Differences between both the concepts are given as follows:
Table Of Contents
What Is Leg In?
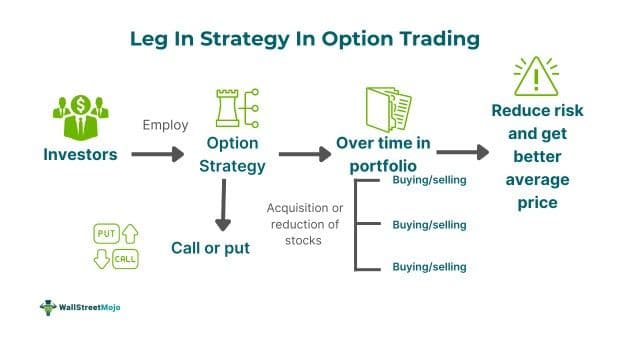
Leg In trading involves gradually constructing a position through smaller trades over time, where each leg represents an individual option within the strategy. Traders prioritize one leg position at a time over establishing it once and for all, and this is known as legging.
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc.. Please provide us with an attribution link.
The leg-in strategy is important as it permits traders to enter positions, incrementally adjusting to evolving market dynamics. This approach offers flexibility and risk mitigation by minimizing initial exposure and granting chances to evaluate the market before full commitment. Traders employ legging to capitalize on price shifts, enhance entry timing, and potentially attain more favorable prices.
Key Takeaways
- Leg in is an option strategy that involves gradually building a position over time, prioritizing one "leg" or option at a time, allowing flexibility and risk management. It involved components of Long Call, Long Put, Short Call, and Short Put.
- Advantages of it include risk control, adaptability, enhanced pricing, strategy flexibility, and optimized capital allocation.
- Disadvantages include pricing vulnerability, timing challenges, transaction expenses, sensitivity to market shifts, and complexity.
- Legging in and out are different concepts. Legging in gradually builds a position, adjusting to market conditions; leg out systematically exits a position, aiming for controlled profits or losses.
Leg In In Options Trading Explained
Leg in or legging in is a practice in options trading that entails investors gradually entering multiple individual positions to build an overall position. In the realm of options trading, a leg signifies an individual component within a multi-part options strategy. These strategies involve diverse combinations of acquiring or selling off multiple options contracts, each differing in strike prices, expiration dates, and types (either calls or puts). Hence, every unique option contract within such a strategy is recognized as a leg. Typically, traders begin with one leg, such as buying a call or put option, and subsequently add more legs over time, like selling another option or adjusting the position. The foundational components in options trading include the following: Long Call, Long Put, Short Call, and Short Put.
It is a common approach used by investors to decrease the overall cost involved in executing complex strategies that incorporate options and futures contracts. This strategy allows traders to effectively manage risk and make adjustments based on evolving market conditions or changes in their outlook or prevailing prices. These types of spreading strategies allow investors to design their desired profit and loss structure based on intended outcomes.
This method enables traders to gradually initiate positions, thus decreasing the initial investment and providing increased flexibility. It allows for a comprehensive assessment of market conditions, volatility, and price shifts before making a full commitment. Furthermore, it allows for adaptability and strategy refinement in response to constantly changing market conditions and newly emerging information.
Examples
Let us look into a few examples to understand the concept better:
Example #1
Suppose Dan, an options trader, adopts the legging-in strategy to position himself in a bullish stock.
He buys a call option for a smaller portion of his desired position and waits for a dip or favorable market conditions to add more legs. When the stock price temporarily declines, Dan adds another call option at a more favorable price, lowering his initial cost basis and maximizing potential gains if the stock price rises.
Let's say initially, he purchases a call option for Company X at a price of $50, representing the first leg of his strategy. As time progresses and Dan observes favorable market conditions, such as increasing bullish sentiment or upward momentum in the stock price of Company X, he adds to his position by purchasing additional call options at higher strike prices, such as $150 and $200. Each of these purchases represents another leg of his strategy.
This approach reduces his initial cost basis and increases potential gains if the stock price rises. Throughout the trading period, Dan carefully monitors the market and adds additional call options whenever he identifies advantageous entry points or sees further potential. By gradually building his position, Dan effectively manages risk, gains a better understanding of the stock's behavior, and can potentially enhance his overall trade profitability.
Example #2
A study investigates the optimization and analysis of a versatile and effective multi-leg stock trading system. The term multi-leg in trading stems from the concept that these strategies comprise several individual options contracts, with each contract serving as a separate leg within the overall strategy. Major performance bottlenecks in traditional atomic commitment protocols, like 2-Phase Commit or 2PC, were identified in the study. A new look-ahead algorithm was proposed to enhance transaction concurrency and minimize performance decline. Both a baseline 2PC prototype and an optimized look-ahead prototype were implemented on IBM z10 z Series e Server mainframes. Experimental findings reveal that the look-ahead optimization enhanced throughput and reduced latency by 30%.
Advantages And Disadvantages
Some of the disadvantages and advantages are given as follows
Advantages of Utilizing the Legging-In Approach:
#1 - Risk Control:
Employing the legging method empowers traders to regulate risk by gradually entering positions and making adjustments in response to market fluctuations.
#2 - Adaptability:
Traders enjoy the freedom to evaluate market trends, asset volatility, and pricing dynamics before fully committing to a position. This enhances their decision-making process.
#3 - Enhanced Pricing:
Executing trades at different intervals may help traders secure more favorable average prices, particularly in volatile market conditions.
#4 - Strategy Flexibility:
Legging in grants traders the flexibility to modify their positions, incorporate hedging techniques, or construct spread strategies to accommodate evolving market conditions.
#5 - Optimized Capital Allocation:
Initially, deploying a smaller portion of capital allows traders to maximize resources, enabling them to pursue additional opportunities effectively.
Disadvantages of the Legging-In Approach:
#1 - Pricing Vulnerability:
Execution of individual legs separately can expose traders to unfavorable pricing, slippage, or missed opportunities, particularly in swiftly moving markets.
#2 - Timing Hurdles:
Precisely timing the entry and exit of each leg necessitates vigilant market monitoring and may heighten the overall trade complexity.
#3 - Transaction Expenses:
Engaging in multiple legs within a trade can lead to elevated transaction costs, encompassing commissions and bid-ask spreads, which may impact overall profitability.
#4 - Sensitivity to Market Shifts:
Throughout the legging-in process, alterations in market conditions may influence the efficacy of the strategy.
#5 - Complex Execution:
Legging in demands a strong understanding of options trading fundamentals and the capacity to manage multiple positions concurrently, posing challenges for less-experienced traders.
Leg In vs Leg Out
| Parameters | Leg In | Leg Out |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Definition | It entails entering gradually through individual legs and establishing a position by initiating trades over a period. | Leg out entails gradually diminishing or terminating a position by exiting trades over a period. |
| 2. Risk Control | Legging in facilitates risk management by reducing initial exposure and evaluating market conditions before committing fully. | Legging out serves as a method of managing risk by progressively reducing exposure and capturing profits throughout the process. |
| 3. Purpose | The aim of legging in is to capitalize on favorable market movements and adjust the position in response to evolving conditions. | The aim of legging out is to systematically exit a position, potentially realizing profits or minimizing losses in a controlled manner. |
