Table Of Contents
What Is Gordon Growth Model Formula?
The Gordon growth model formula refers to the expression used to calculate the intrinsic value of the stocks of a company. It is computed by discounting the future dividend payouts of the company and helps in assessing the relation between the constant dividend growth and the share prices of the company
The formula lets users calculate the approximate value of the price of a company’s share. It is one form of the Dividend Discount Model (DDM), which calculates the stock price based on the probable dividends one would pay.
Key Takeaways
- The Gordon Growth Model formula determines the company's intrinsic Value by discounting the future dividend company payouts.
- The first component is the estimated dividends for the next period. One must look at the historical data and the past growth rate to find the estimated dividends.
- Moreover, one can also take help from financial analysts and projections. Though the estimated dividends are inaccurate, they may forecast something closer to future dividends.
- The second component of the formula has two parts – the growth rate and the required rate of return.
Gordon Growth Model Formula Explained
Gordon Growth Model Formula works in two ways. While one form of the expression helps figure out the constant growth in future dividends, another lets users learn about zero growth in future dividends.
#1 – Constant Growth in Future Dividends
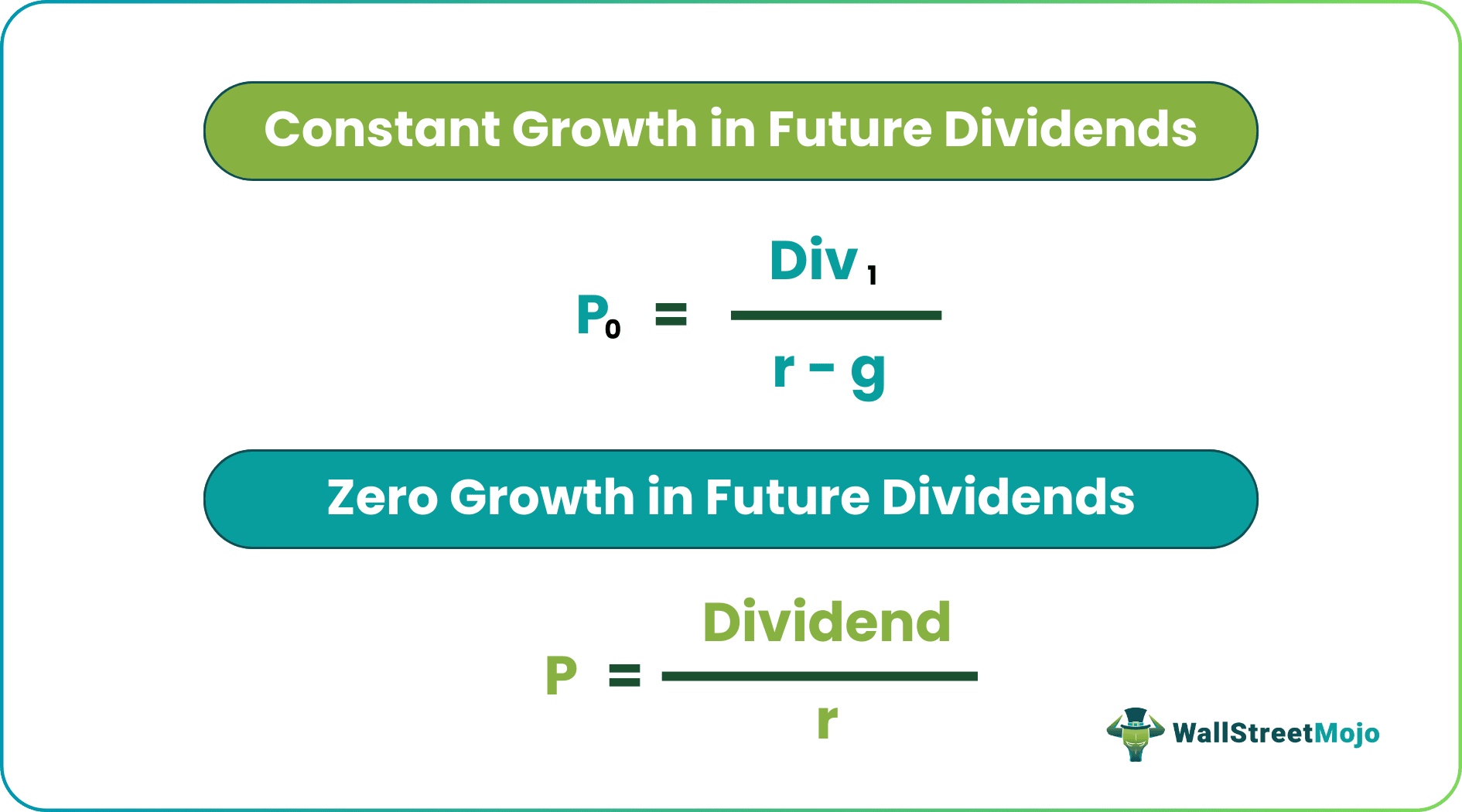
The Gordon growth model formula with the constant growth rate in future dividends is below.
First, let us have a look at the formula: -

Here,
- P0 = Stock price
- Div1= Estimated dividends for the next period
- r = Required Rate of Return
- g = Growth rate
Video Explanations of Gordon Growth Model
Calculation Examples
Let us consider the following examples to understand the calculation:
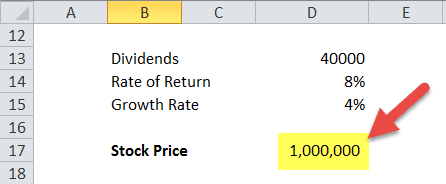
Example 1 - Gordon Growth Model For Constant Growth
Hi-Fi Company has the following information –
- Estimated dividends for the next period - $40,000
- The required rate of return – 8%
- Growth rate – 4%
Find out the stock price of Hi-Fi Company.
We know the estimated dividends, growth rate, and required return rate in the above example.
By using the stock – PV with constant growth formula, we get –
- P0 = Div1 / (r – g)
- Or, P0 = $40,000 / (8% - 4%)
- Or, P0 = $40,000 / 4%
- Or, P0 = $40,000 * 100/4 = $10, 00,000.
Using the above formula, we can find out the present stock price. It can be an excellent tool for investors and the management of any company. We should notice that the stock price is the total stock price since we assumed the estimated dividends for all the shareholders. By simply taking the number of shares into account, we could determine the stock price per share.
Gordon Growth Model Calculator
You can use the following Stock – PV with Constant Growth Calculator.
Example 2 - Gordon Growth Model For Zero Growth
Let us take an example to illustrate the Gordon growth model formula with a zero growth rate.
Big Brothers Inc. has the following information for every investor –
- The estimated dividends for the next period - $50,000
- The required rate of return – 10%
Find out the price of the stock.
By using the Stock - PV with Zero Growth Formula, we get –
- P = Dividend / r
- Or, P = $50,000 / 10% = $500,000.
- The stock price would $500,000.
You should notice that $500,000 is the total market price of the stock. And depending on the number of outstanding shares, we would find out the price per share.
In this case, let us say that the outstanding shares is 50,000.
That means the stock price would be = ($500,000 / 50,000) = $10 per share.
Gordon Zero Growth Calculator
You can use the following Gordon Zero Growth Rate Calculator.
Gordon Zero Growth Formula in Excel
#1. Constant Growth Excel Template
Let us now do the same example above in Excel. It is straightforward. One must provide the three dividends, rate of return, and growth rate inputs.
It is easy to find the company's stock price in the provided template.

You can download this Gordon Growth Model Formula template here - Gordon Growth Model Formula with Constant Growth Excel Template
#2. Zero Growth Excel Template
Let us now do the same example above in Excel. That is very simple. You need to provide the two inputs of dividend and rate of return.
You can easily find out the stock price in the template provided.

Uses
The uses of the two Gordon Growth Models are:
Constant Rate Gordon Growth Model
We will understand the present stock price using this formula. Let's look at both of the formula components. We will see that we use a similar present value method to determine the stock price.
First, we calculate the estimated dividends. Then, we divide it by the difference between the required rate of return and the growth rate. That means the discounting rate is the difference between the required rate of return and the growth rate. By dividing the same, we can easily find out the present value of the stock price.
Zero Growth
This formula estimates dividends for the next period. And the discounting rate is the required rate of return, i.e., the rate of return that the investors accept. There are various methods of using which investors and financial analysts can find out the present value of the stock, but this formula is the most fundamental.
Thus, before investing in the company, every investor should use this formula to find out the present value of the stock.