Table Of Contents
What is Goodwill Amortization?
Goodwill amortization refers to the process in which the cost of the goodwill of the company is expensed over a specific period, i.e., there is a reduction in the value of the goodwill of the company by recording the periodic amortization charge in the books of accounts.
In simple words, Goodwill Amortization means writing off the value of Goodwill from the books of accounts or distributing the cost of Goodwill in different years. It is because the value appearing in the books of account does not show the true value. The need for amortization arises to show the correct value of Goodwill In books of accounts, the need for amortization arises.
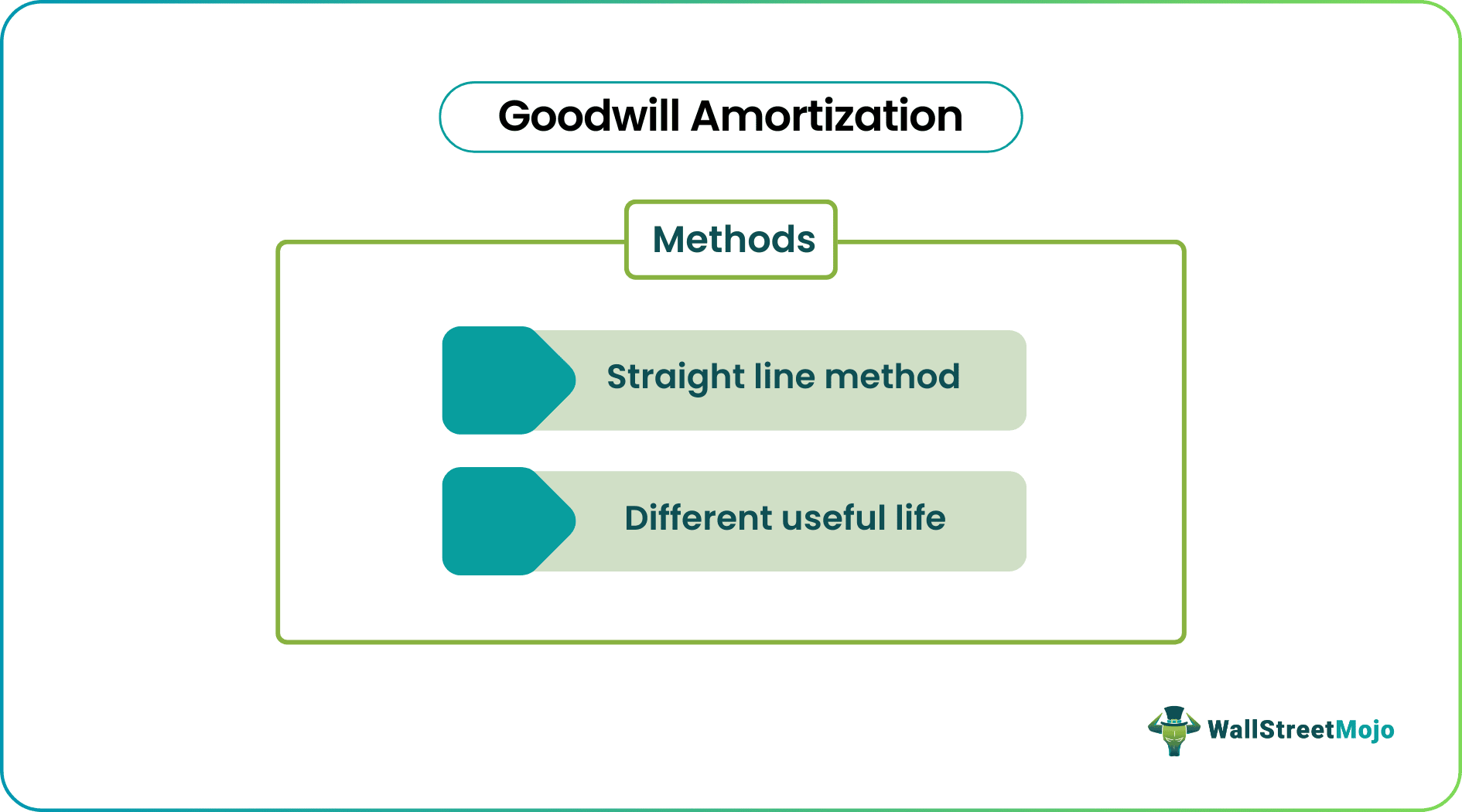
Methods of Goodwill Amortization
#1 - Straight Line Method
In the Straight Line Method, amortization is allocated over ten years (maximum up to 40 years) unless the shorter life is more appropriately known. An equal amount will be transferred to the Profit and Loss Account every year.
Amount Transfer to Profit and Loss Account Every Year = Amortization Amount / Number of Years
The straight-line amortization method is the same as the straight-line method of depreciation. The logic behind this method is assets are operated consistently or evenly over time. This method is very simple to apply.
#2 - Different Useful Life
In different useful life methods of goodwill amortization, allocate the asset's cost to expense over its useful life. For every entity, useful life can be different. Every entity has its policy according to its nature of business.
Video Explanatiosn of Goodwill
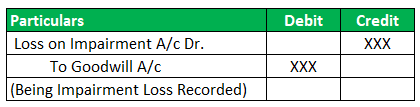
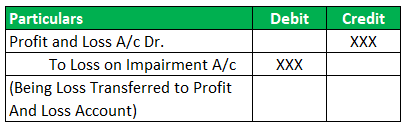
Journal Entries
Examples of Goodwill Amortization
Let’s see some practical examples to understand it better.
Example #1
Suppose Company BCD is planning to purchase Company XYZ. The Book value of Company XYZ is $50million, but Company XYZ has a good market reputation that Company BCD can pay more than $50million. In the final deal, ABC agrees to pay $65 million. Calculate the value of goodwill amortization.
Solution:
Calculation of Goodwill can be done as follows -

Value of Goodwill = $65 million - $50 million
Value of Goodwill = $15 million
After purchasing XYZ, $15 million will be the goodwill amount that BCD will record as Goodwill in their books of account.
Example #2
In the above Example, one year later, Company BCD changed the product features and now deals in a different product. This new product is not as successful as the earlier product was. As a result, the company's fair value starts declining. The new fair value is $58 million book value is $65 million. Calculate the Impairment loss.
Solution:
You can do the calculation of impairment loss as follows -

Impairment Loss = 65-58
Impairment Loss = $7 million
In the books, Goodwill is recorded as $15 million.
Now, this amount of Goodwill will reduce by $7million.
Example #3
Small Ltd. has the following assets and liability
| Particulars | Value (Millions) |
|---|---|
| Cash | 85 |
| Investments | 200 |
| Stock | 450 |
| Bank Balance | 92 |
| Property & Equipment | 825 |
| Other Current Asset | 150 |
| Term Loan | 350 |
| Creditors | 144 |
| Current Liabilities | 65 |
Big Ltd acquires small Ltd and pays the purchase consideration of $1300 million; what will be the goodwill value big Ltd will record in his books after the acquisition.
- After 2 years
- The fair value of these assets =$1280 million
- How will Goodwill be amortized?
- Calculate the amortization amount by a straight-line method in 10 years?
Solution:
Calculation of amortization amount in 10 years will be -

Net Worth:
- Net Worth = Total of assets - Total of liabilities = (85+200+450+92+825+150) - (350+144+65) = 1243
Value of Goodwill:
- Value of goodwill =Purchase Consideration - Net Worth = 1300 - 1243 = 57
Amortization Amount:
- The Amortization amount = Book Value of Assets - Fair Value = 1300 - 1280 = 20
Amortization Goodwill :
- Goodwill appears in books = $57
- After Amortization it will be = 57 - 20 = $37 million.
Amortization Amount in 10 Years:
- Amortization Amount in 10 Years = $20million / 10years = $2 million
- Every year up to 10 years to be written off by debiting Profit and Loss account.
You can refer to the given above excel template for the detailed calculation of goodwill amortization.
Conclusion
- Private companies can amortize goodwill over ten years using the straight-line method.
- Only purchased Goodwill record in books of accounts. Self-generated Goodwill is not recorded in books of accounts.
- Goodwill, which no longer exists, should be written off in the form of amortization.
- Conditions that may trigger an impairment of Goodwill are increased competition, a big change in management, change in a product line, deterioration in economic conditions, etc.