Table Of Contents
What Is A Kanban Card?
A Kanban Card is a ticket that represents visual information about a particular work item on either a physical or digital board. It is a structured alternative to sticky notes that contain production data like the number of units, lead time, order date, due date, type of work, etc.
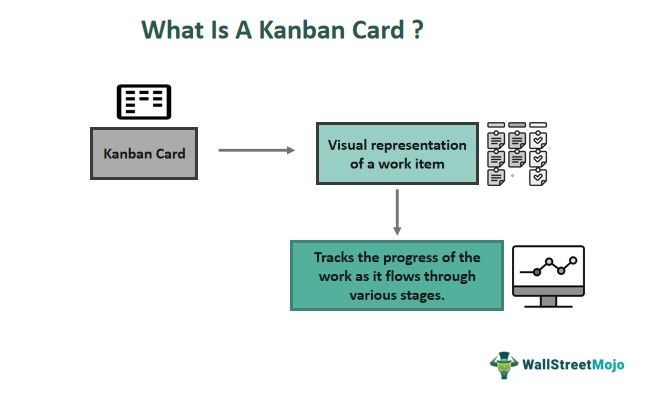
It is a crucial component of a work management framework, Kanban, which aims to visualize the work, confine work in progress, and help attain efficiency. These cards enable teams to keep up with the work status at different stages of production.
Key Takeaways
- A Kanban card is a visual sign or ticket that states a specific work item like the order quantity, due date, task description, type of work, work status, etc.
- Taiichi Ohno, a Japanese industrial engineer at Toyota, developed the concept of Kanban, which the Kanan cards are a part of.
- The different types of Kanban cards include production, withdrawal, emergency, express, through, and supplier kanban.
- It is represented under the different columns (each showcasing the different stages of production) on the Kanban board. It can be moved from one column to another as the work progresses.
Kanban Card Explained
A Kanban card facilitates visual communication on the work progress among the team members working on the same project. These cards represent crucial insights into the ongoing project, such as the order quantity, order date, due date, work in progress (WIP) limits, task assignment, work status, problem areas, source of documents, etc., which are visible to all the teammates at the same time. It even states the work status and ensures the efficient movement of items or other deliverables from one stage to another.
Kanban was initiated by Taiichi Ohno, a Japanese industrial engineer of Toyota Motor Corporation, in the 1940s. Initially, these visual signs were shown as pinned paper notes on a physical board to depict the work status or progress. Today, using advanced technology, these cards aim to enhance production efficiency and reduce the production wastage that occurs with the unnecessary piling up of the stocks.
At first, Kanban cards were tucked into the final products and taken off at the time of sale. Subsequently, the Kanban card system evolved and was later used in inventory management to introduce the just-in-time concept. The front side of these cards contains the title, task description, assignee name, work type, estimated time, due date, etc. On the other hand, the back of the card shows the start day, blocked days, blocked location, finish date, lead time, etc.
Let us check the Kanban card template to get an idea of what it looks like:

Types
The Kanban cards often serve a particular purpose during the production process. Based on the purpose of its creation, it can be categorized as follows:
- Production cards: They indicate that it’s time to begin the production process. These consist of order information such as the quantity, material required, production timeline, etc. Plus, these help track the resources required to achieve production successfully.
- Withdrawal cards: These serve as the green signal when an item or part is ready to move from one production stage to another.
- Emergency cards: They are pulled in the middle of the production process in case of a change in the production quantity or when there is damage or loss.
- Express cards: They indicate the shortfall of a particular part or material in the middle of the production process, initiating the immediate purchase of the same.
- Through cards: These are time-saving cards that jointly serve the purpose of producing and withdrawing when these workstations are situated together.
- Supplier cards: These are used to order the material from the supplier. The cards, in this case, contain the contact details of the suppliers and also the suitable mode of communication for the parties. In addition, a business can keep track of the suppliers using this tool.
Examples
Let us consider the following instances to understand the concept better:
Example #1
Imagine Weaves, which is a garment-making unit, has to process the flow of each stage of production minutely to guarantee timely deliveries in the market. Hence, it uses Kanban cards to represent different manufacturing stages. Suppose one team cuts the cloth in the desired sizes, another stitches the shirts, while additional teams handle tasks such as tucking the buttons and collars and labeling and packaging the shirts.
As one team finishes the task, it uses the card on the board to show that the stage is complete, and the other takes over the charge of the same. This way, the work flows from the cutting stage to stitching to finishing to packaging. The teams can also transfer this card manually to another team after the former completes the task and the other has to take over. The sequential flow, in turn, guarantees timely production and delivery of products.
Example #2
Software Solutions Provider ConnectWise has come up with a revolutionary change in its Business Management Solutions. The new update incorporates the Kanban system, including the Kanban board and cards mechanism, and it aims to deal with the issues and struggles that the partners have been facing as this new change has come following the partners’ feedback.
The new feature would have a drag-and-drop feature included to make it easier for members to retrieve the project’s progress with ease. It will allow the partners to manage team productivity and streamline the project management aspects. It would help project managers monitor the progress of each step of the workflow.
Benefits
Kanban cards are essential for the smooth flow of the production process in an organization. It has several advantages for the team and the company, including:
- Information At A Glance: It clearly shows the work progress information, allowing teammates to view the status at a glance.
- Just-in-time Delivery: With all related information readily available on the card, teams can easily follow up with each other. This greatly reduces the time taken to retrieve information. It also prevents order delivery delays as everyone completes their part of the work on time.
- Flexibility: These cards allow flexibility to incorporate changes in priorities, making them a lot more useful for continuous workflow.
- Better communication And Teamwork: Since it is accessible to all stakeholders, they can quickly figure out the work progress of the other teams, enhancing visual communication.
- Improves Efficiency: The card’s visual feature helps the managers spot inefficiencies and take corrective measures to improve the workflow.
- Adaptability: Kanban methodology, which the card is part of, is suitable for all the departments of an enterprise, such as production, marketing, software development, sales, etc.
