Table Of Contents
Full Form of OEM - Original Equipment Manufacturer
The full form of OEM is an Original Equipment Manufacturer. In the computer industry, original equipment manufacturer is a misleading term that doesn’t mean the original manufacturer but refers to a company that buys equipment from other manufacturers. In addition, it customizes products, sells them in its name and brand, and offers a warranty, license, and support. However, it normally means a manufacturer producing products used in other companies. The other company here refers to as the value-added reseller.
How Does it Work?
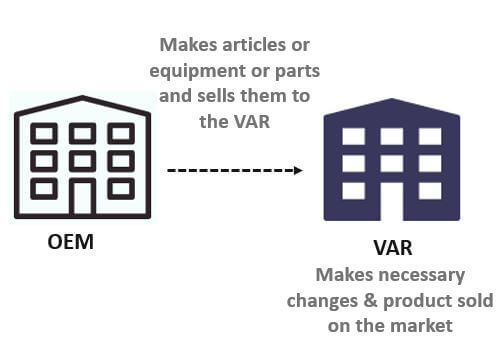
The value-added reseller (VAR), referred to above, and the original equipment manufacturer works in tandem. First, the original equipment manufacturer makes articles, equipment, or parts and then sells them to the VAR. The VAR then makes necessary changes, customizes the products, and does some rework on the product supplied by the OEM. Finally, after all such tasks are performed, sells the product is sold in the market.
Examples of OEM
Example #1
Let us first consider the example of Hewlett Packard.
Many enterprises have OEM partnerships with Hewlett Packard, such as C3, Cohesity, GRC, etc. Hewlett Packard Enterprise has almost 6 decades of experience as an OEM. It acts as a supplier that provides support by offering products of high quality globally. It is said to understand customer needs, provide high-quality customized solutions and products to its customers over the lifecycle, and helps in third-party integration.
Example #2
Let us take another example of Panasonic TVs.
Panasonic purchases electronic components, assembles those parts, makes TVs, and sells them to customers.

Advantages
- Customization: The products supplied meet the specified needs and demands of the customers to the components. They make it with high precision.
- Support: There is after-sale support that the manufacturers provide. The staff will provide technical and engineering support for all the parts-related needs.
- Response: The response will be quicker. They aim to ensure the delivery on time and check the performance closely.
- Quality: They shall give VARs the confidence that it would provide them with the original products and the products that meet the original specification if they require a part replacement.
- Warranty: If a product receives any defects, the parts manufacturer will replace the part because they usually come with the warranty of spare parts.
- Valuable Products and Longevity: The products manufactured and sent by OEMs are usually of high value than that of the aftermarket and are durable.
- Single Option: The VARs provide only one option for parts replacement, so they need not select a brochure full of options.
Disadvantages
- Price: The price mentioned by OEMs is usually much more than that of the aftermarket body parts.
- Delays: Original equipment manufacturer body parts are usually subject to availability. The manufacturers and dealers may usually create delays in delivery or delay in manufacture.
- Partnership Relations between OEMs and VARs: Original equipment manufacturers and aftermarkets are opposite each other. Aftermarket uses reverse engineering on original OEM products to attain the same quality and better technology at better prices. The following are the other differences between OEM and Aftermarket:
Difference between OEM and Aftermarket
Original equipment manufacturers and aftermarkets are opposite each other. Aftermarket uses reverse engineering on original OEM products to attain the same quality and better technology at better prices. The following are the other differences between OEM and Aftermarket:
| OEM | Aftermarket |
|---|---|
| They make products to be used specifically for the original product. | They are used as a replacement by another company as spare parts. |
| Products are costlier compared to the aftermarket. | Products are cheaper. |
| Since original products are obtained, it may be less convenient. | More convenient to obtain and available in lots. |
| A single option, i.e., an original part from the manufacturer, is available to the VAR. | There may be multiple choices available in the market for a single part. |
| These products come with after-sale service and warranties. | Such facilities may not be available in aftermarket supplies. |
| Quality is guaranteed while purchasing from OEMs as the original product is delivered. | Because of the low price, there may arise situations where the buyer has to compromise with the quality. |
Conclusion
In simple terms, for a vehicle repair, if you reach out to the dealership of the vehicle’s brand, you are opting to get it repaired by an OEM. Whereas, if you go to a vehicle repair shop, you opt for the aftermarket. It all depends on individual preferences and choices. If premium quality is preferred, an original equipment manufacturer would be the best choice, whereas the aftermarket may be the best option if the best price is preferred. That said, it does not imply that the aftermarket products do not have good quality. A wide range of products is available, and one must ensure it uses the right products.
