Table Of Contents
What Is Junior Company?
Junior Company undertakes the development of natural resources, including research, confirmation of the existence of resources at the exploration site, actual extraction, etc. It bears the immediate risk of failure of such exploration activity. The senior companies oversee their activities and provide them with the necessary funds.
The companies which undertake the initial study for the existence of natural resources and then team up with larger companies either financially or structurally to undertake the extraction activities are known as the Junior Companies. Once they come up with a positive study result, they may either take up exploration activity themselves or sell out their findings and the explored site to an interested party, which might then take up the extraction activity.
Key Takeaways
- Junior companies in the natural resource exploration industry take on the risky exploration process, while senior companies provide oversight and funding to reduce the likelihood of failure.
- Junior companies encounter various challenges, including obtaining environmental permits, navigating geopolitical risks,
- addressing the rights of indigenous people, handling potential failures, and addressing socio-economic challenges.
- While this opportunity offers the potential for substantial rewards, it comes with a high level of risk. As a result, only confident investors comfortable with significant risks should consider investing in this opportunity.
Junior Company Explained
Junior company refers to any small organization that is engaged in searching for and developing of deposits of natural resource in any area. It may obtain funds for the above purpose from outside sources or may look for big and established companies who may be interested in investing in them or buying them to provide for the funding.
They are usually companies with a small market capitalization of $500 million or less. But usually, they approach venture capitalists to finance their venture.
However, since they are new in the market and have just started a business, they do not have a good market share and customer base. They need to prove their worth and build the asset base so as to expand and growth in future. It is an interest venture for those entrepreneurs who have the risk taking capacity.
Over the years, this type of ventures have grown in the market significantly. But along with that the rewards of taking the risk has also grown. It is high risk and high reward work. Therefore, it is not an investment opportunity for all kinds of investors; only those with high risk-taking capacity and willingness should take up such investments.
Characteristics
Let us go through some of the characteristics of this kind of business which can help us in identifying them.
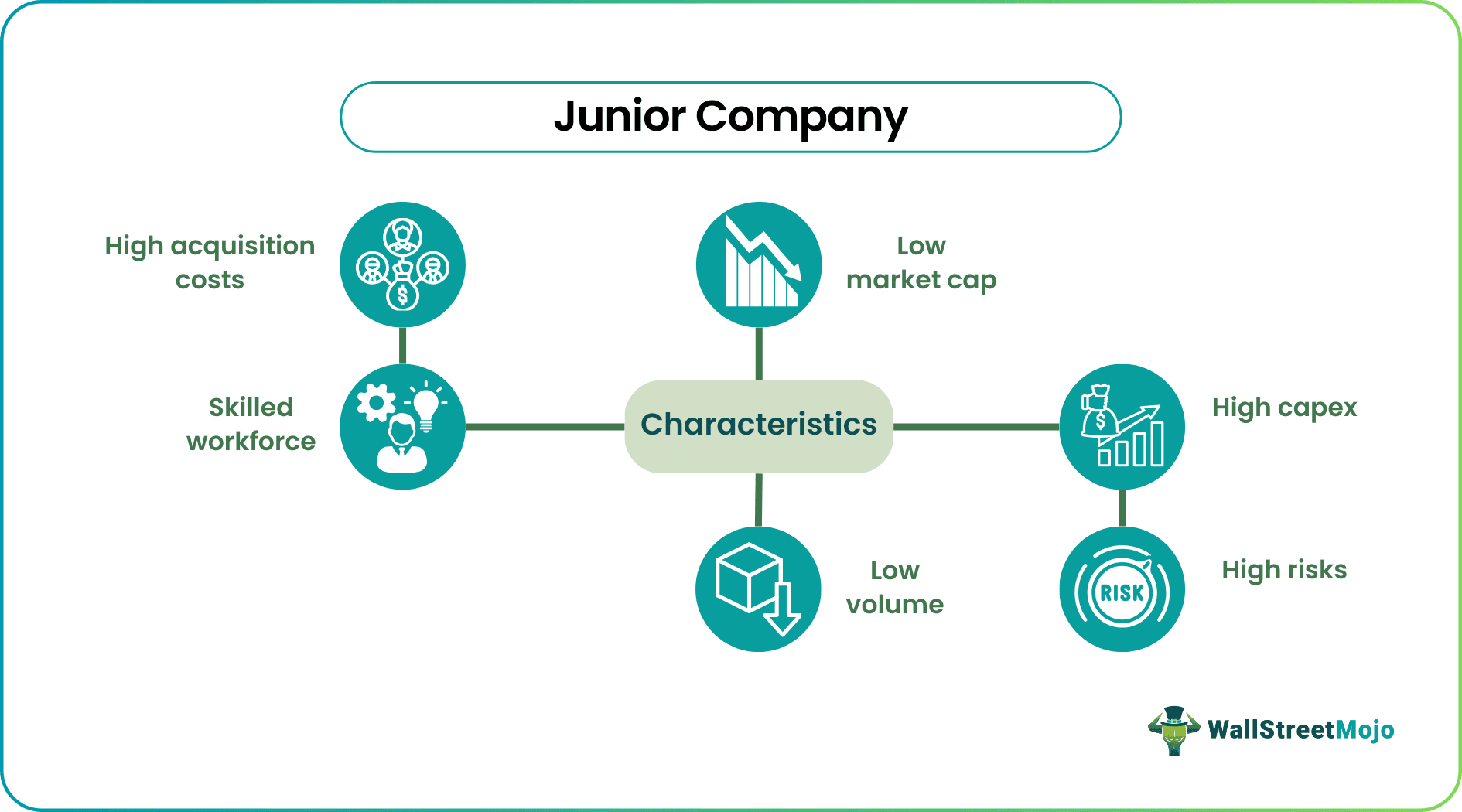
- Low market cap: Mostly, these companies have lower than 500 million market-capitalization and therefore fall under the small-cap category.
- Low volume: These are thinly traded stocks, and therefore, the volume on a day to day basis is very low or may even be negligible.
- High Capex: As the projects require a lot of site excavation work, the investment in R&D and equipment is high. Therefore such companies have very high fixed asset investment.
- High acquisition costs: A study of resources can be conducted only after the site has been acquired, and therefore acquisition costs become a very high component of overall costs
- High Risks: As the sole reward rests on the positive results of the study, the risks are very high for junior companies because if the study fails, they won't get further funding for exploration and trading of the resources, whereas the initial funds used in the acquisition and conducting of the study all become a sunk cost.
- Skilled workforce: Junior companies require skilled management and technical experts to handle the local government laws and environmental regulations and the scientific viability of the proposed acquisition targets.
Examples
Now we will try to understand the concept with some suitable examples.
Atalaya Mining PLC, previously known as EMED mining public ltd., has a market cap of CAD 432 million with 137.339 million listed ordinary shares on the TSX and the AIM as on Nov 12, 2019, 3:14 AM EST. It is a mining and development company in the copper concentrates and silver by-product domain
Its operations are concentrated in south-western Spain at the Rio Tinto project site, among others, of which it acquired 100% ownership in October 2008 and is currently in an expansion phase.
One of the most appropriate ways of understanding a junior company is its shareholding pattern, which shows the sources of capital for its operational activities. The below image shows the significant shareholding of Atalaya Mining PLC as of Sept 16, 2019:
- Urion Holdings (Malta) Ltd ("Trafigura"): This is a wholly-owned indirect subsidiary of one of the market leaders in the global commodity trading industry, Trafigura, and one of its core operations is to acquire a shareholding in various commodity exploration companies, such as Atalaya Mining PLC.
- Yanggu Xiangguang Copper Co. Ltd ('XGC'): This is a wholly-owned direct subsidiary of XGC, one of the largest copper processing and refining companies in Shandong, China.
- Liberty Metals & Mining Holdings LLC ("Liberty"): This is based out of Boston, the U.S., and is a subsidiary of Liberty Mutual Insurance (LMM), which is an insurance company that invests in various sectors to be able to fulfill the insurance payouts to its policy-owners.
- Orion Mine Finance (Master) Fund I LP ('Orion'): This is a fund of Orion Resource Partners, an investment management firm in the alternative investment domain with an AUM of approx. $6 billion.
- Management and Board of Directors: This could be due to the requirement of qualification shares, or sweat equity, or any other reason.
We can see that none of its major investors take up the mining operations at the ground level. Most of their involvement is for providing the funds. However, the largest shareholders are in related businesses such as trading or processing, and refining the produce of Atalya or mining is their core investment domain.
Other examples could be Great bear resources, Novo resources, Silvercorp Metals, Pacific Booker Minerals, and Kirkland Lake Gold.
Challenges
Every idea faces a lot of challenge in the market when it is introduced for the first time. So it is necessary to be well informed about those problems and be ready to face them as and when they come. However, let us first try to identify such challenges in case of Junior Company.
- Environmental permits: These days, one of the most critical factors which can make or break the spine of junior companies is the environmental regulations of the governments of the countries where such exploration sites are located. Certain countries offer environmental permits, while some countries have less liberal policies.
- Geopolitical risks: The interest of junior companies is affected by the geopolitical risks of the countries of exploration sites. E.g., if the country faces a civil war, the junior company is affected the most.
- Rights of Indigenous people: Most sites are located in the tribal areas or the unexplored and therefore require rehabilitation of these people. Further, due to being accustomed to their ways of living, it is challenging for them to adjust to a new environment, and they may or may not possess the skills required for survival. It creates a barrier to exploration activities. Proper compensation may not always be feasible. A very recent example is the Niyamgiri hill-Vedanta Group case from India. The Supreme court finally ruled in favor of the indigenous people and against the Vedanta resources.
- Failures: The sites need to be acquired before the study for resource existence can be undertaken. It requires a lot of capital, and if the study results are negative, all the investments go down the drain and produce no return. Therefore at times, failures even lead to the bankruptcy of the junior company if its debt is very high.
- It is because of the requirements of the Black economic empowerment regulations. Socio-economic: In most African countries, such companies have to operate in a joint venture with a local corporation or the local communities. The resources present on the lands of these local communities also belong to these people. E.g., the Blue Rock Diamonds group, based out of the U.K., operates in South Africa in collaboration with Ghaap Mining (Pty)Ltd. Kimberly owns 26% of its capital structure.
