Table Of Contents
Top 10 Examples of Journal Entry
An example of a journal entry includes the purchase of machinery by the country where the machinery account will be debited, and the cash account will be credited.
The following journal entry examples in accounting provide an understanding of the most common journal entries used by business enterprises in their day-to-day financial transactions. It is the summary of debits and credits of financial transactions with a note of which accounts these financial transactions will affect, maintained in chronological order. Passing the journal entries is very much required as they allow the business organization to sort their transactions into manageable data.
Table of contents
- Top 10 Examples of Journal Entry
- Example #1 - Revenue
- Journal Entry Examples Video Explanation
- Example #2 - Expense
- Example #3 - Asset
- Example #4 - Liability Accounting
- Example #5 - Equity Accounting
- Example #6 - Transaction with Journal Entries
- Example #7 - Practical
- Example #8 - Practical
- Example #9 - Practical
- Example #10 - Practical
- Conclusion
- Recommended Articles
Example #1 - Revenue
Sales Journal Entry:
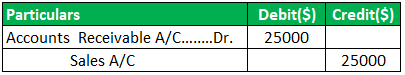
When sales are made on credit, the journal entry for accounts receivable is debited, and the sales account is credited.
If cash sales happen, then the cash account is debited.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts Entry:
At times customers are unable to pay. For such scenarios, setting up or adjustment for bad debt expenses is made. Bad debt expense is debited for such entry, and allowance for doubtful accounts is credited.

If such provisions are found, the doubtful accounts are debited, and the account receivable is credited.
Example #2 - Expense
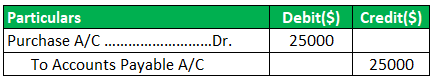
Journal Entry for Accounts Payable:
In this case, the related asset or expense account is debited, and the journal entry for the payable account is credited.
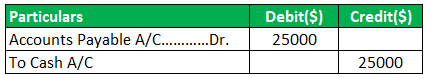
When payment is to account payable, accounts payable is debited, and the cash account is credited.
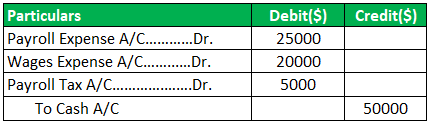
Journal Entry for Payroll:
In the case of payroll expenses, the wages expense, these accounts are debited, and the cash account is credited.
Journal Entry for Accrued Expense:
In this case, the applicable expense is debited, and accrued expense is credited.
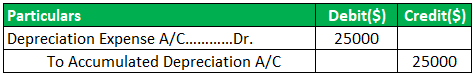
Journal Entry for Depreciation:
For depreciation expense, depreciation expense is debited, and the accumulated depreciation account is credited.
Petty Cash Journal Entry:
To establish a petty cash fund, petty cash is debited, and the cash account is credited.

Example #3 - Asset
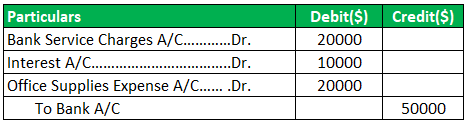
Cash Reconciliation Entry:
There is usually a debt to the bank fees account, Office Supplies Account, Interest Account, etc., to recognize charges made by the bank, with a credit to the cash account.
Journal Entry for Prepaid Expense Adjustment:
In this case, the expense account debits and the prepaid expense account credits.
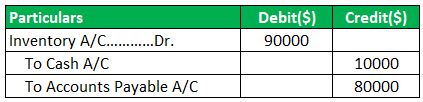
Purchased Inventory Journal Entry:
If the inventory purchased is worth $90000, $10000 in cash, and $80000 on the account;
Journal Entry for the Fixed Asset:
When a fixed asset is added, the applicable fixed asset account is debited, and accounts payable is credited.

Purchased Equipment for $600,000 in Cash;

Fixed Asset De-Recognition Entry:
When a fixed asset is removed, the accumulated depreciation account is debited, and the applicable fixed asset account is credited. There could be a chance of a gain or loss in this regard.
Journal Entry Examples - Explained in Video
Example #4 - Liability Accounting
Accrued liabilities account is credited. If a debt is owed but not yet billed, accrued liability entry is to be made. In this case, the accrued expense is a debit to the expense account.

Example #5 - Equity Accounting
Dividend Declaration:
When dividends are declared, the retained earnings account is debited, and the dividends payable account is credited.

Once dividends are paid, this is a debit to the dividends payable account and a credit to the cash account.
Stock Re-Purchase:
When shares in a business are repurchased, debit treasury stock, and credit cash.
Debt Raised from Bank Entry:
If the company borrowed $300,000 from the bank, the journal entry would look like this:

Example #6 - Transaction with Journal Entries
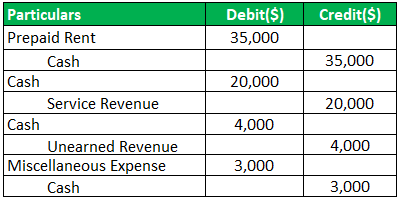
Let us see another example of accounting transactions and their respective journal entries.

The journal entries for the above transactions are:
Example #7 - Practical
Pen World Ltd. has the following transactions during the month of Feb-2019. Pass the necessary Journal Entry.
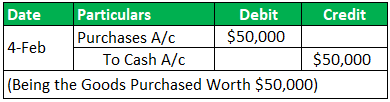
Transaction 1:
On Feb 4, 2019, I Purchased material worth $50,000;
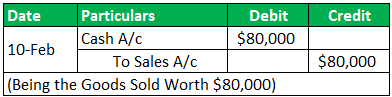
Transaction 2:
On Feb 10, 2019, Sold Pens worth $80,000
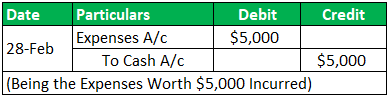
Transaction 3:
On Feb 28, 2019, Incurred Expenses worth $5,000
Transaction 4:
On Feb 28, 2019, Purchased furniture worth $7,000
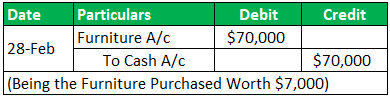
Example #8 - Practical
The following are the transactions of Fun Ltd. Record the transaction in the Journal.

Journal Entry:
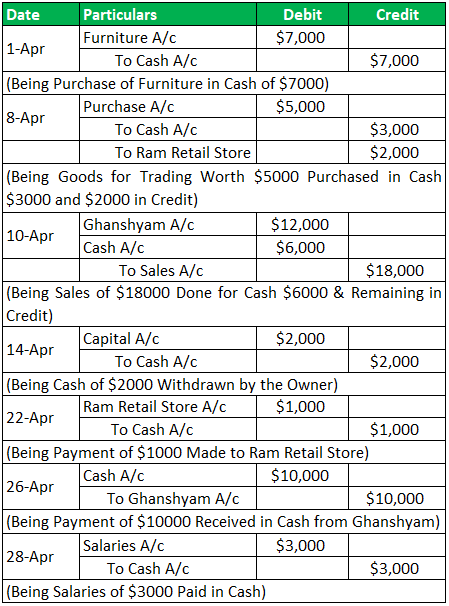
Example #9 - Practical
Small Finance International Ltd was incorporated in April 2019 with the capital initially of 10,000 common stocks of $ 10 each. During the first month of its operation the company had the following transactions. Record the journal entries of all the transactions.
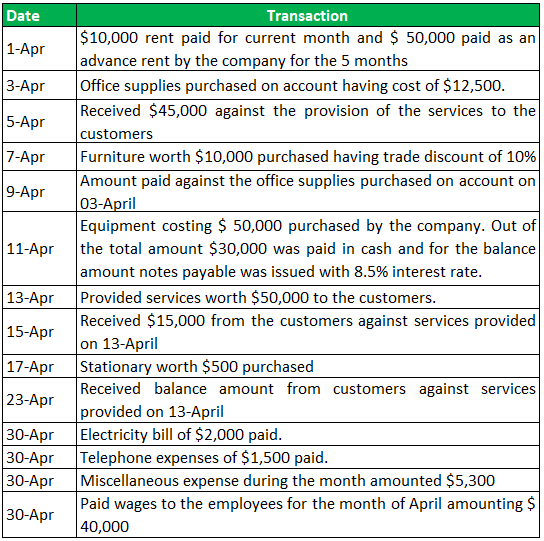
Journal Entry:
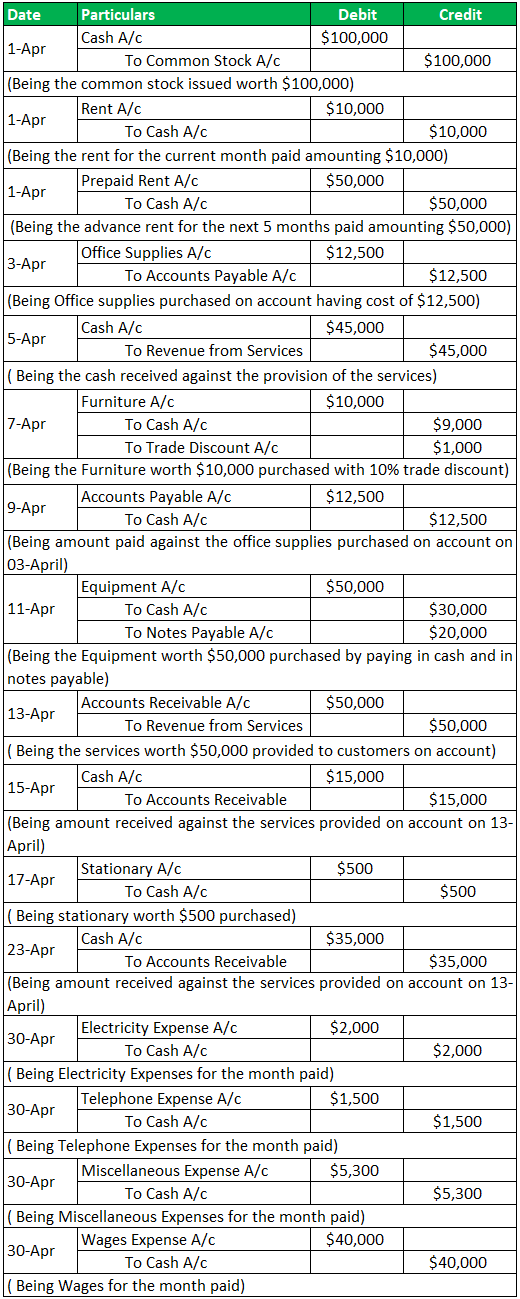
Example #10 - Practical
Other purchases related to transactions in Company Material Ltd. are given below. Record the journal entry for each transaction.
Transaction 1:
On 05- Mar- 19 goods were purchased worth $5,000
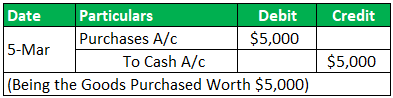
Transaction 2:
On 07-Mar-19, Goods worth $500 were lost by fire;
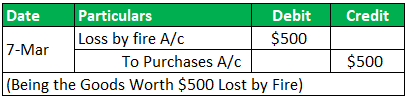
Transaction 3:
On 10-Mar-19, Goods worth $900 were lost by theft;

Transaction 4:
On 15-Mar-19, Goods worth $700 were distributed as a charity;
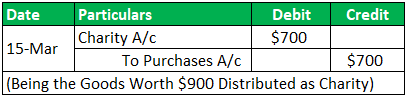
Transaction 5:
On 20-Mar-19, Goods worth $600 owner withdrew.
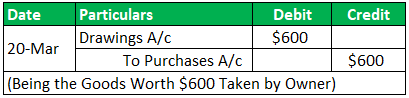
Conclusion
The business enterprise benefits, in many ways, by bypassing journal entries. Firstly it can get at one place the full effect of any transactions. Secondly, it provides records of transactions in chronological order helping and easing out to locate any transaction based on their date. Thirdly it helps mitigate the errors because the debit and credit of individuals and total transactions can be easily compared. Moreover, any entry which does not go into any books maintained by the company is recorded in the journal.