The differences between both the concepts are given as follows:
Table Of Contents
What Is An Inflation Swap?
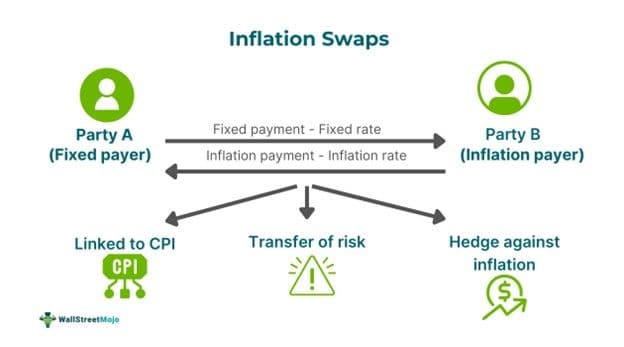
Inflation swaps are contracts that are signed between parties on an agreement that the parties exchange payments periodically according to the inflation rate explained in the contract. The payment is determined based on changes in the CPI (Consumer Price Index) over the life of the contract.
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc.. Please provide us with an attribution link.
They are a form of inflation derivatives. The swaps are used as a means to transfer the risk of inflation between parties. It helps analyze real interest rates and inflation rates based on market expectations across countries. The spot and forward rates on inflation swaps are one way of finding market-implied inflation measures.
Key Takeaways
- Inflation swaps are instruments used to transfer risks associated with inflation between parties. As per the agreement, one party pays a fixed rate based on the notional principal, while the other pays a floating rate linked to an inflation index.
- Inflation swaps provide insight into market expectations of future inflation.
- Inflation swap pricing and payments are calculated based on agreed terms. These include start and end dates, notional amounts etc, and settlements are based on differences of rates.
- Benefits include inflation hedging, predictability of income, risk management etc.
Inflation Swap Explained
Inflation swaps are agreements between parties to swap or exchange a floating rate linked to a specific inflation index for fixed-rate payments in the same currency. The terms of the swap can be customized to suit the specific preferences of the parties involved. The counterparties involved may agree on various factors such as the start and end dates, the notional and currency amounts, the notional amount's profile along the term of the transaction, the inflation index that is agreed to be swapped etc. additionally, the frequency at which inflation has to be reset, the periodic span of payments. These factors are typically considered in the case of fixed-rate coupons. On the other hand, the floating rate is determined based on the inflation index specified in the agreement.
Payments are calculated per the agreed-upon notional amount. They are paid on predetermined dates within predetermined periods. If the floating rate exceeds the fixed rate, the floating-rate payer compensates the fixed-rate payer for the difference. Also, if the floating rate is lower than the fixed rate, the fixed-rate payer compensates the floating-rate payer for the difference. If the floating inflation index is negative, the floating rate payer may owe payments to the fixed-rate payer.
Examples
Let us look into some examples to understand the concept better
Example #1
Imagine ABC Ltd is a clothing company and its revenue changes based on the inflation index. The company wants to fix the revenue changes it's going to encounter in 10 years. To execute this, it has to enter into an inflation swap with a bank named XYZ. After the swap, ABC forwards the revenue changes annually to XYZ for 10 years. Under the agreement, ABC receives fixed-rate coupons for a notional amount and agrees to make annual payments. This arrangement helps ABC to hedge revenue against inflation and be involved in risk management.
Example #2
The Pension Protection Fund (PPF) based in the UK is a statutory fund that provides compensation to members of defined benefit pension schemes if their employer goes bankrupt and the pension scheme is underfunded. Inflation swaps play an important role in this PPF asset allocation strategy. It protects the portfolio from inflationary pressures. In other words, integrating inflation swaps into an asset allocation strategy can enhance protection against inflation, ensuring the portfolio remains resilient and aligned with long-term financial goals.
Benefits
Given below are some of the points that convey the benefit of the swaps:
- Hedge against inflation: The parties involved in the swap agreement can hedge or leverage the differences in the rates.
- Predictability: The involved parties can gain leverage through a fixed rate as agreed at the beginning of the contracts. The inflation swaps data can help investors predict the incoming cash flow, budget and plan for the future.
- Risk management: Inflation swaps data helps investors to plan their investments and manage risks effectively. This helps them achieve their short and long-term goals.
- Reducing inflation risk: The swaps facilitate the transfer of risk from one contractual party to another. This is particularly helpful for institutions with long-term liabilities, such as insurance institutions and pension funds.
Inflation Swap vs Interest Rate Swap
| Basis | Inflation swap | Interest Rate Swap |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Concept | Inflation swaps are agreements between two parties who make payments based on differences in the first agreed-upon inflation rates. | Interest rate swaps are contracts that are formed on the basis of an agreement between two parties to exchange a stream of future payments to another. These are based on a specified principal amount. |
| 2. Risk Associated | Inflation rate swaps deal with risks associated with changes in inflation. | Interest rate swaps deal with risks associated with changes in the rates of interest. |
| 3. Reference index | Inflation swap rate is often associated with inflation indexes such as CPI. | Interest rate swaps are agreed upon using benchmark interest rates such as Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR). |
