Table Of Contents
Herd Mentality Meaning
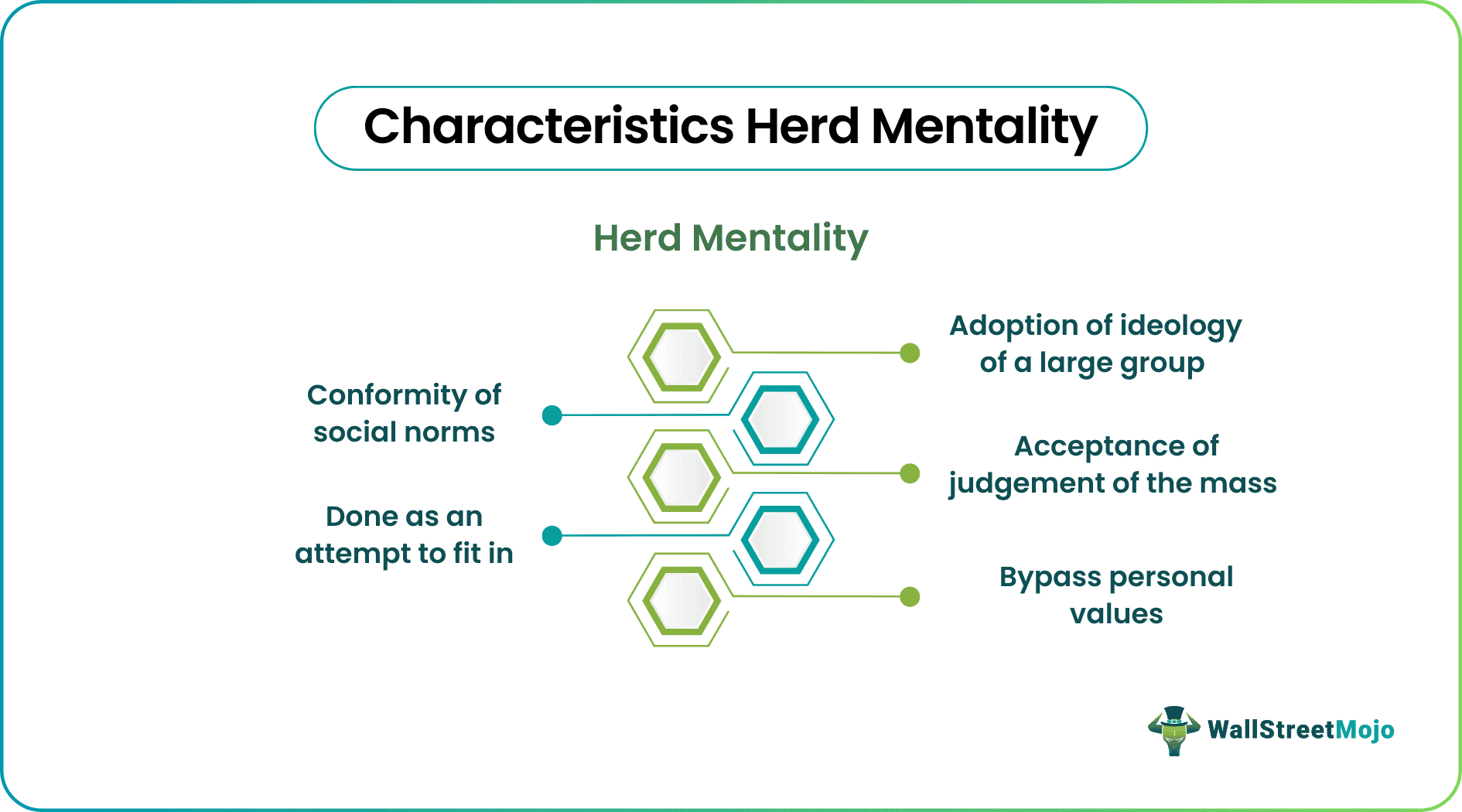
Herd Mentality is a concept where individuals adopt the ideology of a larger group bypassing personal critics and rationality. They act in conformity to the group's beliefs assuming that everyone else has done their research. It mostly stems from an individual's need to fit in and adhere to social norms.
It arises from a human being's natural desire to belong somewhere, which masks and challenges personal decision-making skills. Clouded judgments of an individual can lead to undesirable outcomes. Investors lose money if they follow trends without proper research. At large scales, it can disrupt the market and economic growth.
Table of contents
- Herd Mentality Meaning
- Herd Mentality is an ideology where the beliefs of a larger group influence individuals. They operate following the group's beliefs, believing that everyone else has done their homework. It can also be considered an attempt to conform to social norms.
- Here, individual ideals and principles are overtaken by group values. It leads them to make decisions beyond their sense of personal identity.
- Herding mentality bias can be commonly seen in financial markets. Investors can lose investments, and it can suspend economic growth if the market is disrupted.
Herd Mentality Explained
Herd mentality stems from an emotional part of the human psyche rather than logical thinking. It is not uncommon to observe people develop an inclination to act the same way as most of their peers, even in a globalized age. The values of the group replace individual values and principles. It results in making consensus decisions beyond their sense of personal identity.
Herd or mob mentality is not always bad; political associations and protests have paved the way for many countries to taste freedom. However, it is considered a dangerous notion as it suppresses individual opinions. People act in conformity because of the fear of being left out.
The herding mentality among investors is common, especially in the stock market and cryptocurrencies. It is visible when large groups of investors act irrationally and emotionally; they tend to buy positive news too soon in hopes of making huge returns, only to lose their money and vice versa. Their risk-taking nature is not backed by proper research as they assume the price rise is inevitable because of the market beliefs in that asset.
Capital markets are an important source of funding and the foundation of economic growth. However, there can be adverse effects when cognitive biases envelop the markets are enveloped by such as the herding mentality bias and other psychologically-driven prejudices. As a result, they might encounter miscalculations, extreme volatility, panic buying, and selling. This will result in huge losses and an increased cost of capital for individuals seeking funds within the economy.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
Examples
The following are some herding mentality examples illustrated to give the readers a basic understanding of the concept.
Example #1
Dan is an investor and wants to invest in the stock market. He looks for information on the internet and thinks about investing in the healthcare industry. From his research, he understood that there has always been a growing demand for healthcare, and these companies consistently gave a good rate of return. However, the news was full of pictures of the booming IT sector, and a famous mobile application company was trending because of a newfound technology. The information influenced people, and Dan decided to invest in IT instead because the rate of returns seemed good, and he wanted to make money. He arrived at that decision without much research and because his investor peers invested in it.
Example #2
Cryptocurrencies have been in the trend for quite some time now. Names such as Bitcoin and Etherium have become popular. Many industrialists and popular business figures are jumping on the bandwagon, Elon Musk being one of them. People know him as a smart investor and a successful businessman, and naturally, the community will believe that he knows something that they do not. Therefore, they tend to follow his actions blindly.
Musk endorsed a popular meme coin which made the coin's price soar to rocket highs. The prevailing trend is that people invest in it whenever he puts up a tweet, and when the effect wears off, the prices go down. Despite the creation of coin being a joke, people invest in it because a famous and successful person invested in it; for whatever reasons. This can and has led to many investors suffering losses who had put in huge money to make a handsome profit.
These herding mentality examples prompt investors to research and think critically before making investment decisions and not to blindly follow anyone.
Impact of Herd Mentality on Investment
Herd behavior leads to imitation of collective actions of other investors while investing. Herding generally occurs on the belief that group actions carry information unknown to others. Herd Mentality Investment becomes a key factor that drives speculative episodes in a financial market. In the absence of central control mechanisms, local group interactions can shape patterns that push asset prices closer to their fundamental value.
However, continued periods of such activities disregarding the real value can lead to the formation of bubbles. They are situations where the prices of an asset move to exorbitant rates and face inflation to their highest potential. These bubbles inevitably come down and lead to market inefficiency. This happens because making profits is the fundamental driving force behind making investments. This often leads investors to look at short-term performances and take in peer reviews, which are never a good choice in the absence of good research. Herding can strengthen people's motives and guide them towards rash investment decisions and loss of money.
How to Overcome?
Investors can avoid the herding mentality by incorporating the following while investing:
Make informed decisions
Stock investments require thorough research and analysis, as they involve high risks for their high returns. Investors usually invest by looking at the company's name or the industry/ sector they belong to. However, they need to go above and beyond and look for places where these companies have underperformed and then decide.
Invest in what can be understood
Investing solely in stocks may not benefit people in the long run. Instead, if the investor concentrates on the company's business, there are minimal possibilities of making mistakes. Examining their current state and future potential is always a good idea. This helps avoid investments, especially in unknown technological companies that promise a new tomorrow, such as the Dotcom bubble.
Timing the market
Catching tops and bottoms is a gamble. If an investor invests a large sum of money in hopes of gaining huge returns in short periods, the risk involved is magnanimous. The general masses tend to hype up certain assets to gain attention, and when they gather attention, the herd mentality kicks in, and they sell it off. This may happen multiple times, and new investors can think this is how the stock market works. However, it is not how they work. Research on socio-economic and political aspects becomes key factors in the working of financial markets.
Disciplined investment:
Markets are the embodiment of volatility. Even bull markets have witnessed panic selling moments. Having a detailed layout of the plan and goal with a systematic approach to investments can improve confidence. Having a broad picture in mind decreases the chances of panic buying or selling by giving into herd mentality.
Avoid emotional decisions:
Fear and greed are the two essential driving factors of most financial judgments. Investors may sell for short-term profits in a bull market through subsequent trades. The chances of making quick wealth are alluring but can have disastrous effects on investments. Therefore speculations and investing in unknown companies and instruments should be avoided as market sentiments can reverse at any time.
Strong portfolio:
A good portfolio consists of investments backed by thorough research and is not the product of rash decisions. A smart investor distributes one's investment so that the investments balance out the overall risk. This approach guarantees steady and sure returns. It improves confidence and resists the temptations of going behind the general opinions for quick profits.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions
It is the tendency of people, in general, to follow a common ideology and act in conformity to it.
The desire to be accepted forms the base for being part of the herd. The strong sense to live in conformity with social standards can be another cause. At the same time, emotions such as fear and greed drive such mentality in financial markets.
Following the masses without second thoughts has adverse effects. For example, the social media trend of eating tide pods resulted in the damaging health of those involved, and herding mentality investment has a disastrous impact on individual investors and the market.
Society can use common beliefs for the community's benefit, such as forming an organization that gives charity or planting trees. When peers become part of organizations that promote social good, it inevitably influences the individuals around them to take part in them. These groups can mold humanity for a progressive future.

