Table Of Contents
Gap Analysis Meaning
In Gap Analysis, the actual performance of a company is compared to the desired goals. It determines the deviation between the current state and the expected future state. In response, an effective action plan is strategized to straighten the deviation.
A company lags behind competitors when assets, materials, human resources, capital, and technology is not employed efficiently. In such scenarios, a Gap Analysis offers companies detailed feedback, highlighting potential causes of deviation.

Key Takeaways
- Gap analysis is an approach used to recognize the difference between a company’s current position and its desired future state.
- It studies the efficient utilization of capital, assets, human resource, material, and technology.
- The Four popular tools used for such studies include PESTLE analysis, SWOT analysis, McKinsey 7s Framework, and Nadler-Tushman Congruence Model.
- The steps in gap analysis involve analyzing the focus area, deciding future goals, interpreting the current state, comparing the current state with the future state, enforcing corrective measures, formulating an action plan and preparing the final report.
How to do a Gap Analysis?
Such a study contributes significantly to business growth and goal achievement in various aspects. As a result, most start-ups adopt this practice to set performance benchmarks. The Gap Analysis process involves the following steps.
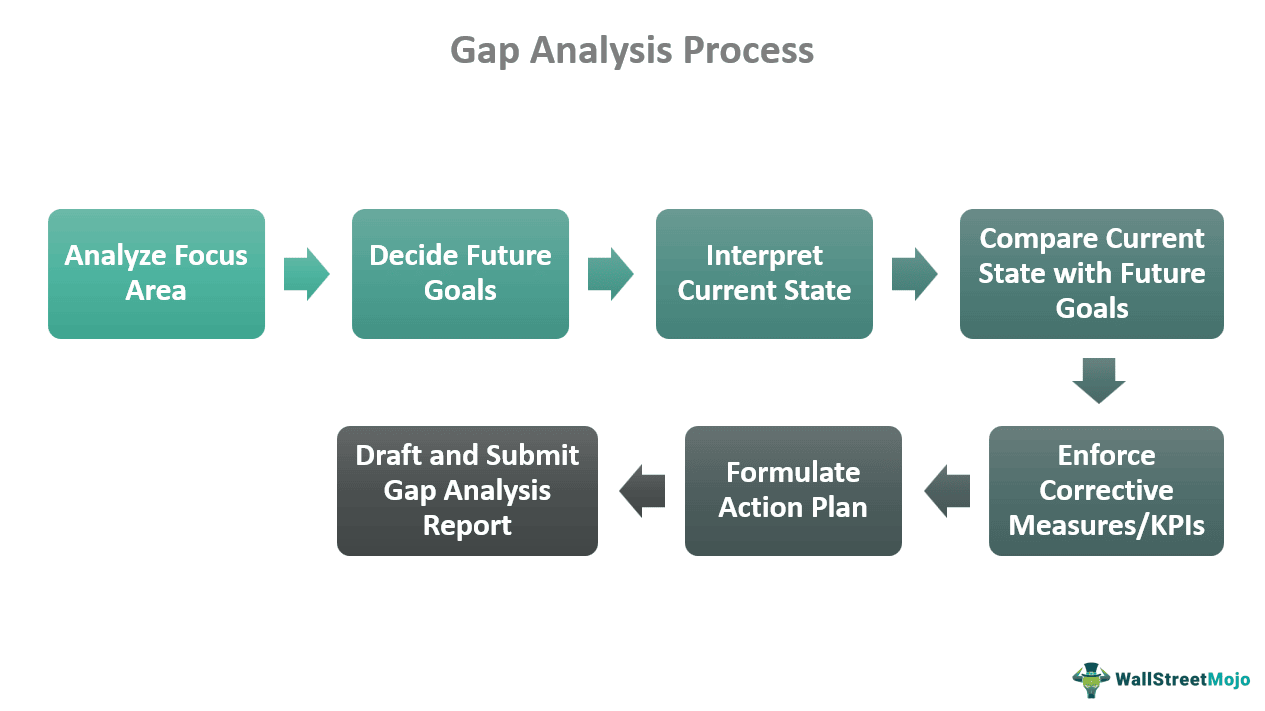
- First, companies recognize the problems. They ascertain whether the issue is related to profit, product, performance, or human resources.
- Then, they ascertain a realistic and attainable future target.
- Additionally, companies comprehend the current situation in terms of performance, resources, and process.
- Using that data, companies evaluate the gap or difference between the desired future position and the present situation. This includes calculating the gap density, reasons, and shortcomings.
- At this stage, analysts propose imperative measures to eliminate the identified difference. Additionally, they set the key performance indicators (KPIs) for periodical analysis of subsequent progress.
- To apply the corrective measures, companies strategize a course of action.
- Finally, a report incorporating the findings and suggestions is presented to the company’s management.
Types of Gap Analysis
Evaluation is applied from different perspectives. The four possible scopes of improvement in any company are as follows.
#1 - Profit Evaluation
It determines the reasons behind low profitability. It is ascertaining whether it is due to internal factors or the external environment. For example, the negative impact of the pandemic on business sales and profit are analyzed.
#2 - Product/Market Evaluation
A product’s incompetency is evaluated through this technique. Problems could be potentially caused by outdated features, change in consumer preference, or emerging competitors.
#3 - Performance Evaluation
This method reviews the company’s strategic objectives and highlights the factors causing the lag in performance.
#4 - Manpower Evaluation
This method discovers human resource insufficiency and highlights a lack of skills among the personnel if any.
Gap Analysis Examples
XYZ Pvt Ltd is a detergent manufacturing company. It conducted an evaluation intending to increase its profits by 30%. Following is an example of a gap analysis report.

It is evident that to increase the profit by 30%, the company has to ramp up sales by 30%. Also, it needs to set up new depots to reach more retailers.
The IT industry carried out a Supply-Demand Gap Analysis to discover the reasons behind the global chip shortage. There was a boost in demand during the pandemic. The analysis also studied the impact on the automotive industry, which has a great need for the chips. According to CNBC, the chip shortage will continue till 2023.
Gap Analysis Uses
Companies use such a study for realizing short-term business goals both at strategic and operational levels. The various use of such analysis is as follows.
- Sales: The study reviews sales targets and highlights the reasons for inadequate profitability.
- Productivity: Companies use this technique to check whether they can meet the target production levels. If not, the method discovers the reasons behind low productivity.
- Quality Control: Companies pay significant attention to product quality and identify any non-adherence through this study.
- Product Performance: It determines the market acceptability, demand for a product, and the need for product improvisation.
- Supply Chain Management: Companies study delays in the supply cycle, raw material acquisition, and product delivery.
- Asset Management: This study ascertains the risk associated with rate-sensitive assets and liabilities.
- Human Resource: Companies diagnose workforce shortages, skill gaps, and talent gaps hindering human resource efficiency. Based on such analysis, companies plan relevant training and employee development strategies.
- Employee Satisfaction: Companies can use this study to gather essential input from employee feedback about job satisfaction. Based on the conclusions, companies incorporate changes.
- Individual Assessment: Employees can also make use of such a study for self-analysis and personal development.
Gap Analysis Tools
To find out why they are lagging behind the target, a company adopts one or more of the following techniques.
#1 - SWOT Analysis
The SWOT Analysis lists out strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Being aware of strengths and weaknesses gives companies an edge over their competitors.
#2 - McKinsey 7s Framework
The McKinsey 7s model emphasizes the impact of internal factors on business performance. These seven factors are as follows.
- Strategy
- Structure
- System
- Style
- Staff
- Skills
- Shared Values
#3 - PESTLE Analysis
PESTLE analysis focuses on the external factors, namely political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental causes. These are potential causes for the performance gap.
#4 - Nadler-Tushman Congruence Model
Under this tool, the structure, people, work, and culture are studied to understand how they impact business performance. The two prominent factors contributing to a company’s success are finding the inputs and transforming inputs into desired outputs.
