Table Of Contents
What Is Hacktivism?
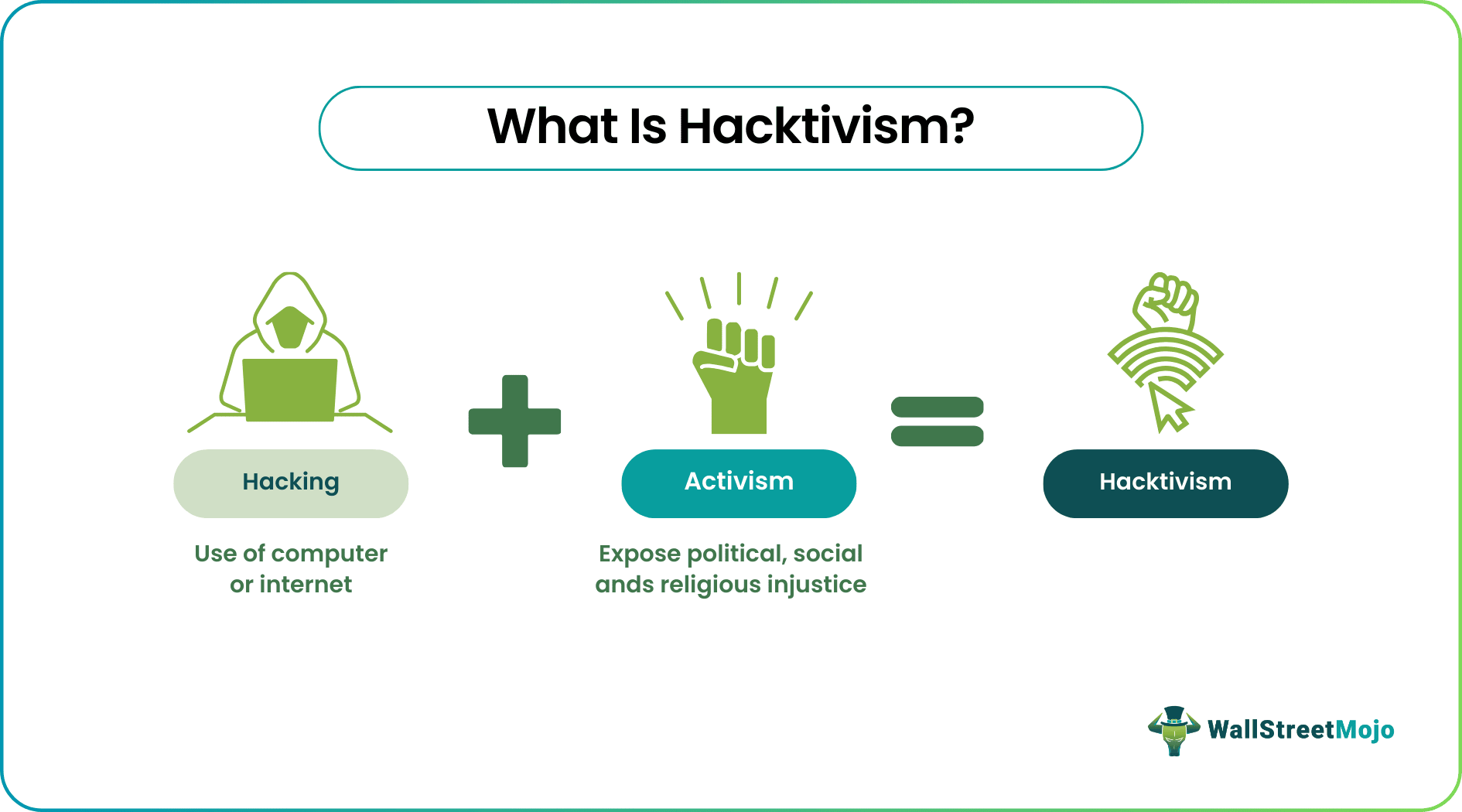
Hacktivism combines the terms "hacking" and "activism," referring to the use of hacking techniques and computer tools in promoting or advancing political or social causes. The act employs various digital tools and methods to achieve its objectives of focusing on different issues and bringing about a change in society.
It challenges established power structures by targeting entities that may be seen as oppressive, corrupt, or acting against the interests of the public. In addition, hacktivists contribute to public discourse on relevant issues through their activities, advocate for stronger legal protections, and raise awareness about the importance of safeguarding privacy and individual freedoms in the digital age.
Table of Contents
- What is Hacktivism?
- Hacktivism, in simple terms, refers to the use of computer technology and hacking techniques by activists to promote their social or political causes.
- It involves hacking into computer systems, websites, or networks to raise awareness, expose wrongdoing, or challenge powerful institutions.
- Hacktivists aim to bring attention to important issues, spark public discussion, and advocate for change through their actions in the digital realm.
- The legal status of hacktivism varies across jurisdictions, with some actions falling within protected forms of free speech and others being considered illegal hacking or cybercrimes.
Hacktivism Explained
Hacktivism is a form of activism involving the use of computer technology and hacking techniques to promote political or social causes. It typically targets government or corporate entities but can also extend to other significant institutions.
Hacktivists use their technical skills to gain unauthorized access to computer systems, networks, or websites, often to make a political or social statement. The methods employed by hacktivists can vary, ranging from website defacement and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks to data breaches and leaking sensitive information. In cybersecurity, hacktivism and cyberterrorism represent distinct phenomena that must be differentiated.
While hacktivism aims to raise awareness and pressure entities through peaceful means such as digital protests, website defacements, or data leaks, cyberterrorism involves illegal and harmful activities that can cause destruction, disruption, or endanger lives. However, when conducted within legal boundaries, hacktivism in cyber security can serve as a channel for societal scrutiny, accountability, and the initiation of constructive dialogue surrounding essential issues.
Hacktivists employ various techniques to make their voices heard and challenge established systems. It involves unauthorized access to computer systems, networks, or websites to disrupt operations, expose sensitive information, or spread their message.
For example, hacktivists may deface websites, launch DDoS attacks to overwhelm servers, breach databases to leak confidential data or compromise social media accounts to disseminate their views. The ultimate goal is to raise awareness, provoke dialogue, and draw attention to perceived injustices or unethical practices.
Types
Here are some common types of hacktivism types mentioned below-
- Website Defacement: This involves altering a website's visual appearance or content to convey a political or social message. Hacktivists may replace the original content with their messages, images, or videos, often leaving behind a digital signature or manifesto.
- DDoS Attacks: Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks involve overwhelming a target's servers or network infrastructure with excessive traffic, rendering the targeted website or service inaccessible to legitimate users. This disruption aims to draw attention to a cause or voice dissent.
- Data Breaches and Leaks: Hacktivists may gain unauthorized access to databases or systems to steal sensitive information, such as documents, emails, or user data. They might then release this information to the public or journalists to expose misconduct, corruption, or other actions they deem unethical or oppressive.
- Hacking and Defacing Social Media Accounts: Hacktivists may target the social media accounts of individuals, organizations, or institutions to spread their message or disrupt the communication channels of their adversaries. It can involve unauthorized access, posting provocative content, or hijacking accounts temporarily.
- Botnets and Bot Attacks: Hacktivists sometimes employ botnets, networks of compromised computers, to amplify their actions. Bots can be used to automate DDoS attacks, spread propaganda, or engage in other activities that advance the hacktivist's cause.
Examples
Let us look at hacktivism examples to understand the concept better-
Example #1
A group of hacktivists concerned about animal rights targets a fur industry website. First, they deface the site's homepage with images and messages that unveil the cruelty of fur production. Additionally, they go a step further by leaking internal documents that expose unethical practices within the industry.
They share the leaked information through social media, urging followers to boycott fur products and support cruelty-free alternatives. The hacktivists aim to raise public awareness, generate outrage, and pressure the industry to adopt more ethical practices. Their actions spark media attention and ignite discussions about the ethical treatment of animals in fashion, leading to increased scrutiny and potential change.
Example #2
Anonymous represents a real-life example of hacktivism. In 2010, Anonymous launched a series of cyber-attacks that targeted financial institutions and payment processors, including MasterCard, Visa, and PayPal, in response to their decision to suspend financial services to the whistleblower organization WikiLeaks.
Operation Payback was a notable campaign organized by Anonymous to retaliate against these companies for succumbing to pressure from the U.S. As part of the campaign, Anonymous launched distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks against Visa, MasterCard, and PayPal websites, disrupting their services and making a statement against perceived censorship.
In this instance, the actions taken by Anonymous illustrate the hacktivist group's use of hacking techniques to promote their causes and hold potent entities accountable for their actions.
How To Prevent?
Preventing hacktivism is a complex challenge, as it involves addressing the underlying motivations and grievances that drive individuals or groups to engage in such activities.
However, there are measures that individuals, organizations, and governments can take to reduce the risk and impact of hacktivist attacks. Here are some preventive measures:
- Strong Cybersecurity: This involves implementing robust security measures to protect computer systems, networks, and websites. It includes keeping software and systems current, using strong and unique passwords, employing multi-factor authentication, encrypting sensitive data, and regularly conducting security assessments and audits.
- Employee Awareness and Training: This makes educating employees about cybersecurity best practices, including safe browsing habits, email phishing awareness, and strong password management. In addition, training programs can help reduce the likelihood of falling victim to social engineering tactics used by hacktivists.
- Vulnerability Assessments: This facilitates conducting vulnerability assessments and penetration testing regularly to identify and address potential weaknesses in your systems and infrastructure. Promptly patch any discovered vulnerabilities and regularly review and update security measures.
- Incident Response Planning: This involves developing a comprehensive incident response plan that outlines steps to be taken during a cyberattack, including hacktivist actions. This plan should involve procedures for minimizing damage, preserving evidence, notifying appropriate authorities, and restoring systems and services.
- DDoS Mitigation: DDoS mitigation strategies and solutions are implemented to mitigate the impact of Distributed Denial-of-Service attacks. It includes using traffic monitoring and filtering tools, working with service providers offering DDoS protection services, or employing cloud-based solutions to handle sudden traffic increases.
Pros And Cons
Hacktivism, the fusion of hacking and activism, presents a double-edged sword in digital activism. Therefore, understanding the pros and cons of hacktivism is crucial in evaluating its impact on society and the broader landscape of activism in the digital era.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| It can bring attention to important social, political, or environmental issues that may otherwise receive limited coverage in mainstream media. Hacktivists can raise awareness and stimulate public discourse by targeting high-profile entities or conducting disruptive actions. | Hacktivism is often associated with anonymity and a lack of accountability. It makes it difficult to distinguish between well-intentioned activism and malicious actions and hinders responsible oversight and the potential for dialogue and constructive engagement. |
| It allows individuals or groups to challenge established power structures and institutions. It can disrupt the status quo, highlighting inequalities, systemic injustices, and the abuse of power. | Hacktivist actions can provoke retaliatory responses from targeted entities or governments. It can result in a cycle of escalation, where hacktivists face legal consequences or become the target of counter-hacking or surveillance activities. |
| Hacktivism can amplify the voices of marginalized groups or individuals lacking traditional platforms to express their concerns or grievances. In addition, it can provide a powerful tool for those seeking to challenge oppressive regimes or advocate for social justice. | Hacktivism is sometimes viewed negatively by the public, media, and governments. It can be confused with cybercrime or vigilantism, potentially overshadowing the underlying message or demands of the activists and diminishing public support. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Hacktivism in cyber security can exert significant pressure on targeted entities, be it corporations or governments, by highlighting their vulnerabilities, misconduct, or unethical practices. By exposing such issues, hacktivists have the potential to inflict damage on the reputations of these entities and pose a persistent threat of future cyberattacks, compelling them to respond or take remedial actions.
Hacktivism, a form of activism involving hacking techniques and tools, often operates in a legal gray area. The legality of hacktivist actions depends on the specific activities performed and the jurisdiction in which they occur. However, hacktivism usually involves illegal actions under existing laws related to unauthorized access, data breaches, disruption of computer systems, and other cybercrimes.
The difference between hacking and hacktivism is that hacking involves unauthorized access and exploitation of systems for personal gain or malicious intent. In contrast, hacktivism combines hacking techniques with activism to promote political or social causes. Hacking is generally illegal and unethical, while hacktivism exists in a legal gray area and raises ethical questions due to its methods and the potential collateral damage it may cause.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to what is Hacktivism. Here, we explain the concept with its examples, pros, cons, types, and how to prevent it. You can learn more about it from the following articles –
