Table Of Contents
What Is Index Number?
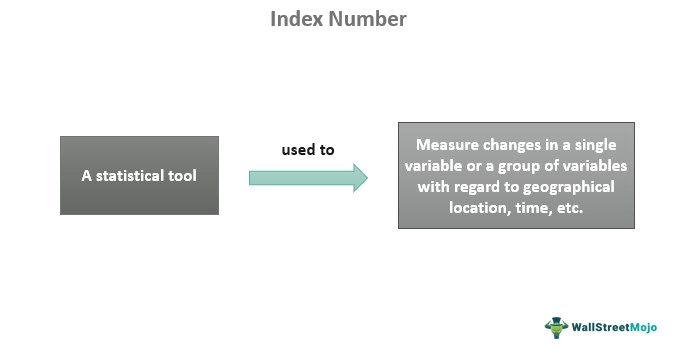
An index number is a statistical tool used in economics and business to quantify changes in an individual variable or a group of variables concerning geographical locations, time, or other aspects. The primary objective of this statistical measure is to simplify complex comparisons.
It is extremely helpful when comparing currencies with different nominal values. Moreover, some nations even utilize this method to make changes to public policy, for example, modifying government benefits for inflation. In statistics, one can use it to measure economic indicators, inflation, stocks, etc. There are four types of index numbers — value, quantity, price, and special purpose.
Table of contents
- Index number meaning refers to a statistical instrument used to evaluate changes in multiple variables or a single variable over time. It helps in expressing economic data time series and comparing contrasting information.
- This tool has various types. A few popular ones are quantity, price, value, and special purpose. Moreover, individuals use different formulae to compute index numbers, for example, the simple aggregative method and the simple average of price relatives method.
- There are various uses of index numbers. For example, they help governments to formulate new policies and adjust existing ones.
Index Number In Economics Explained
Index number meaning refers to a process of evaluating variations in different variables and fields over time. Typically, it has a base value of 100, indicating price, production level, price, and more. In economics, it simplifies comparison, which can be difficult when using raw data. In other words, it helps one quantify the changes in a sector, industry, or variable. Moreover, one can utilize this statistical measure to monitor changes in data sets over time.
This tool is very useful for comparing currencies having multiple nominal values. In addition, various countries use this technique to change their policies.
It has the following features. Let us look at them in detail.
- These are a special type of average utilized to measure a relative or net change in a single or group of variables when measuring absolute change is impossible.
- It represents the early changes in factors that one might not be able to measure directly.
- The technique for calculating this average subset varies from one variable to another.
- One can use this method to compare the levels of any phenomenon on a specific date with its levels on a previous date.
One can change index numbers to any unit of measurement. Experts often apply indexing methods to employment, production, unemployment, inflation, etc.
Types
Although there are different types of index numbers, most of their primary objective is to simplify data to make comparison easier. One often uses this method in public and private sectors to make well-informed decisions regarding policies, prices, and investments. Let us look at some of the popular types of this statistical tool:
- Quantity : It measures the changes in the volume or quantity of the products produced, sold, and consumed over certain durations. Hence, they measure the relative changes in the volume of a certain set of items between timeframes. One can use it to measure construction, production, or employment. It has two subtypes — weighted and unweighted.
- Price : It computes the change in the price of a single or group of variables between two time periods. A series of numbers organized to compare the values of two durations make it up. One often uses this method to compare the price of products from one timeframe to the base period. An example of this tool is the Consumer Price Index or CPI.
- Special Purpose : Its main purpose is not the same as the other types. Typically, the primary objective of this tool is to track the changes in a unique variable group, particular sector, or industry. Index numbers tracking the changes in the securities market are an example of this type.
- Value : It measures the change in the aggregate value of a single or group of variables compared to its value in the base period. One can use this statistical measure to track the changes in sales, inventory, trade, etc.
Index Number Formula
Formula
There are multiple formulae for calculating index numbers. Two popular techniques are as follows:
- Simple Aggregative Method
The formula is as follows:
P01 = ΣP1 ÷ ΣP0 x 100
Where:
P01 is the index number.
ΣP1 is the sum of all prices in the year for which one has to compute the index number.
ΣP0 is the base year.
- Simple Average of Relatives Price Method
Let us look at the formula for computing via this method.
P01 = ΣR ÷ N
Where:
ΣR = The sum of the price relatives or R = P1 ÷ P0 x 100
N = Total number of items
Calculation Examples
Let us look at two index number examples using the above formulae to understand the concept better.
Example #1: Using The Simple Aggregative Method
| Product | All Prices (Rs.) In The Base Year 1980 (P0) | All Prices (Rs.) In The Current Year 1985 (P1) |
| B | 15 | 30 |
| C | 20 | 25 |
| D | 45 | 55 |
| E | 30 | 40 |
| Total | ΣP0 = 110 | ΣP1 = 150 |
P01 = 150/110 x100
Or, P01 = 136.36
Example #2: Using The Simple Average of Relatives Price Method
| Product | All Prices (Rs.) In The Base Year (P0) | All Prices (Rs.) In The Current Year (P1) | Price Relatives (R = ΣP1 ÷ ΣP0 x 100) |
| C | 20 | 30 | 30/20 x 100 = 150 |
| D | 25 | 50 | 50/25 x 100 = 200 |
| E | 50 | 75 | 75/50 x 100 = 150 |
| F | 32 | 40 | 40/32 x 100 = 125 |
| N = 4 | ΣR = 625 |
P01 = ΣR ÷ N
Or, P01 = 625/4
Or, P01 = 156.25
Importance
Some uses of index numbers are as follows:
1. General Importance
Generally, this tool helps in many ways. Some of them are as follows:
- It helps one compare separate data sets concerning different durations or different places.
- The tool simplifies complicated facts.
- It helps one make future predictions.
Moreover, this tool is useful for individuals engaging in practical or academic research.
2. Measurement of Changes In Price Level
This tool measures the difference in the price levels or the value of money. Additionally, it warns about inflationary tendencies, enabling a government to take effective anti-inflationary measures.
3. This statistical measure provides information concerning the production trends of different sectors in an economy. This helps one evaluate different industries’ conditions.
4 . Formation And Modification of Economic Policies
They help governments formulate and assess policies. A government can formulate new policies or adjust the existing ones based on the changes occurring in the economic conditions.
Besides these, the tools have specific uses in economics. They are as follows:
- They help analyze markets for particular commodities.
- In the stock market, they provide information regarding the price trends of stocks.
Also, by using this tool, bank officials can get information regarding the changes in deposits.
5. Highlights Variation in Cost Of Living
This tool highlights the changes in a nation’s cost of living. It indicates if a country’s cost of living is increasing or decreasing. As a result, the government can modify workers’ wages to minimize the impact of inflation on wage earners.
Limitations
The statistical measure has the following limitations:
- It is never 100% accurate owing to the practical difficulties associated with the calculation process. Moreover, it quantifies average change, thus indicating only broad trends.
- One cannot use Index numbers prepared for a particular purpose for another purpose.
- The tool does not consider the items’ quality. A general increase in the index may be possible because of a product’s quality improvement, not because of a price increase.
- Different nations use different base years of the computation of index numbers. Moreover, they include different items having different qualities. Hence, this technique is not reliable for making international comparisons.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The Laspeyres method shows upward bias and exaggerates the price increases compared to the other price indices. This is because it does not consider substitution among items induced by relative price changes.
Prepared with reference to the important goods and services consumed by the general public, this tool measures the changes in a country’s cost of living. It considers only the representative items that form the consumption pattern of the common people in a country.
Like a barometer used to measure atmospheric pressure, it is extremely helpful in quantifying the pressure of business and economic behavior on a country’s economy.
It helps one compare and measure the prices of various commodities. Many economists use this tool to measure an economy’s inflation level. Moreover, one can utilize it to evaluate the standard of living of the general public in a country.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to Index Number and its definition. Here, we explain its use in economics, types, formula with calculations along with its benefits. You can also go through our recommended articles on corporate finance –
