Table Of Contents
What Are Governance Issues?
Governance Issues refer to problems with how an organization, institution, or system is managed, directed, or regulated. They often encompass concerns such as corruption, conflicts of interest, inadequate policies, lack of transparency, and ineffective leadership. In finance, such issues pose significant threats to the integrity of financial systems and reporting mechanisms.
Good governance fosters trust among stakeholders, including customers, investors, employees, and the public, enhancing an entity or government’s reputation. Transparent governance mechanisms ensure that actions and decisions are open to scrutiny, while accountability ensures responsible conduct, reducing corruption and unethical practices. In finance, governance challenges revolve around the administration and stability of financial institutions and markets.
Key Takeaways
- Governance issues arise from internal problems or external challenges that impede effective management, decision-making, transparency, compliance, and corporate ethics within organizations, institutions, or systems.
- By tackling these issues, it is possible to establish ethical conduct, mitigate risks, boost stakeholder confidence, and contribute to long-term organizational sustainability and success.
- A conducive environment for ethical practices and subsequent growth is typically the result of handling governance problems well.
- Addressing these issues involves implementing robust frameworks, policies, and practices to enhance transparency, accountability, and ethical behavior.
Governance Issues Explained
Governance issues encompass a range of challenges that can hinder the effective functioning and ethical conduct within organizations, institutions, or systems. These issues often manifest in various forms and have widespread implications. One fundamental governance issue is the lack of transparency. When organizations operate with a lack of openness, it leads to suspicion and erodes trust among stakeholders. Transparency is crucial for ensuring that decisions are made in an accountable manner and information is accessible to those affected by these decisions.
Another critical aspect of governance issues centers around accountability. Ineffective or absent mechanisms for holding individuals or entities responsible for their actions can lead to a misuse of power, corruption, and ethical lapses. Without accountability, decision-makers may act in their self-interest rather than in the best interest of the organization or the public they serve.
Corruption is a severe governance issue prevalent across various sectors globally. It involves the misuse of entrusted power for personal gain. It undermines the integrity of institutions, distorts decision-making processes, and diverts resources from their intended purposes, ultimately affecting the delivery of services and the overall functioning of societies.
Inadequate policies or regulatory frameworks also contribute significantly to governance issues. When policies are outdated, ambiguous, or not effectively implemented, it creates loopholes for exploitation or introduces confusion in decision-making. Clear, well-defined policies, along with their proper implementation and enforcement, are crucial for ensuring fairness, equity, and consistency within an organization or society.
Leadership plays a pivotal role in addressing governance issues. Weak or unethical leadership can exacerbate existing problems or lead to the emergence of new governance challenges. Effective leadership that promotes values like integrity, transparency, and accountability is essential in setting the tone for ethical conduct throughout an organization.
Addressing governance issues requires a comprehensive approach involving legal reforms, organizational restructuring, fostering a culture of accountability, enhancing transparency through information dissemination, and promoting ethical leadership. Resolving these issues is crucial not only for the well-being and credibility of individual entities but also for the overall trust and stability of societies at large.
Governance Issues In Finance
Governance issues have particularly begun affecting participants in the field of finance. It is important to understand that such issues can be a result of internal or external factors that impact an entity, a government, or an organization.
Due to complex financial systems, global markets, and high-stake private equity, effective governance to safeguard investors from fraud is pivotal. With fintech gaining prominence, governance structures need to be adaptive and agile, covering all possible threats to the system. The rise of cryptocurrencies is another key development that requires extensive and intensive governance to ensure appropriate risk management and maintain market integrity.
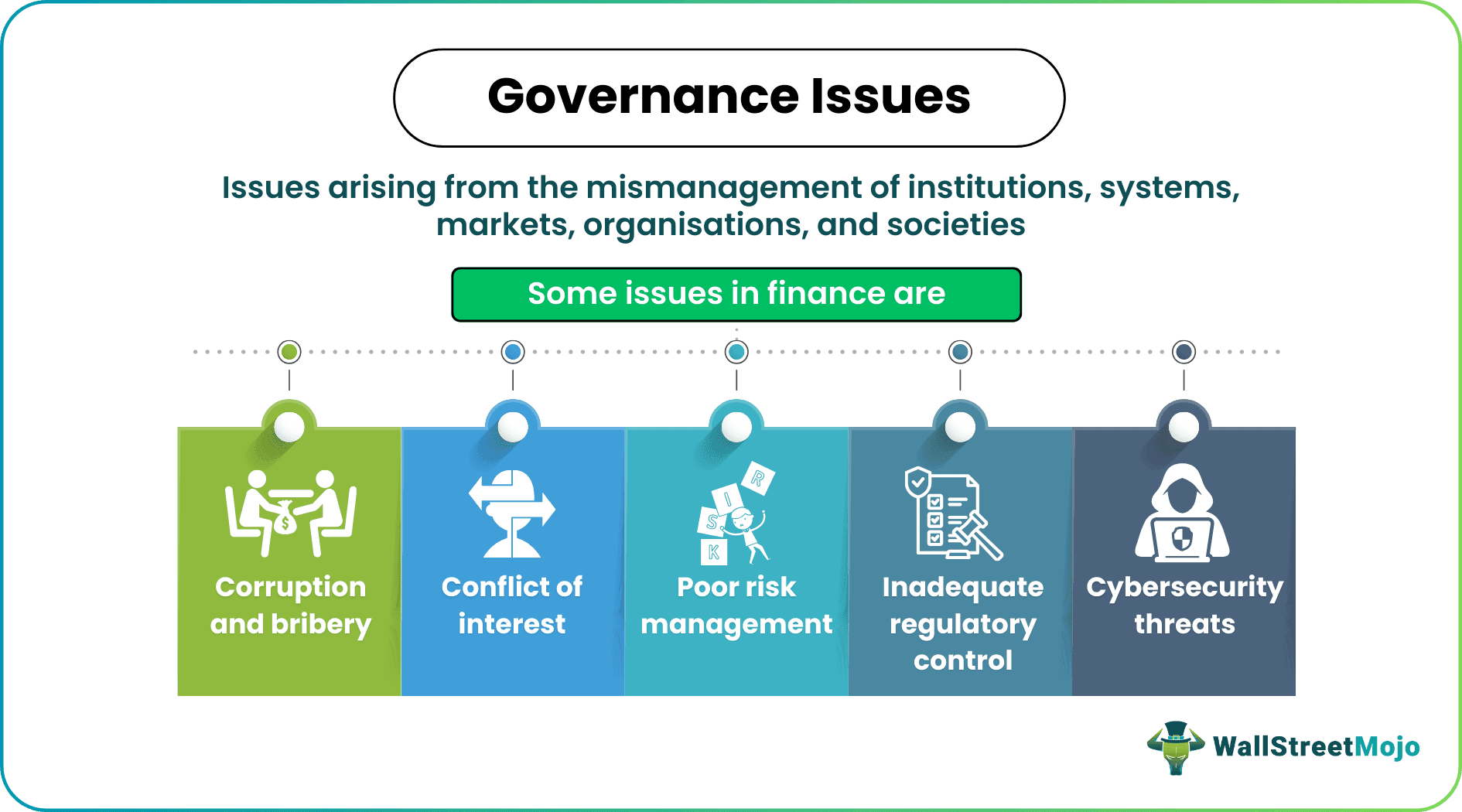
As the field evolves, governance issues due to global business deals, international taxation laws, and nuanced financial reporting processes have been increasingly observed. As most of these activities take place online, cybersecurity is a real danger. Cybersecurity threats in finance need to be addressed through good governance and control structures. A stable and secure financial ecosystem can thrive only when information flow, data security, and access control are prioritized.
Other issues in finance include tax evasion and avoidance, money laundering, financial crime, market manipulation and abuse, statutory compliance, financial reporting and disclosures, etc.
Examples
Let us study examples of governance issues to dissect the concept further.
Example #1
Suppose Addie Boston Group is a healthcare organization in Texas. Governance issues emerged when financial mismanagement came to light. The lack of transparency in budget allocations and expenditures led to suspicions among stakeholders. As investigations unfolded, it was revealed that a few board members had been involved in directing funds toward personal ventures rather than the organization's intended healthcare initiatives.
The absence of robust checks allowed this misallocation of resources to continue unnoticed for an extended period. Consequently, this eroded trust among donors, staff, and the community, highlighting the severe implications of poor governance in such organizations. The institution's credibility and its ability to fulfill its healthcare objectives were questioned.
This shows why it is important to handle issues related to governance before they turn into major problems.
Example #2
Suppose Starlight Ltd. is a tech startup, and governance issues arose at the firm due to a leadership vacuum. The company's rapid growth had outpaced its governance structure. Decisions were made without clear oversight, resulting in conflicting strategies and resource misallocation.
With no defined hierarchy, clashes among department heads became frequent, impacting productivity and creating a chaotic work environment. The absence of a coherent governance framework led to a lack of strategic direction and inconsistent decision-making, hindering the company's potential for sustained growth and profitability.
This illustrates the significance of developing and complying with governance structures to gain the trust of every stakeholder in the organization and earn profits.
Example #3
According to a November 2023 article, Britain planned a stricter corporate governance and auditing code to combat large-scale corporate failures like Carillion, BHS, and Patisserie Valerie. Since these foundering companies affected many people financially, revisions became necessary. However, many believed that governance changes might affect competitiveness, and the Financial Reporting Council (FRC) faced significant criticism for considering such revisions.
The revised code, expected in January 2024, is likely to reduce the stringency of internal control proposals, especially those rules that earlier mimicked the US’s approach regarding the publication of accurate financial statements. Also, the proposed provisions related to the role of audit committees on environmental and social governance will not be pursued anymore.
The issue here revolves around how to balance stringent corporate governance measures to prevent business failures while maintaining the UK's competitiveness, particularly in the post-Brexit scenario. The revisions highlight the delicate balance needed between regulatory control and maintaining a business-friendly environment without compromising governance standards. This proves that the right laws and regulations are necessary to avoid governance issues and their adverse consequences.
Solutions
Addressing governance issues often involves a multifaceted approach. Here are some solutions that can help mitigate them.
- Transparency and Accountability: Implementing transparent processes and mechanisms for decision-making, financial transactions, and reporting fosters accountability. Establishing clear lines of responsibility and ensuring that individuals are answerable for their actions and decisions goes a long way in maintaining stability.
- Robust Policies and Regulations: Developing and enforcing comprehensive policies and regulations that govern the conduct of individuals and entities within an organization or society is key. Regularly reviewing and updating these frameworks to adapt to changing circumstances and evolving best practices promotes stability.
- Ethical Leadership: It is crucial to encourage and promote ethical leadership across all levels of an organization. Leaders who exemplify integrity, honesty, and ethical behavior set the tone for others to follow, fostering a culture of trust and accountability.
- Effective Oversight and Compliance: Strengthening oversight mechanisms such as independent audits, regulatory bodies, and internal controls is recommended. These measures help ensure compliance with established policies and regulations, identifying and addressing issues before they escalate.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Involving stakeholders in decision-making processes helps increase transparency and gather diverse perspectives. Engaging stakeholders helps build trust, fosters a sense of ownership, and allows for a more holistic approach to governance.
- Capacity Building and Education: Organizations and governments should invest in training programs and educational initiatives to enhance the understanding of governance principles among employees, leaders, and stakeholders. Building capacity and knowledge about governance practices can lead to better compliance and ethical conduct.
