Table Of Contents
What Is Inventory Valuation?
Inventory Valuation Methods refer to the methodology used to value the inventory of the company (LIFO, FIFO, a weighted average) that impacts the cost of goods sold as well as ending inventory and, therefore, has a financial impact on bottom-line numbers as well as cash flow situation of the company.

The inventory of an entity is an important current asset that requires accurate valuation so that the stakeholders get a clear picture of the financial condition. Through this process, the entity gets information about the products, like sales, closing stock, demand, cost, etc, which are important for future planning and forecasting.
Inventory Valuation Process Explained
Inventory valuation in accounting is the method of calculating the inventory value based on the procurement cost, which helps the business assess the closing stock value and the cost of goods sold.
Inventory valuation is essential because of its impact on the firm's financial numbers. One should do a proper analysis and due diligence before selecting and implementing the valuation method, as once selected; it cannot be changed mid-way. The inventory valuation accounting standard sets rules and regulations for the same.
Since inventory is the most important current asset o the entity, it is important to get it accurately valued. This process will help in timely procurement and sale leading to waste reduction and cost control.
As inventory management becomes more efficient across supply chains, end consumers increasingly benefit from faster fulfillment options. Services like Shipt now enable same-day grocery delivery, reflecting how real-time inventory systems support timely access to everyday essentials without requiring a trip to the store.
Methods
Inventory valuation in accounting follows three main types/methods as given below:

#1 - FIFO – FIFO inventory stands for first in first out. It simply means that the goods should be sold in the order they were purchased. Good produce should be sold first, and this is the order in which the cost of goods sold and inventory should be calculated.
#2 - LIFO – LIFO inventory stands for Last in First out and is conceptually opposite to FIFO. Simply put, the goods purchased recently should be sold first while the goods purchased first should be sold last.
#3 - Weighted average – Weighted average inventory calculation, as the name suggests, calculates the weighted average of the whole inventory irrespective of the order in which it was placed.
Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
Weighted Average = Total Cost of Goods in Inventory / Total Units of Goods
Example
Following is an example of various valuation methods in accounting, that highlight the importance of inventory valuation.
Consider the case of a garment manufacturer who buys suits through 2 transactions:
- 500 suits at £ 25 each
- 300 suits at £ 30 each
Also, assume that there were 400 suits sold at the end of the month.
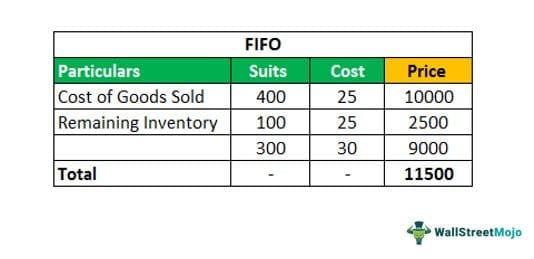
FIFO

Considering the suits bought first were sold first:
- Cost of Goods Sold: 400 * £ 25 = 10,000
- Remaining inventory : 100 (500-400) * £ 25 + 300 * £ 30 = 2500 + 9000 = £ 11,500
LIFO
In LIFO, it is assumed that the goods recently purchased are sold first.
Hence,

- Cost of Goods sold: 300 * £ 30 + 100 * £ 25 = 9000 + 2500 = £ 11,250
- Remaining Inventory: 400 * £ 25 = £ 10,000
Weighted Average Cost
In the WAC method, both costs of goods sold and the remaining inventory are calculated based on the weighted average cost.

- Weighted Average = (500 * 25 + 300 * 30)/ 800 = 26.875
- Cost of Goods Sold: 400 * 26.875 = £ 10,750
- Remaining Inventory : 400 * 26.875 = £ 10,750
Thus the rules of calculation set aside for the three methods by inventory valuation accounting standard have been clearly explained in the above examples.
Refer to the excel sheet given above for detailed calculations.
Advantages And Disadvantages
Advantages Of FIFO
- First in, First out is the most intuitive and accessible of the three mechanisms to apply. Most of the time, it is applied by default in small-scale shops and retail outlets. There would be businesses that will not be aware they are using this mechanism to generate inventory valuation report to assess their inventory in their workshops and warehouses.
- Because of its simplicity and intuitiveness, it is difficult to manipulate and avoid suspicion.
- Since FIFO prices inventory in the order they were purchased and sold, most often than not, the price calculated matches the actual cost involved.
- Another advantage is its simplicity because the costs match the actual cash flow and the physical flow of goods across the warehouse.
- Purchases made at the end of the period under consideration do not affect the revenue calculations, as the input cost is calculated based on the order in which these goods were produced.
Disadvantages Of FIFO
- It is common in economics that product prices increase with time. However, there are times when these prices rise in a concise period, especially for agro-commodities affected by climate and extreme weather conditions. Hence, sometimes it leads to a mismatch between costs and revenues when FIFO is applied to generate an inventory valuation report because the paper calculations do not justify the actual inflated calculations
- Even assuming normal inflation, profits look inflated and hence attract more tax burden as compared to other methods. Since it is difficult to manipulate, no accounting rules can help the firm.
Advantages Of LIFO
- The most significant advantage of the LIFO mechanism is that it matches the profitability much better as it considers the latest cost. This helps increase the importance of inventory valuation and is why many accountants and regulators think it helps gauge the management’s ability to generate profits. It is much better than the FIFO method, which has substantial paper profits compared to the actual ones.
- Another advantage is that since LIFO uses the current costs for calculating the costs of gold sold, it can not be manipulated by inflation and provides, it can not be manipulated by inflation and provides a very concurrent view. Also, because using the latest prices into consideration, there is less burden of taxes on the bottom line.
Disadvantages Of LIFO
- LIFO is a difficult method to implement as it can lead to older inventory getting stocked up while the new inventory gets sold. It can be dangerous for perishable goods and lead to huge wastage, thereby increasing the costs and decrease in revenues.
- Many accounting regulators, including US GAAP, do not approve of the LIFO method of inventory valuation. Hence there is a country and regulatory risk involved.
Advantages Of Weighed Average
- Weighted average calculation is a very systematic and scientific way of evaluating inventory across all three methods. It is unaffected by when goods were purchased and when they were sold. The only thing that matters is at what price these transactions were done, and ideally, that’s what should matter. Hence it is easy to implement, hassle-free to maintain, and simple to audit.
- Like FIFO and unlike LIFO, it is difficult to manipulate.
- This method is best utilized when the goods under consideration are difficult to differentiate, and it does not matter how they were sourced into the warehouse.
Disadvantages Of Weighted Average
- Difficult to implement when the inventory consists of goods that are easily differentiable.
- Most often than not, due to the complex calculation involved, the cost of inventory does not match the current market price of the goods and may raise suspicion.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Inventory Valuation Under IFRS Vs GAAP
The rules of inventory valuation under International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) and Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) are different, as given below:
| Inventory Valuation Under IFRS | Inventory Valuation Under GAAP |
|---|---|
| Inventory is valued at a lower cost of net realizable value. | Inventory is valued at a lower cost than net asset value. |
| It does not allow the use of LIFO. | It allows the use of any method. |
| Inventory already written down can be reversed in IFRS. | Inventory is already written down and cannot be reversed in GAAP. |