Table Of Contents
What Is Internal Equity?
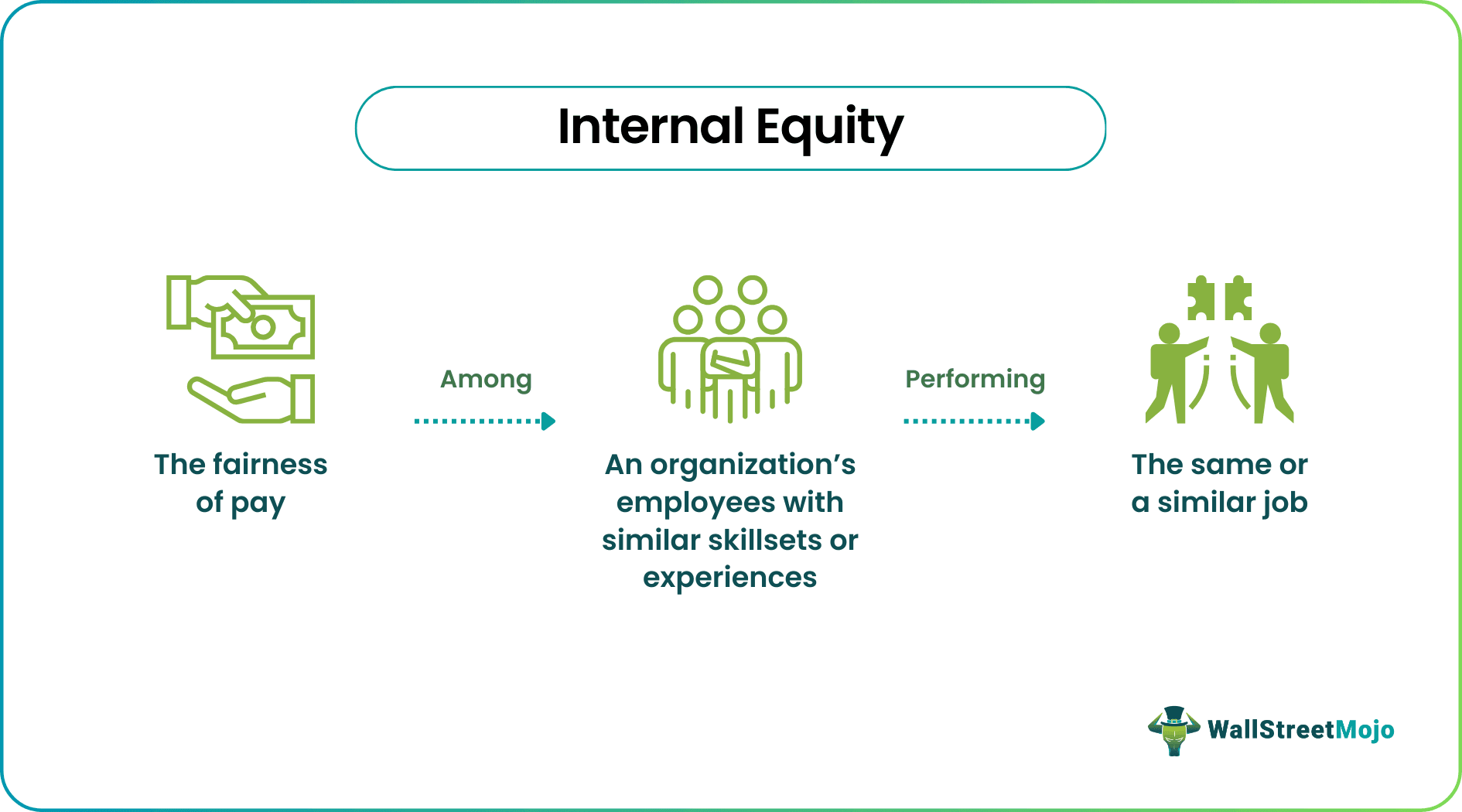
Internal equity means employees with a similar skillset, experience, and position receive similar compensation, for example, salary, additional benefits, or any other form of payment. It helps organizations decrease employee turnover and increase productivity. Moreover, it significantly improves a company’s work culture.
This concept is essential for various human resource management (HRM) aspects. It boosts employee morale and increases employee loyalty. Moreover, it makes all employees feel valued and helps an organization attract top talent. Internal equity is crucial for employee retention and engagement. Businesses must treat every employee fairly to abide by the law and avoid discrimination lawsuits.
Key Takeaways
- Internal equity meaning refers to paying fair and equal remuneration to all employees in a company having the same position in a particular field of work, with each of them having the same skillset and employment duration.
- Internal equity’s focus is within the company and involves comparing one employee to another.
- In contrast, external equity’s focus is the external job market.
- It explores if employees are equally paid compared to the ones with the same skillsets, positions, and job roles in other organizations.
- A few benefits of internal equity are improved work culture, increased productivity, and higher employee retention.
Internal Equity Explained
Internal equity meaning refers to offering equal pay to employees working in a similar field and having the same designation, considering their experience and duration of employment with a company. Based on the provisions of the Equal Pay Act of 1963, employers must treat their employees fairly and equally. After the introduction of this act, paying women and men within the same organization different compensation for similar responsibilities or work became illegal.
Certain states in the U.S. have strict rules concerning equal pay. Hence, all business owners nationwide must check with their state to ensure they fulfill all requirements. That said, one must note whether entrepreneurs offer their employees the same compensation depending on the scenario. For instance, if a company has two employees with the same responsibilities, but one has an additional degree specific to that job, it may decide to pay that person a higher salary.
Depending on a business’s structure, there are multiple ways to build an internal pay structure aligned with the legal requirements. For example, business owners can decide that every director-level position, irrespective of the department, receives compensation within a fixed pay range and a predetermined number of leaves.
Although the employees’ daily work could differ, the job titles could be sufficiently similar to warrant a specific pay rate. That said, one must remember that regardless of how a business owner wants to compensate employees in similar positions, the form of payment must be the same at that level for every employee.
How To Calculate?
Business owners can compute internal equity in human resource management by following these steps:
- An entrepreneur must conduct an internal audit to compare what they currently pay each employee and ensure equal compensation.
- While reviewing the audit, one must try to spot any discrepancy in pay between similar positions.
- One must seek logical explanations for the pay discrepancies. Location, seniority, and educational qualification are a few examples of the factors that cause such discrepancies.
- Business owners must make the required adjustments if they identify inequalities but cannot find any explanation regarding the pay difference.
All entrepreneurs must ensure to remain transparent throughout the above process. This helps prevent conflicts or disputes in the workplace. For example, if employees ask questions about their salary, business owners must state why they offer that amount.
Examples
Let us look at a few internal equity examples to understand the concept better.
Example #1
Suppose a supermarket has two-floor attendants. Both of them have the same responsibilities and experience. Moreover, their work hours are identical. Since they have the same position, duties, work experience, and work hours, the supermarket’s owner pays them the same amount as their salary.
Example #2
Per Salary.com’s second yearly survey — Employer Pay Equity Pulse Survey, organizations have the following three challenges:
- Incorporating their pay philosophy into the corporate culture
- Getting their leadership team members to be supporters of pay transparency
- Learning how they must carry out a pay equity analysis.
Over half of the organizations participating in the survey have set up a process to address internal equity. Additionally, half of such organizations have the resources to address the identified pay disparities.
In total, 41% of the companies participating are finding it difficult to achieve pay equity.
Advantages
Let us look at some advantages of internal equity.
- It helps businesses reduce their employee turnover. This, in turn, reduces their recruitment costs.
- Businesses can reduce and avoid discrimination claims by offering fair and equal pay. This enables them to save a significant amount of money.
- Internal equity in human resource management increases the productivity of employees, which can positively impact a business’s earnings.
- Companies can entice top talent by demonstrating that they offer fair and equal pay.
- Ensuring fair pay keeps a business’s work culture collaborative and positive.
- The chances of retaining the top team members increase.
- By offering equal and fair pay, companies can fight the race and gender pay gap.
Internal Equity vs External Equity
Individuals often have confusion when understanding the concepts of Internal and external equity. They must note that these two concepts are not the same; they have distinct characteristics. One must look at their critical differences to eliminate any confusion. So, let us look at them.
| Internal Equity | External Equity |
|---|---|
| It looks at fairness within an organization. | External equity considers how the benefits and pay offered by an organization measure up against other businesses in the industry. |
| It ensures the maintenance of fairness throughout a business based on similar skills, knowledge, performance, experience, and responsibilities. | External equity offers a basis for salary adjustments, structures, and competitive job offers. |
