For example, a software company may license its product to other businesses, allowing them to use it in exchange for payment.
Table Of Contents
- What Is A Licensing Agreement?
- A licensing agreement is a contract between two parties allowing the licensee to use the licensor's intellectual property in exchange for payment.
- The agreement outlines the scope of the license, payment terms, duration of the agreement, and any restrictions on the use of the intellectual property.
- Different licensing agreements include exclusive, non-exclusive, cross-license, sub-license, compulsory, and joint venture agreements.
- Licensing agreements can provide a way for companies to monetize their intellectual property while allowing other companies to access and use valuable intellectual property without investing in its development.
How Does A Licensing Agreement Work?
A licensing agreement is a legal contract between the licensor and the licensee that outlines the terms and conditions under which the licensee can use the licensor's intellectual property, such as a patent, trademark, or copyright.
The licensing agreement typically includes important details such as the scope of the license, the duration of the agreement, any restrictions on the use of the intellectual property, payment terms, and any warranties or representations made by the licensor. Overall, licensing agreements are an important tool for companies to protect their intellectual property and generate revenue from their creations.
The licensor retains ownership of the intellectual property. Still, it grants the licensee the right to use it for a specified period within the terms and conditions specified in the agreement. The licensee may be required to meet certain obligations, such as maintaining confidentiality, complying with applicable laws and regulations, and paying the required fees or royalties.
Licensing agreements can be exclusive, meaning that the licensee is the only party authorized to use the intellectual property, or non-exclusive, meaning that other parties may also be authorized to use it. They can also be global or limited to a specific geographic region.
Licensing agreements are commonly used in business and commerce, allowing companies to monetize their intellectual property without investing in production or marketing. They also allow other companies to access and use valuable intellectual property without investing in its development or creation.
Types
There are several types of licensing agreements, including:
- Exclusive License: In an exclusive license, the licensor grants the licensee exclusive rights to use the intellectual property, meaning no one else can use it. This can be limited to a specific geographic area, period, or product type.
- Non-Exclusive License: In a non-exclusive license, the licensor grants the licensee the right to use the intellectual property, but other parties may also be granted similar rights.
- Cross-License: A cross-license is an agreement where two or more parties exchange licenses to use each other's intellectual property. This can be useful in situations where each party has the important intellectual property to the other.
- Sub-License: In a sub-license, the licensee grants another party the right to use the licensed intellectual property. This can be useful when the licensee needs to allow others to use the intellectual property but wants to retain some control over its use.
- Compulsory License: A compulsory license is a legal requirement that allows a third party to use a patent, copyright, or other intellectual property without the owner's consent. This is typically done to promote competition or public interest.
- Joint Venture Agreement: A joint venture agreement is a licensing agreement where two or more parties work together to develop, produce, and market a product or service using their combined intellectual property.
Examples
Example #1
Let's say a company called "BioMed" has developed a new drug that is highly effective in treating a rare disease. BioMed seeks to license the drug to a pharmaceutical company with the expertise and resources to bring it to market.
BioMed may enter into a licensing agreement with "PharmaCo," a large pharmaceutical company with a strong track record of developing and marketing drugs. The licensing agreement would outline the terms and conditions of the use of the drug by PharmaCo.
The licensing agreement may include details such as the scope of the license, which could specify the geographic territories in which PharmaCo can market the drug, the duration of the agreement, payment terms, and any restrictions on the use of the drug.
In exchange for the license, PharmaCo would pay a fee to BioMed, either as a one-time payment or as ongoing royalties based on the drug's sales. This licensing agreement would allow BioMed to monetize its intellectual property without investing in the drug's development, manufacturing, or marketing while also providing PharmaCo with a new product to add to its portfolio and potentially help patients in need.
Example #2
Example of a company called "InnoTech" that has developed a new software program to analyze large amounts of data quickly and accurately. InnoTech is seeking to monetize its software by licensing it to other companies.
InnoTech may enter into a licensing agreement with a large financial institution, "BigBank," looking for a tool to help analyze its transaction data. The licensing agreement would outline the terms and conditions of using the software by BigBank.
The licensing agreement may include details such as the scope of the license, which could specify the number of users allowed to access the software, the duration of the agreement, payment terms, and any restrictions on the use of the software.
In exchange for the license, BigBank would pay a fee to InnoTech, either as a one-time payment or as ongoing royalties based on the use of the software. This licensing agreement would allow InnoTech to monetize its intellectual property without investing in marketing or production while also providing BigBank with a powerful tool for analyzing its data.
Advantages And Disadvantages
Advantages of Licensing Agreements:
- Provides a way for companies to monetize their intellectual property without investing in production or marketing.
- Allows companies to generate revenue from products or technology that may not fit their core business strategy.
- It gives licensees access to valuable intellectual property without investing in its development.
- It can help establish a mutually beneficial partnership between the licensor and the licensee.
Disadvantages of Licensing Agreements:
- Licensors may lose control over intellectual property use or be concerned about competition.
- Difficult to enforce and protect intellectual property rights in some jurisdictions.
- It can be costly to negotiate and draft a comprehensive licensing agreement.
- This may lead to disputes between the licensor and licensee over the terms and conditions of the agreement.
Licensing agreement vs Lease vs Franchise
| Licensing Agreement | Lease | Franchise | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | A legal agreement that allows the licensee to use the licensor's intellectual property in exchange for payment. | A legal agreement that allows the lessee to use the lessor's property in exchange for rent payments. | A legal agreement allows the franchisee to use the franchisor's business model, brand, and operating system in exchange for initial fees and ongoing royalties. |
| Property Rights | Licensee is granted rights to use intellectual property owned by the licensor. | Lessee is granted rights to use tangible property owned by the lessor. | Franchisee is granted rights to use intangible property owned by the franchisor, including brand, business model, and operating system. |
| Ownership | Licensor retains ownership of intellectual property. | Lessor retains ownership of tangible property. | Franchisor retains ownership of intangible property. |
| Use | Licensee is permitted to use intellectual property for specific purposes within the scope of the license agreement. | Lessee is permitted to use the tangible property for specific purposes within the scope of the lease agreement. | Franchisee is permitted to use the franchisor's business model, brand, and operating system for specific purposes within the scope of the franchise agreement. |
| Payment | Licensee pays fees or royalties to the licensor for using the intellectual property. | Lessee pays rent to the lessor for the use of the tangible property. | Franchisee pays the franchisor initial fees and ongoing royalties to use the intangible property. |
| Control | Licensor does not typically control how the licensee uses the intellectual property. | Lessor does not typically control how the lessee uses the tangible property. | Franchisor has some control over how the franchisee operates the business, including branding and operational standards. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Software licensing agreements are legal contracts between a software company (the licensor) and a user (the licensee) that specifies the terms and conditions for using the software.
Any activity that goes against the terms and conditions specified in the licensing agreement, such as exceeding the scope of use, copying or distributing the software without permission, or reverse-engineering the software, represents a violation of the licensing agreement.
To get a licensing agreement, one must first identify the intellectual property to be licensed and potential research licensees and negotiate the terms and conditions of the agreement. The process can involve legal and financial professionals.
A licensing agreement is very important as it is a legally binding contract that protects the interests of both the licensor and licensee. In addition, it defines the terms and conditions of the agreement and helps prevent disputes and legal issues.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to what is a Licensing Agreement & its definition. We explain its examples, types, compare it with lease and franchise, and its advantages. You may also find some useful articles here -
