Table Of Contents
What Is Human Resource Planning?
Human resource planning identifies the present and foreseeable demands of human resources that an organization will require to reach its objectives. It aims to act as a link between human resource management and an organization's overarching strategic plan.
It converts the organization's objectives and plans into an estimated number of employees required to achieve those goals. Estimating the quantity and type of personnel the firm will need over the next several months is the primary step in the human resource process. Businesses that train employees to expand capacity and build skills will see their workforce grow.
Key Takeaways
- Human resource planning concept is a tactic businesses use to keep a regular flow of qualified workers while preventing staff surpluses or shortages.
- A company's productivity and profitability can increase with a robust plan.
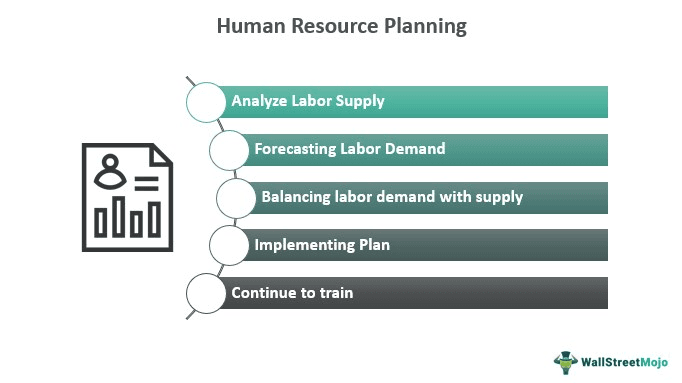
- The planning process generally consists of four steps: assessing the present employee supply, forecasting the workforce, balancing labor supply and demand, and creating plans that support the firm's objectives.
Human Resource Planning Explained
Identifying the organization's current human resource requirements and figuring out how to hire them are included in planning. Strategic human resource planning serves as a blueprint for the current state of the workforce and future human resource requirements.
A firm's operations plan and its total human resources management are connected by such planning. Human resource planning needs are a projection of the fire plan's acquisition and use of human resources. The planning of an organization's human resources, including hiring, screening, paying, training, designing jobs, and setting work standards, is collectively referred to as human resource planning.
The organization's human resources department is in charge of planning its human resources and organizing its hiring process. The planning process aids the business in determining the kind of talent it requires and which departments might profit from adding fresh talent. Maintaining a company's profit and productivity levels depends on hiring the proper type of qualified workers. Modern workforce optimization tools, like a labor management mobile app, can significantly streamline scheduling, task delegation, and performance tracking across teams.
Process Steps
Forecasting the organization's demand for and supply of human resources is done through the planning process.
- Choosing the Goals: Determining the goals for which the process will be carried out is the first step in every cycle. For example, to choose the correct number of people for the right job, it is essential to identify the goal for which workforce planning is to be done.
- Examine the present personnel supply: use the data saved about the staff's expertise, competency, abilities, etc., to carry out a specific job. Additionally, it is possible to predict future openings to plan for the workforce from internal (inside the current employees) and external (hiring applicants from outside) sources. I
- Estimating Demand and Supply: After maintaining an inventory of skilled employees, the next stage is to match anticipated future demand for employees with the organization's current supply of resources.
- Action plan: Once the staffing shortfalls have been assessed, an employment or action plan should be created. If there is a shortfall, the company may pursue recruitment, training, or interdepartmental transfer plans; if there is a surplus, the company may pursue voluntary retirement plans, redeployment, transfer, or layoffs.
- Training and Development: Training is provided for both current personnel and new hires, as both groups must periodically upgrade their skill sets.
Factors
Various internal and external influences influence the planning of human resources. Some of them are:
- Organizational type: The organizational type impacts Human Resource strategy. Two factors—the nature of the company and the ownership structure—can be used to determine the kind of organization.
- Organizational approach to planning: Different businesses use various methods for overall planning. These strategies can be divided into proactive or reactive and informal or formal. In an aggressive approach, a company projects the future and bases its strategic choices on that projection.
- Organizational development cycle: Organizations go through several stages of development: birth, childhood, adolescence, middle age, and old age. At every step of the growth cycle, organizational goals and strategic priorities impact human resource planning.
- Time horizon: Planning for human resources has a time horizon. More ambiguity exists in Human Resource formulation as the time horizon gets longer. This is because it is incredibly challenging—and occasionally even impossible—to foresee the future environment accurately when it is unpredictable.
- Information type and quality: Since information is used to develop Human Resource plans, the effectiveness of human resource planning work depends on the quality and type of information.
Example
Suppose a garments firm ABC Ltd needs help with the supply of staff. First, it will analyze the organization's goals and departmental needs. After this, it will examine the collection available to the organization and plan to fill the vacant positions. Continuous training is the last but not minor step of this process. Timely feedback from management and employees ensures the effectiveness of the staffing position.
Advantages And Disadvantages
The advantages and disadvantages of the planning process can be understood in the following ways.
Advantages
The advantages of such planning are:
- Building abilities - Workers will work more effectively thanks to such planning. In addition, businesses will grow professionally with the present employees instead of depending on independent contractors if they provide the education and training required to develop skills and improve capacity.
- Enhancing retention - Employee retention is higher if they demonstrate appreciation by spending time and money to provide them with the resources they need to advance. In addition, it will make their employees more excited and let them know they appreciate their contribution and length of service.
- Predictability - The market environment, the state of the economy, and supply chain difficulties present enough daily uncertainty for the company. By adding an extra layer of certainty to scheduling, staffing, and managing ongoing workload, putting thought and planning into providing employees with what they require to perform a good job and remain firm over time helps alleviate some of this determinism.
Disadvantages
Disadvantages of such planning are:
- Expensive - Training and putting money into employees is expensive. Therefore, planning may reduce the bottom line in the near term before it enhances profits, whether spending on specialized training or taking employee time away from jobs that are more likely to increase incoming income immediately.
- Unpredictability - There is no assurance that the employee's train will remain with the firm sufficiently to realize the advantages of investment, even if planning for human resources can offer the business a better degree of stability through improving personnel capabilities.
- Illusionary - Planning for human resources can improve the workforce's ability to do their roles. Still, it can prepare them to carry out outdated tasks as businesses and industries develop. As a result, they can experience a false sense of safety and not respond to situations quickly enough.
Difference Between Human Resource Management And Human Resource Planning
The strategic and cohesive approach to managing people in an organization or company in a way that gives them a competitive advantage is known as human resource management. While later is the procedure used by management to decide how to move an organization from its existing personnel position to its target staffing position.
Some of the fundamental difference between them is:
| Basis | Human Resource Management | Human Resource Planning |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Conventional | Contemporary |
| Nature of function | Routine | Strategic |
| Focus | Primarily on routine tasks like hiring, paying, training, and maintaining employee harmony. | Treat the organization's workforce as a valuable resource that should be utilized, respected, and conserved. |
Manpower Planning vs Human Resource Planning
Manpower planning is the strategy for acquiring, utilizing, improving, and preserving an organization's human resources. While human resource planning is a continuous process that a business uses to systematically plan for the future of its human resources to fill open positions with qualified candidates.
Human resource planning and workforce planning are very different in the following manner.
- In human resource planning, managers are concerned with motivating employees, a process in which cost, numbers, control, and systems mix and play a role. Regarding workforce planning, executives are concerned with the quantitative aspects of forecasting availability, demand matching, and management, which include people.
- Manpower planning was once thought of as a strategy for securing the company's human resources, which involved hiring the proper quantity of people with the necessary skills at the correct time. The primary objective was to match up the supply and demand of labor.
- Demand is the term used to describe the organization's present and future needs for human resources. At the same time, supply is the extent to which the current workforce may satisfy those needs internally and externally.
