Table Of Contents
Hire Purchase Meaning
Hire purchase is a buying option where the buyer pays for goods in regular installments. But, first, the buyer has to pay a down payment. The buyer does not get the title of ownership until complete payment is made. This includes the principal and the interest.
Due to the interest, buyers end up paying more. In many countries, this mode of payment is also called the installment plan. A hire vendor is a seller or business entity that offers this mode of purchase to its customers.
Key Takeaways
- Hire purchase is a legally binding agreement. A buyer or hirer disburses a percentage of the total cash price as a down payment. The buyer settles the outstanding sum and interest in periodic installments.
- These transactions can also be executed with the help of a financier. The financier purchases the goods on the buyer's behalf and makes payment to the seller. The financier presents the product to the buyer and collects the amount with interest.
- It is a feasible buying option for low-income groups. Even expensive products can be purchased conveniently. Also, industries facing cash shortages do not want to spend a huge amount at once.
Hire Purchase Explained
Hire purchase is an installment-based method of procuring expensive consumer goods or assets. This method is used both by individuals and firms. The buyer makes a down payment—a partial sum or a percentage of the total price. The remaining amount is paid in installments—inclusive of interest.
The purchaser pays a rent (hiring charge) for an agreed period. The frequency of installments could be yearly, quarterly, or monthly.
The buyer can acquire goods immediately, but the ownership of goods remains with the seller till the final payment is completed. If the buyer defaults, the seller has the right to seize assets. Also, the seller can claim depreciation on sold goods and avail tax benefits. Similarly, the purchaser can claim income tax benefits on hire charges.
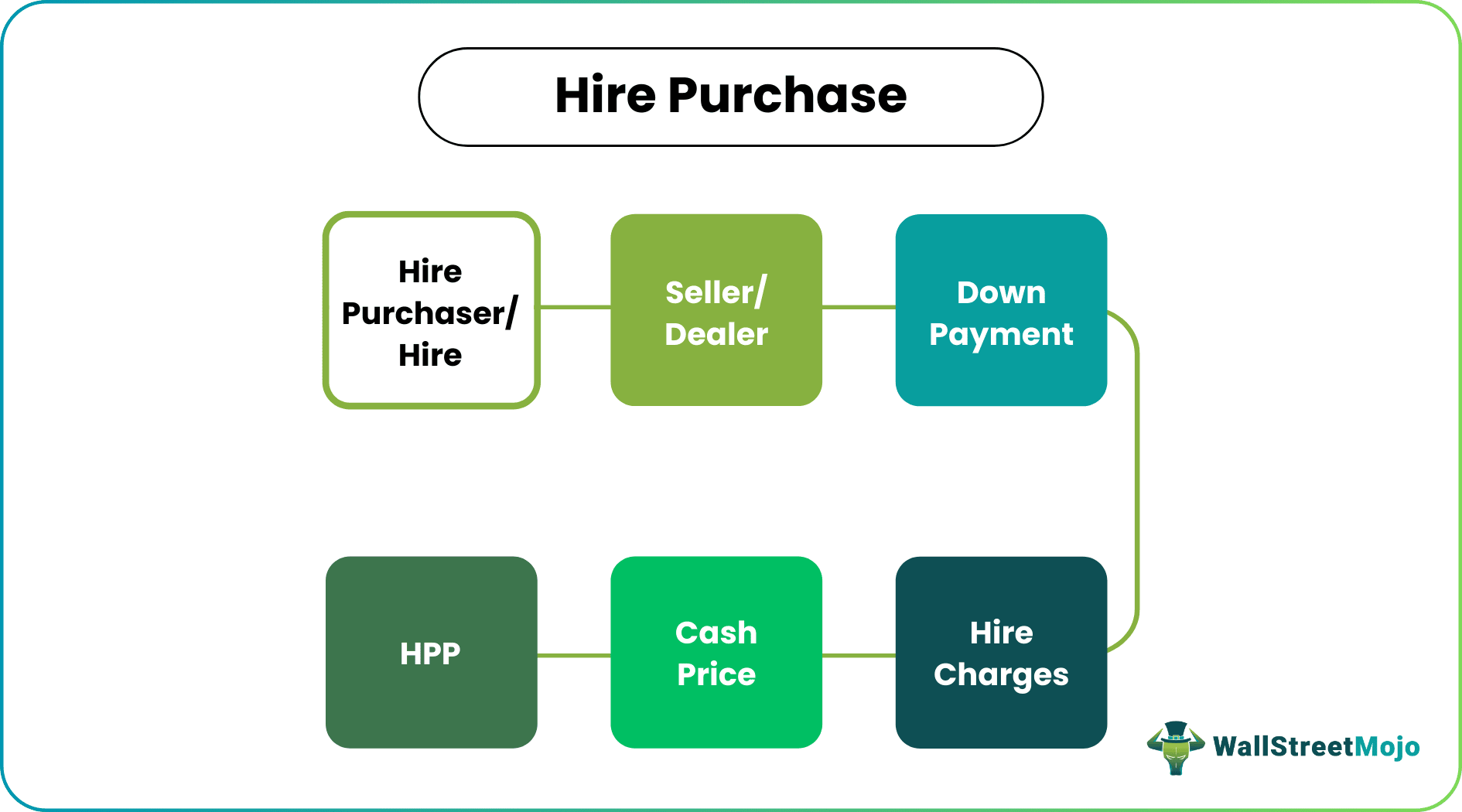
The following parties are involved in a hire agreement:
- Hire Purchaser/Hirer: An Individual or organization purchases goods by paying installments.
- Seller/Dealer: A business entity that sells goods.
- Financier: A finance company funds the purchase.
Hire Purchase Features
The following characteristics differentiate it from other modes of purchase:
- The buyer acquires the goods immediately—as soon as the purchase is made.
- The ownership title of the goods or asset remains with the seller or the financier—till the buyer makes the final payment.
- After the down payment, the buyer pays for the remnant with interest—in periodic installments.
- When buyers complete payment, the ownership title is transferred to their name.
- A flat rate interest (interest is calculated on the full loan amount for the entire period) is applied on these purchases.
- If the buyer defaults, the hire vendor can (legally) take possession of the asset. Also, the buyer’s deposit is treated as a fee for using the asset.
Types
Based on the purpose of the purchase, it is categorized into two types:
Sometimes, a third party, i.e., the financier, purchases goods on behalf of the customer. This third party gets into a purchase agreement with the customer. Based on the agreement, the customer becomes the owner as soon as they pay the final installment. Till then, the financier owns the title of goods; The financier also pays the purchase price to the seller. Later, the lender recovers this amount from the customer—in periodic payments. In case of non-payment, the lender has the right to seize goods.
Alternatively, the consumer can directly enter into a purchase agreement—with the seller. If so, the buyer has to pay a down payment. Over time the buyer repays the remaining amount with interest—in periodic installments. The buyer becomes the owner once payment is completed.
Hire Purchase Calculation
For determining the purchase price, the following formulas are used:



Here,
- Cash Price is the current market price at which goods can be purchased.
- Hire Purchase Price is the price at which goods can be purchased (as mentioned in the agreement).
Annuity to recover $1 over the given period is given by:

Here,
- r is the rate of interest.
- n is the number of installments.
Example
on January 1, 2018. an Inc. purchased a machine on hire purchase from Z Ltd. Inc. paid $80,000 immediately and agreed to three annual installments of $80,000 each. The installments will be paid on December 31 of every year.
The machine’s purchase price is $298,000. If the vendor charges 5% interest per annum, calculate the purchase price, total interest, and the breakup of principal and interest paid by the buyer.
Solution:
Interest expenses can be calculated as follows:
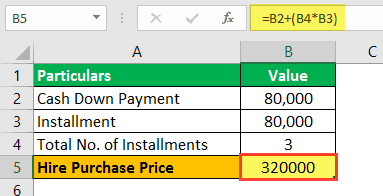
#1 - Hire Purchase Price

#2 - Total Interest

#3 - Principal and Interest Paid Every Year
- The outstanding cash price at the time of the first installment is computed as follows:
Total Purchase Price – Down Payment = $298,000 – 80,000 = $ 218,000
First Installment:
- Interest charged on the first installment:
Interest = 5% of Outstanding cash price = 5% of $218,000 = $10,900
- The principal amount paid in the first installment:
First Installment – Interest Paid = $80,000 – $10,900 = $69,100
- Outstanding amount after the first installment
Total Outstanding Amount – Principal amount paid in first installment = $218,000 - $69,100 = $148,900
Second Installment:
- Interest paid on second installment
Interest = 5% of Outstanding amount = 5% of $148,900 = $7,445
- Principal Repaid in Second Installment
Second Installment – Interest = $80,000 – $7,445 = $72,555
- Outstanding amount after the second installment
Total Outstanding Amount – Principal amount paid in second installment = $148,900 - $72,555 = $76,345
Third Installment:
- Interest paid in the Third Installment
Interest = 5% of Outstanding amount = 5% of $76,345 = $3,655
Advantages and Disadvantages
This mode of purchase has the following benefits:
- It is a feasible buying option for low-income groups.
- Industries facing cash shortages do not want to spend a huge amount at once.
- Since the number and amount of periodic payments are known in advance, it becomes easier for the entity to make budgeting decisions.
- It is not influenced by the buyer's credit rating, which makes it suitable even for customers with a poor credit score.
This mode of purchase has the following drawbacks:
- Such a purchase imposes a fixed payment burden on the buyer, which is difficult to arrange during a cash crunch.
- The interest charged on such a purchase increases the final cost of goods.
- Even after making a significant part of the payment, the ownership of goods or assets lies with the seller or financier.
- If the purchased asset gets stolen or destroyed before it is fully paid for, insurance may not cover the liability.
- Some financiers charge exorbitant interest rates.