Table Of Contents
Hedge Meaning
Hedge refers to an investment strategy that protects traders against potential losses due to unforeseen price fluctuations in an asset. It primarily requires investors to holding in one financial market and then taking a position in a different market to offset the loss.
A hedge mitigates the risk of dramatic price swings in financial assets through alternative investments. Traders can invest in stocks, derivatives, swaps, options and futures contracts, ETFs, etc., designed to balance against the risk of sudden price changes. Although hedging minimizes losses with gains from another investment, it does not guarantee that assets will not lose value.
Table of contents
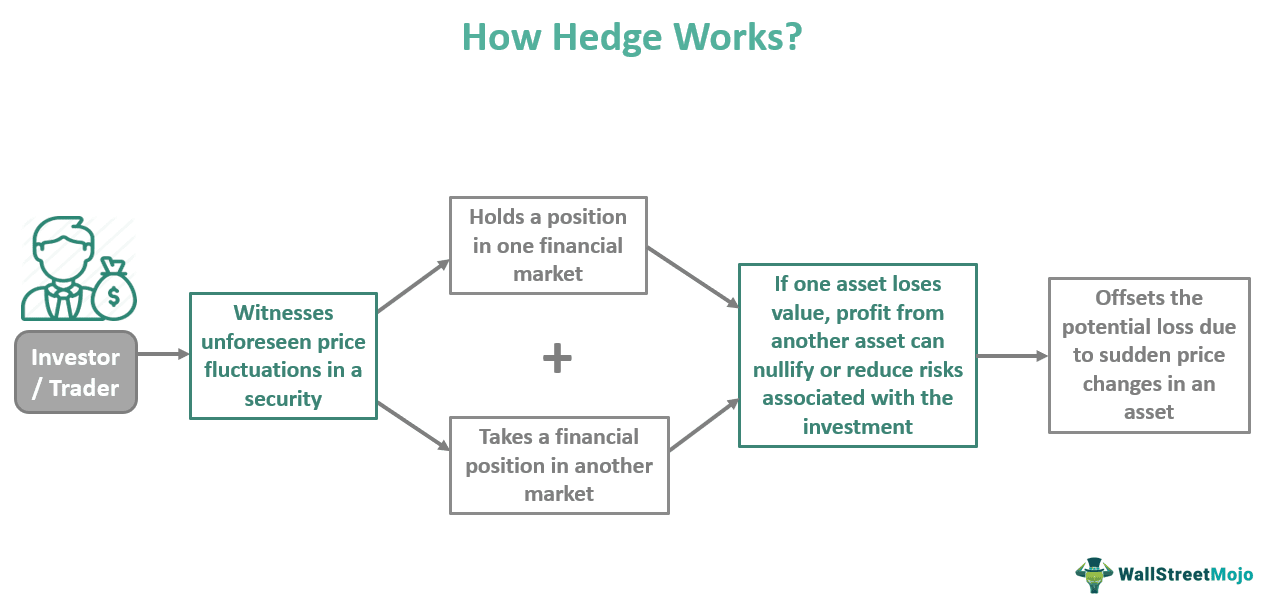
- Hedge definition describes an investment strategy used by traders to protect their investments from risks of heavy price fluctuations in an asset. Alternative investments like stocks, derivatives, swaps, options and futures contracts, and ETFs can help offset losses caused by abrupt price changes.
- It works similar to insurance, which protects a person's assets, such as their home or car, against damage caused by fire or accident.
- Common hedging tactics used by traders include derivatives, diversification, spread, and arbitrage.
- There is no such thing as a perfect hedge, and even if there were, it would not be a fool-proof approach because no loss can be averted ever.
How Does Hedge In Finance Work?
A hedge is a risk management practice adopted by investors and traders to ensure that price fluctuations do not negatively impact their financial position in the market. This investment approach ensures that if one's holdings lose value, investing in another asset can make up for that. Technically, hedge lessens the impact of possible loss, no matter how big it is, rather than eliminating the risk.
It is comparable to insurance, which covers a person's properties, such as a house or automobile, against fire or accidental damage. In a nutshell, hedging is a form of investment insurance.
Investors can protect the share of profits through hedging. Adding a hedge to a position minimizes the risk or reverses the effect in the event of a loss. Similarly, a beta hedge can save a financial portfolio from any adverse market scenario.
Beta hedging signifies investing for a position to avoid unsystematic risks. Investors use this strategy to protect their portfolios by purchasing stocks for beta holdings. Furthermore, there are two ways of hedging a position – single position and group position hedging. Hedging through derivatives and portfolio diversification are two typical methods for taking offsetting positions to a current holding.
Investors suffer no losses when hedging is perfect, i.e., eliminates potential risks in holding a portfolio or financial position. It, thus, provides complete protection against price swings in the most sensitive assets. A perfect hedge, however, cannot be a fool-proof strategy as no loss can be averted. Even the so-called perfect hedging is not fully insured.
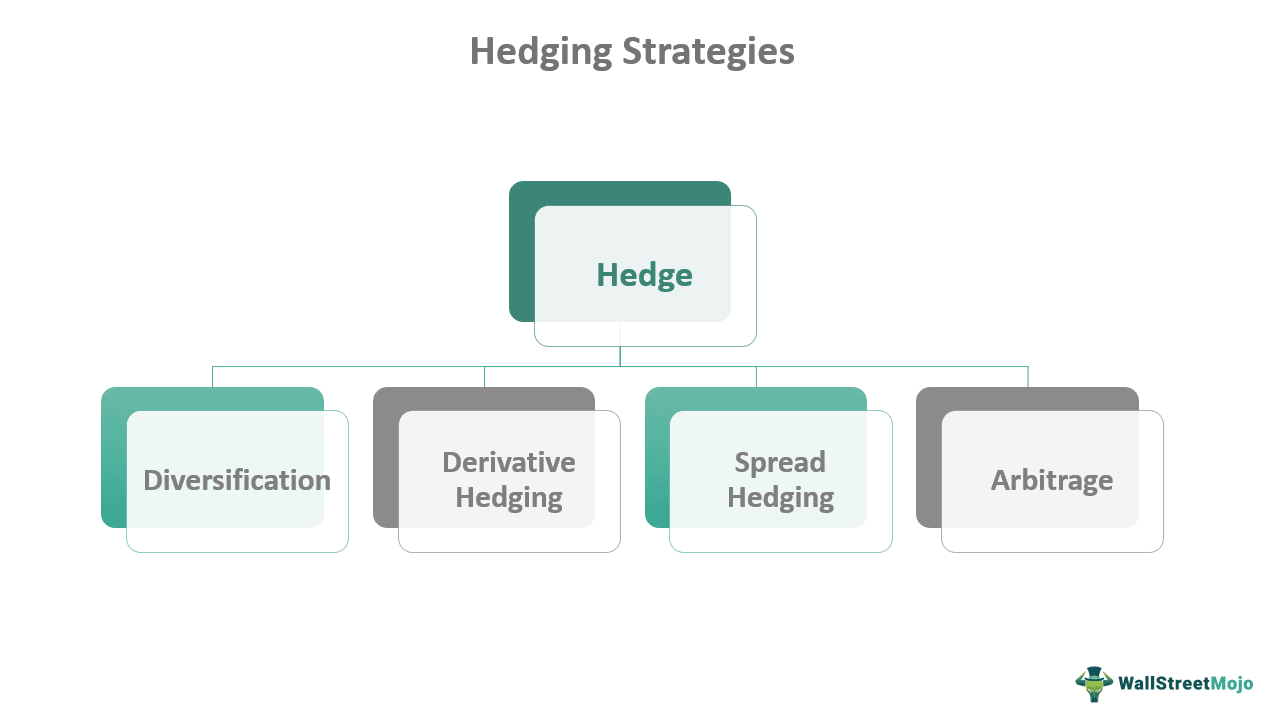
Hedging Strategies
Investing strategically in multiple financial assets is considered the best way to reduce exposure to sudden changes in prices. For example, investors or money managers purchase stocks, expecting the price to rise in the coming days. Then, they plan on selling those stocks when the price goes up. However, if the price drops adversely, they will end up losing. In such a scenario, options trading can help them add a hedge to a position to negate or reduce the effect, thus balancing the loss. However, it limits possible gains owing to risk mitigation.
This concept is not as simple as insurance, where investors pay a premium every month to safeguard their assets. Instead, it is all about investing smartly to offset its side effects. In short, investors, portfolio managers, and traders can protect one investment by investing in other stocks simultaneously. Thus, it might act as a backup plan for traders so that unexpected fluctuations in stock prices do not affect them.
Investors adopt multiple hedging strategies to protect their investments from potential losses. However, these strategies and pricing of respective assets are contingent on the sort of underlying asset and its downside risk. The cost increases as the downside risk grows due to volatility. Some of the common strategies they use are:
#1 - Diversification
Money managers should avoid investing in a single financial instrument or asset. Instead, they should diversify their portfolio by investing in a variety of non-related assets. Doing so would protect them with profits from hedging investments even if they incur huge losses from other trades. Also, no two assets rise and fall at the same time, and hence minimizing the loss. Thus, diversified hedging is one of the best and most recommended ways of ensuring portfolio protection.
#2 - Derivatives
Derivatives are financial contracts that derive their value from an underlying security, making it one of the ideal hedging strategies. Investors can choose to invest in stocks, options and futures contracts, bonds, indices, swaps, and commodities. In this strategy, any gain in the derivative security offsets any loss on a single investment.
For example, gold is a hedge because of its price stability against inflation. Similarly, trading options enables traders to buy or sell equities at a predetermined price within a specified time frame.
#3 - Spread Hedging
It works like this that the investor purchases a put for an index at a higher strike price and then sells it at a lower strike price at the same expiry date. The difference in strike prices acts as a hedge against potential loss due to changes in the index price.
#4 - Arbitrage
A trader uses this arbitrage strategy to buy a financial instrument at a low price and then sell it immediately at a higher price in a different market. It may not yield high returns, but it does provide traders with consistent profits.
Examples
Let us look at the following examples of Hedge to understand the concept even better:
Example #1
Mary invested in stocks of an automobile company, expecting the price to rise in the future. However, as an experienced trader, she was well aware of the stock market's risks. As a result, she decided to have a backup plan in case of a price fall.
She decided to invest in gold to be safe. The best way to protect against currency depreciation is to invest in precious metals. Furthermore, gold preserves its value regardless of the value of the currency.
Example #2
A study from the American investment advisor Vanguard revealed that commodities are the most effective investment instruments to hedge against sudden inflation. It observed that for every 1 percent of inflation beta in the U.S., the commodity market grew by 7-9 percent during the last decade. Since raw materials and agricultural products tend to rise in prices during hyperinflation, commodity investment is a more effective hedge against inflation than equities.
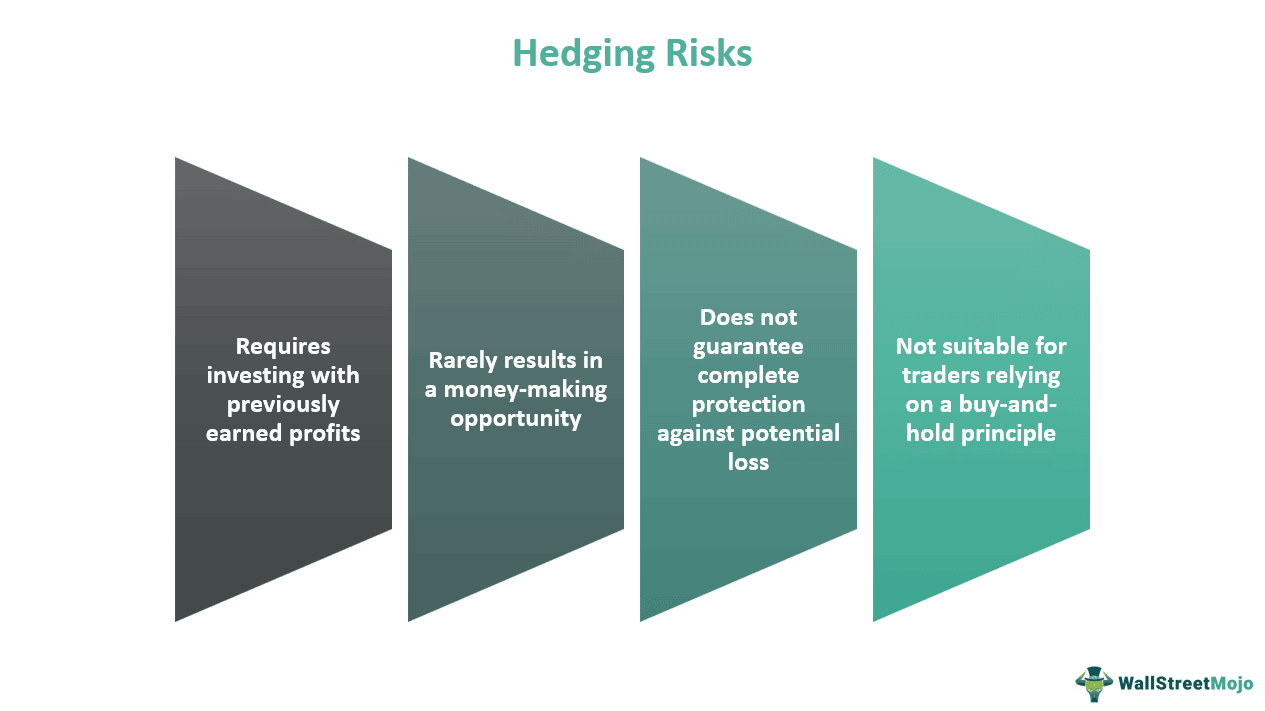
Risks In Hedge
Hedging a position can protect an investment against price swings, but traders should be aware of the following hedge risks:
- Hedging against unfavorable price fluctuations requires investment with previously earned profits.
- It does not guarantee complete protection, and the safety against potential loss could be minimal too.
- It will rarely result in a money-making opportunity.
- It is not a viable strategy for traders who trade on a buy-and-hold principle.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Hedge refers to an investment strategy that protects traders against the dangers of volatile asset prices. It entails investors holding a stake in one financial market and then acquiring a position in another marketplace to compensate for the loss. It limits the amount of money lost in addition to minimizing or offsetting the potential risk.
The most common hedging strategies include:
• Diversification (making diverse investments)
• Derivatives (investing in stocks, options and futures contracts, bonds, indices, swaps, and commodities)
• Spread hedging (buying a put on an index at a higher strike price and selling it at a lower strike price at the same expiration date)
• Arbitrage (buying an asset and selling it immediately in a different market when the price increases)
Not all types of hedging are illegal. However, hedging against Forex trading is considered illegal in the United States. It is because it involves buying and selling currency pairs at the same or different strike prices.
