Table Of Contents
What is an Independent Auditor Report?
An independent auditor report is a report given by an independent auditor after examining financial statements, books of accounts, financial transactions, accounting practices, and internal and external control of an organization.
An Independent auditor is an independent person who is not associated with the company by any means and is appointed by the company with the consent of the board of directors. He may be a chartered accountant or certified public accountant.
Table of contents
- An independent auditor gives a separate auditor report after analyzing financial statements, books of accounts, financial transactions, accounting practices, and internal and organization's external control.
- Unmodified reports and modified reports are the two types of independent auditor reports.
- Title, addressee, the responsibility of the management and the auditor, the scope of the audit, auditor opinion, basis of the opinion, other reporting responsibility, the auditor's signature, place of a signature, and date of the audit report are the independent auditor reports format.

Types of Independent Auditor Report
There are two types which are as follows –
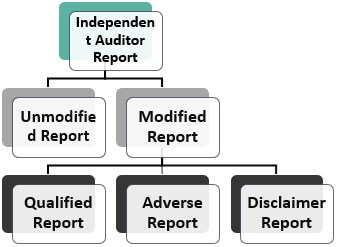
#1 - Unmodified Report
The unmodified report is also called a complete report or clean report. This report is issued by auditors when they are satisfied with the financial statement hat it presents the true and fair value of the business operation. It gives investors and shareholders confidence to decide.
#2 - Modified Report
It is issued when an independent auditor is not satisfied with the financial statement or cannot obtain sufficient and appropriate evidence to believe that the financial information is free from any misstatement.
There are three types of modified reports that the auditor gives:
- Qualified Report – Qualified audit report is given when there is a reason to believe that misstatement is provided in the financial statement or the auditor cannot obtain appropriate and sufficient evidence. However, some misstatements in financial statements may not be so high that they will become unacceptable.
- Adverse Report – The auditor reports negative reports by examining financial statements and evidence obtained. They believe a material misstatement in the financial information can affect stakeholders' decisions.
- Disclaimer Report – When the auditors cannot form an opinion on financial statements in the absence of sufficient and appropriate audit evidence, they cannot perform an audit and give a disclaimer report.
Format of Independent Auditor Report
Below is the format of independent auditor reports –
- Title – It remains the same in all reports as "Independent Auditor's Report."
- Addressee – Addressee means the persons to whom this report will address or who will receive it. The addressee can be the board of directors, shareholders of the company, or any other person depending on the nature of the report.
- Responsibility of the Management and Auditor – In this paragraph, auditors and management responsibilities will be defined, like auditors will give an unbiased report after examining financial statements.
- Scope of the Audit – In this paragraph, the auditor mentions the scope of the audit as it was conducted per generally accepted auditing standards.
- The Opinion of the Auditor – It is the primary and most crucial paragraph of the auditors' report. In this paragraph, the auditors give their opinions based on examining financial statements. Auditors provide four types of views, which are already described in the kind of auditor reports.
- Basis of the Opinion – In this paragraph, the auditors provide facts and grounds on which they have given their opinions.
- Other Reporting Responsibility – In this paragraph, the auditor mentions any additional responsibility apart from primary responsibilities.
- Signature of the Auditor – The partner of the audit firm, which the company appoints, will sign the audit report.
- Place of Signature – Here the auditor has to mention the name of the city where the auditor will sign the audit report.
- Date of Audit Report – The date of the audit report is the date on which the auditor will sign the audit report.
Advantages
- It gives confidence to the person who is not involved in the company's day-to-day operations like shareholders.
- It gives an accurate and fair financial picture of the company to the management and board of directors based on which they can take action for the future.
- The audit helps identify costs, which can be saved with proper control.
- The auditor checks the company's internal control and reports whether internal controls are adequate or not.
- It safeguards the company and the responsibility of its employees, who fear that they can be caught in an audit if they are doing some bad practice.
- Banks will easily give loans to the company based on a qualified auditor's report.
Disadvantages
- It is an extra cost to the company, and sometimes it becomes a costly affair for small businesses.
- Sometimes employees get harassed and do not express their ideas if they fear an audit.
- If the auditor does not give the correct opinion in the audit report, management may likely take wrong actions or decisions.
- Auditors must know the business nature and processes; otherwise, it will impact the audit report.
Conclusion
The Independent audit report is nothing but an independent auditor's opinion after examining books of accounts, business transactions, accounting policies and practices, and internal controls adopted by the company. It is an essential requirement of banks and creditors for lending loans to the company.
There is a specific format and content of the independent auditors' report, which auditors have to maintain. These reports are good for the company because external and independent parties issue them. Therefore, it is unbiased and provides a clear picture of the organization. However, management must give actual, correct, sufficient, and appropriate evidence; otherwise, it will misguide the auditor and the report.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The independent auditor's ordinary audit objective of financial statements is the expression of the fairness they present, in all material respects, financial position, operations results, and cash flows per generally accepted accounting principles.
Auditors must keep independent audit reports confidential. They must protect the client's business secrets with their work product. One may access the information which is allowed to see it.
An independent audit report is addressed to the shareholders and the board of directors, or equivalents for companies not organized as corporations.
The independent auditor enables reasonable assurance to decision-makers that the company's financial statements are fairly presented in all material respects and according to the U.S. GAAP.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to the Independent Auditor Report. Here, we discuss independent auditor reports' contents and their advantages and disadvantages. You may learn more about financing from the following articles –
