The differences between a franchisee and a franchisor are as follows:
Table Of Contents
Franchisee Meaning
A franchisee is an individual or a company that purchases the right to operate a business using an established company's name, branding, and business model (franchisor). It allows a business to grow rapidly and reach new markets without requiring substantial capital investment from the franchisor.
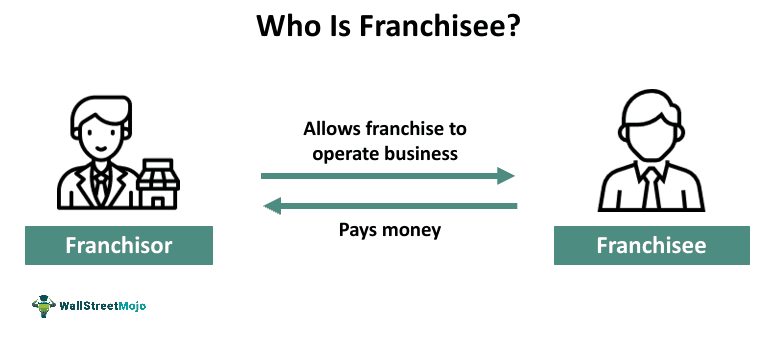
The franchisee typically pays the franchisor initial fees and ongoing royalties in exchange for operating under an established brand and proven business system. It enables a brand to establish a presence in various locations quickly. As a franchise network grows, it can benefit from economies of scale in purchasing, marketing, and other operational aspects, leading to cost efficiencies.
Key Takeaways
- A franchisee is an individual or company who has the license to run a business using the branding and name of an established business model.
- This model allows the franchisee to run their business independently while benefiting from the proven success and support provided by the franchisor.
- The franchisor, at the same time, can enjoy more business growth and a wider network of institutions.
- The franchisor maintains overall control over the brand and business system, ensuring consistency across all franchise locations.
Franchisee Explained
A franchisee achieves the right to operate an existing business model, which they buy from another individual or company. Franchising is a business model that has revolutionized the way companies expand and establish their presence in various markets. It involves a mutually beneficial relationship between a franchisor and a franchisee.
The franchisor, typically an established brand, grants the franchisee the right to operate their business using the franchisor's name, trademarks, and proven business system. In exchange, the franchisee pays initial fees and ongoing royalties. Thus, this arrangement allows the franchisee to leverage the strength of a well-known brand, benefit from established marketing strategies, and receive continuous support and training from the franchisor.
Franchising enables rapid expansion without needing significant capital investment from the franchisor while distributing business risks to individual franchisees. Moreover, franchisees contribute their local expertise, ensuring the business adapts and thrives in different regions.
This model has proven to be a win-win scenario, offering entrepreneurs the opportunity to run their own businesses with a tried-and-tested formula and established brand while empowering franchisors to grow their brand's reach and influence in the marketplace.
How To Become?
Here are the steps to become a franchisee:
- Research and Identify Opportunities: Start by researching different franchising opportunities in industries that are of interest. Then, look for reputable franchisors with a successful track record and a business model that aligns with a person’s goals and skills.
- Evaluate Financials: Consider the initial investment required, ongoing fees, and potential return on investment. In addition, ensure one has enough capital to cover the initial franchise fees, setup costs, and working capital for the early stages of the business.
- Contact Franchisors: Reach out to the franchisors of the businesses one is interested in and request detailed information about their franchise offering. One should also attend franchise expos or seek advice from franchise consultants to explore more options.
- Review Franchise Disclosure Document (FDD): Franchisors are legally required to provide an FDD, which contains crucial information about the franchise system, costs, obligations, and support. Then, study this document carefully to understand all aspects of the agreement.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consider consulting with a franchise attorney and an accountant specializing in franchising to review the legal and financial aspects of the franchise agreement.
- Attend Discovery Day: Many franchisors organize a discovery day, where one can visit their headquarters, meet the team, and get a firsthand experience of the business model.
- Secure Financing: Arrange financing for the initial franchise fee and setup costs if needed. Some franchisors may offer financing assistance or recommend lenders familiar with their franchise system.
- Sign the Franchise Agreement: If a person is satisfied with the terms and has completed all due diligence, they can sign and become an official franchisee.
Roles And Responsibilities
The roles and responsibilities of a franchisee typically include:
- Business Operations: The primary responsibility of a franchisee is to operate the franchise location according to the standards and guidelines set by the franchisor. This includes managing day-to-day operations, overseeing employees, and ensuring the smooth functioning of the business.
- Compliance: Adhere to the franchise agreement and follow the rules, policies, and procedures outlined in the FDD provided by the franchisor. This includes using approved suppliers, maintaining quality standards, and upholding the brand's reputation.
- Customer Service: Provide excellent customer service to maintain customer satisfaction and loyalty. The franchise's success relies on building a positive reputation with customers.
- Marketing and Promotion: The franchisor directs marketing and advertising initiatives to attract customers and promote the franchise brand in the local market.
- Financial Management: Handle the financial aspects of the franchise, including budgeting, bookkeeping, and managing expenses to ensure profitability.
Examples
Let us look at franchise examples to understand the concept better-
Example #1
Suppose Cozy Treats is a small franchise in the bakery industry specializing in freshly baked goods and gourmet coffee. A passionate baker, Emily decides to become a franchisee and opens her Cozy Treats bakery in her local community. With the support of the franchisor's recipes, branding, and marketing materials, Emily quickly gains a loyal customer base.
Thus, her warm and inviting bakery has become a neighborhood favorite, known for its delicious treats and personalized service. Through her dedication and the strength of the Cozy Treats brand, Emily's bakery flourishes. It brought joy to her community and fulfilled her dream of owning a successful bakery business.
Example #2
One real-life example of a franchise is McDonald's. It is a global fast-food restaurant chain with thousands of franchise locations worldwide. In addition, the company offers franchise opportunities to entrepreneurs who want to operate their McDonald's restaurant under the well-known brand name. Each franchise follows McDonald's standardized business model, which includes menu offerings, operational procedures, and customer service standards.
McDonald's provides training, ongoing support, and marketing assistance to its franchisees, helping them succeed while expanding the brand's presence in various regions. Thus, this franchise model has played a significant role in McDonald's becoming one of the most recognizable and successful fast-food chains globally.
Advantages And Disadvantages
The advantages and disadvantages of franchises are as follows -
Advantages
- Established Brand: Franchising allows one to operate under an already established and recognized brand name, which can lead to faster customer acceptance and loyalty.
- Proven Business Model: Franchisors provide a tried-and-tested business system, reducing the risks associated with starting a new business from scratch.
- Training and Support: Franchisors offer franchisees comprehensive training and ongoing support, helping them learn the ropes and navigate challenges effectively.
- Economies of Scale: As part of a larger franchise network, one may benefit from bulk purchasing, shared marketing costs, and other economies of scale that can lead to cost savings.
Disadvantages
- Initial Costs: The initial franchise fee and setup costs can be significant, and ongoing royalty payments can impact profitability.
- Limited Flexibility: Franchisees must adhere to the franchisor's rules. This restricts their ability to make independent decisions.
- Royalty Payments: Franchisees are required to pay ongoing royalties to the franchisor, which can affect profit margins.
- Reputation Risks: The actions of other franchisees or the franchisor can impact the reputation of one's local franchise, even if it's not within the person's control.
Franchisee vs Franchisor
| Basis | Franchisee | Franchisor |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Definition | The franchisee is an individual or entity that purchases the right to operate a business using the franchisor's brand name, trademarks, and business model. | The franchisor is the established company that grants the franchisee the right to use its brand name, intellectual property, and business system in exchange for fees and royalties. |
| 2. Ownership | The franchisee owns and operates the individual franchise location under the terms and conditions specified in the franchise agreement. | The franchisor earns revenue from selling franchise licenses, and ongoing royalties and may also provide products, equipment, or services to franchisees. |
