Table Of Contents
What Is The Information Ratio Formula?
The information ratio formula (IR) refers to the expression that helps measure an active investment manager’s success strategy by comparing the excess returns generated by the investment portfolio to the volatility of those excess returns.
There is a series of steps that must be followed to ensure the calculation of the information ratio is accurate and reliable. The figure obtained after the calculation helps individuals make ideal investment decisions to be safe and avoid losses.
Key Takeaways
- The information ratio is a measure of risk-adjusted performance that evaluates the ability of an investment manager to generate excess returns relative to a benchmark index.
- It is calculated by dividing the active return (the difference between the portfolio return and the benchmark return) by the tracking error (a measure of the volatility of the active return).
- A higher information ratio indicates that the investment manager has successfully generated consistent excess returns while effectively managing risk.
- The information ratio is a valuable tool for comparing the performance of different investment managers or strategies and can help investors identify managers who consistently outperform their benchmarks.
Information Ratio Formula Explained
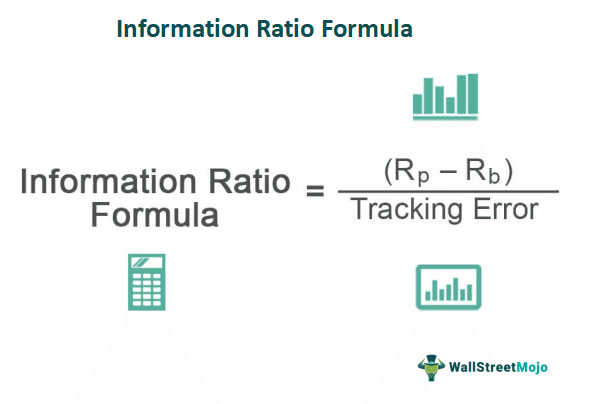
The formula for information ratio is derived by dividing the excess rate of return of the portfolio over and above the benchmark rate of return by the standard deviation of the excess return with respect to the same benchmark rate of return.
Mathematically, the information ratio formula is represented below:
Information ratio Formula = (Rp – Rb) / Tracking error
where,
- Rp = rate of return of the investment portfolio
- Rb = Benchmark rate of return
- Tracking error = Standard deviation of the excess return with respect to the benchmark rate of return
In case this ratio has been calculated based on daily returns, it can be annualized by multiplying the ratio by the square root of 252 i.e., the number of trading days in a year.
Steps For Calculation
The formula for the calculation of information ratio can be obtained by using the following steps:
Below are the steps for calculation of information ratio -
- Firstly, gather the daily return of a particular investment portfolio over the course of a significant period of time, which may be monthly, annually, etc. The return is computed based on the net asset value of the portfolio at the beginning of the period and at the end of the period. Then the average of all the daily returns is determined, which is denoted as Rp.
- Now, the daily return of the benchmark index is gathered to compute the benchmark rate of return, which is denoted by Rb. SP 500 is an example of such a benchmark index.
- Now, investors calculate the excess rate of return of the investment portfolio by deducting the benchmark rate of return (step 2) from the rate of return of the investment portfolio (step 1), as shown below.
Excess rate of return = Rp - Rb - Now, they determine the tracking error, which is the standard deviation of the excess to calculate the return of the portfolio.
- Finally, users calculate the information ratio by dividing the excess rate of return of the investment portfolio (step 3) by the standard deviation of the excess return (step 4).
- Further, this ratio can be annualized by multiplying the above ratio by the square root of 252, as shown above.
Examples
Let’s see some simple to advanced examples of the Information Ratio Formula in Excel to understand it better.
Example #1
Let us take an example of an investment portfolio with a rate of return of 12% while the benchmark rate of return is 5%. The tracking error of the portfolio’s return is 6%.
Let’s use the below-given information for the calculation of the Information Ratio Formula.
| Portfolio Rate of Return, Rp | 12% |
| Benchmark Rate of Return, Rb | 5% |
| Tracking Error | 6% |
Therefore, the calculation of Information ratio will be as follows,

- IR Formula = (12% - 5%) / 6%
IR will be -
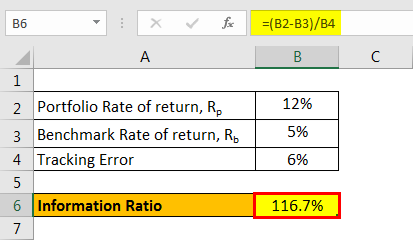
- IR = 116.7%
This means that the investment portfolio generates a risk-adjusted return of 116.7% for every unit of additional risk with respect to the benchmark index.
Example #2
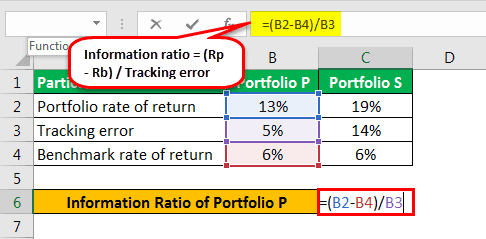
Let us take an example of two investment portfolios P and S, with the rate of return of 13% and 19%, while during the same period, the benchmark rate of return is 6%. On the other hand, the tracking error for portfolio P and S is 5% and 14%. Let us determine which portfolio is the better investment per the level of risk involved.
Given below is the data used for the calculation of Information Ratio for Portfolio P and S.
| Particulars | Portfolio P | Portfolio S |
|---|---|---|
| Portfolio Rate of Return | 13% | 12% |
| Tracking Error | 5% | 5% |
| Benchmark Rate of Return | 6% | 6% |
For Portfolio P
The calculation of Information Ratio for Portfolio P is as follows,

- IRP = (13% - 6%) / 5%
IR for Portfolio P will be -

- IRP = 140.0%
For Portfolio S
The calculation of Information Ratio for Portfolio S is as follows,

- IRS = (19% - 6%) / 14%
IR for Portfolio S will be -

- IR S = 92.9%
From the above example, it is clear that although portfolio S has a higher return compared to portfolio P, portfolio P is a better investment portfolio because it offers a higher risk-adjusted return indicated by the ratio of 140.0% as compared to 92.9% of portfolio S.
Relevance and Uses
From the perspective of an investor, it is important to understand the concept of information ratio because investors use it as a performance metric by fund managers. Further:
- The ratio is also utilized to compare the abilities and skills of the fund managers dealing with investment investment strategies.
- It throws light on the fund manager’s ability to generate sustainable excess returns or abnormally high returns over a period of time.
- A higher value of this ratio indicates a better risk-adjusted performance of the investment portfolio.
- Most of the investors use this ratio while making decisions pertaining to investments in exchange-traded funds or mutual funds based on their risk appetite.
Although it can be argued that past performance may not be the right indicator of future profits, the information ratio still finds its use in the determination of the portfolio performance vis-à-vis the benchmark index fund.