Table Of Contents
What is Forward Integration?
Forward integration is a strategy adopted by businesses to reduce production costs and improve the firm's efficiency by acquiring supplier companies and, therefore, replacing the third party channels and consolidating its operations.
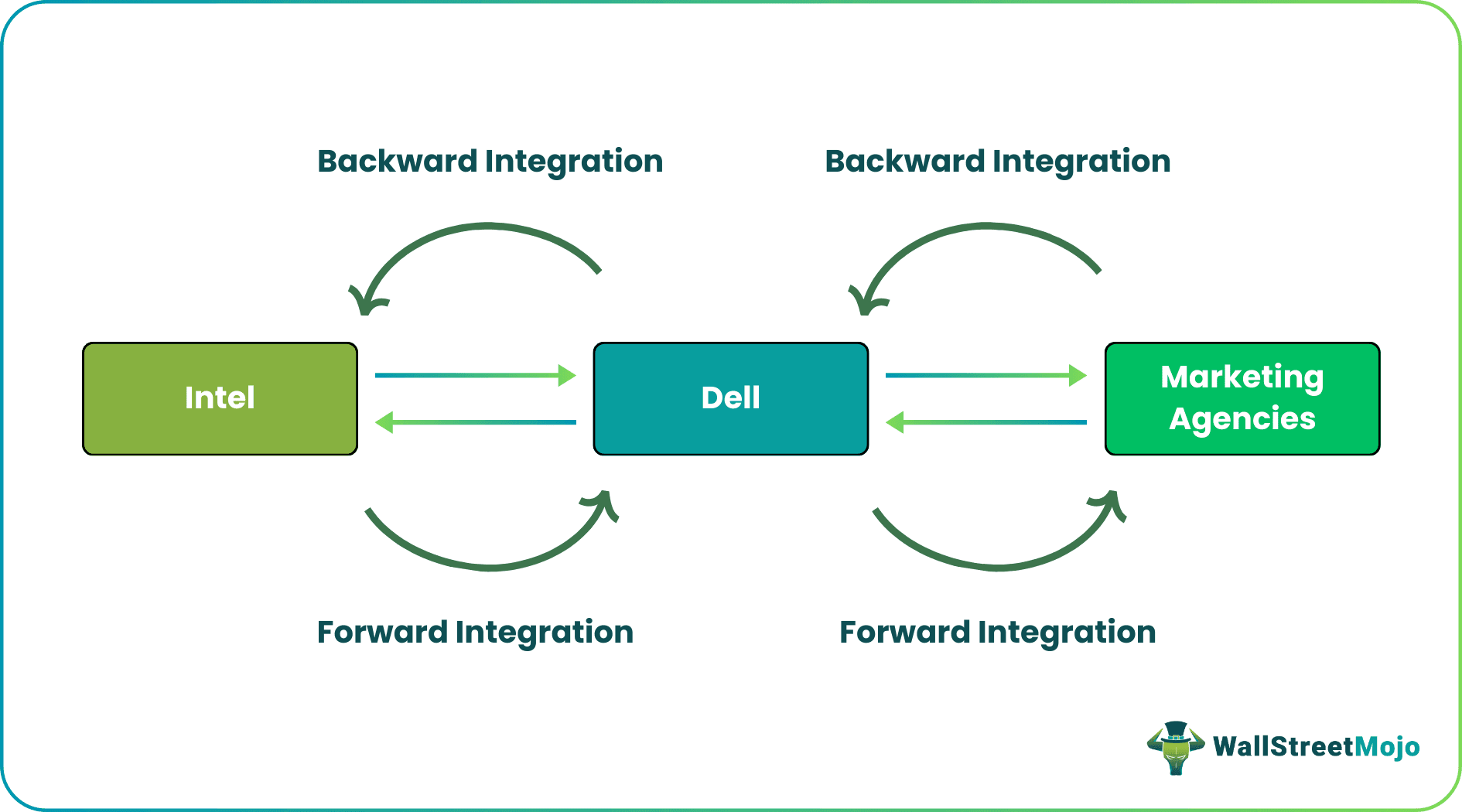
Table of contents
- What is Forward Integration?
- Forward integration is an idea businesses utilize to cut production costs and enhance the firm's capability through acquiring supplier companies. Thus, it replaces the third-party channels and combines the operations.
- The advantages of forward integration are low costs due to the market transaction costs elimination, a decline in transportation expenses, supply and demand and proper coordination in the supply chain, more significant market share, strategic independence, and creating an entry barrier to potential competitors.
- The main objective is meeting a larger market share, and companies expand their distribution or enhance product placement.
Explanation
- In practice, companies can opt for forward and backward integration to gain a competitive advantage. It helps a company extend its reach in the market, helping it get control of the demand side; on the contrary, backward integration helps the company get control of the supply side.
- In general, the industry comprises five steps in the supply chain, raw materials, intermediate goods, manufacturing, marketing and sales, and after-sales service.
- If a company plans to implement this strategy, it has to move forward in the supply chain while maintaining control of its initial place. This integration achieves greater economies of scale, higher market share, or greater control over distribution.
- By removing the third parties, the company has ownership of the distribution processes, thus having greater control over the flow of the products.
Forward Integration Explained in Video
How does Forward Integration work?

Let us see an example. Company Intel supplies the company DELL with processors, which are intermediate goods placed within DELL's hardware. If Intel decides to move forward in the supply chain, it may think of a merger or acquisition of DELL to own the manufacturing portion of the industry.
Again if DELL wants to implement this strategy, it can take control over the marketing agency that the company previously used to market its end product. If Intel decides to follow them, then, in the long run, it can operate as a monopoly and dominate the market by controlling both raw material and finished product. Buy DELL cannot take over Intel if it plans to integrate forward because only a backward integration allows a movement up the supply chain.
When to Follow Forward Integration?
- When the existing distributors, as well as the retailers, are expensive and are not able to match up to the distribution needs of the company.
- The absence of quality distributors in the market helps the company in gaining a competitive edge over the competitors;
- When the company has adequate human resources, like human resources and the financial advantage to meet the expenses of the distribution channel.
- When the company has very good production facilities to satisfy the customers' demand, in this case, it will help in strengthening the organization's value chain from production to sales and support of the products.
- When the existing retailers and distributors have a higher profit margin, which increases the cost of the product and leads to the higher price of the product, with the help of this integration, the company can reduce the cost of distribution; hence the product price will be lower thus increasing sales.
Amazon's Example - WholeFoods Acquisition

source: money.cnn.com
- Amazon's purchase of whole foods is one of the highest-profile examples of forwarding integration strategy in the current years.
- Amazon publishes the book itself and provides a publishing platform for independent writers.
- It also has its transportation (Amazon Transportation Services) and distribution, which is forward and backward integration-toward suppliers-and forward integration because Amazon directly delivers to the end-users.
- It is a brick and mortar Whole Foods outlet for Amazon. The Whole Foods outlets act as places to sell their products or have the customers pick them up at their convenience.
- Amazon was already in the grocery business in a small way, but this acquisition made Amazon a top player in the market. Shares of traditional food retailers fell to new lows because Amazon could shake up the industry.
- Similarly, DELL sells online directly to the customers, and Apple has its stores to reach out to the customers, which are also good examples of such integration strategy.
Top Examples of forwarding Integration Strategy
- A bicycle tyre manufacturer starts manufacturing bicycles, i.e., the end product.
- An FMCG company like Britannia builds up its distribution network, including regional warehouses, to directly sell to the retailers without going via wholesalers.
- A farmer, i.e., a producer of vegetables, directly sells his products at the farmer’s markets.
- A manufacturing company of ski equipment opens its outlets in various ski resorts to offer customers a brand experience to improve their brand image and recognition, along with direct contact with the customers.
- Myntra, an e-commerce company starts its own logistics service- Myntra Logistics, to reduce costs, improve turnover time, and reach its customers timely.
- A software company starts its own consulting and software development services to not depend on a network of partners to help customers implement its products.
- Flipkart, an e-commerce company, has its customer service functions instead of outsourcing them to improve customer experience.
Key Differences between forwarding and Backward Integration
| Forward Integration | Backward Integration |
|---|---|
| Here the company acquires or merges with a distributor. | Here the company acquires or merges with the supplier or manufacturer. |
| The main objective is to achieve a larger market share. | The main objective of backward integration is to achieve economies of scale. |
| Here the companies are looking to expand their distribution or improve the placement of their products in the market. | Involves internal steps to reduce overall dependency on suppliers and service providers. |
| Gives control over the supply chain; | Gives control over purchasing power; |
Advantages
- Low costs due to the elimination of market transaction costs
- Reduction in transportation costs.
- There is a synchronization of supply and demand and proper coordination in the supply chain.
- Bigger market share.
- Strategic independence
- Better opportunities for investment growth.
- Creates an entry barrier to potential competitors.
Disadvantages
- It leads to higher costs if new activities are not managed properly.
- It may lead to lower product quality and reduced efficiency due to competition.
- Increased bureaucracy and high investments may lead to lesser flexibility.
- The inability to offer product variety as in-house efficiency and skillsets are required.
- Possibilities of monopoly arise.
- Organizational structure may become rigid due to the shortcomings of such implementations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Factors to consider during this integration involve the potential impact on existing business relationships, the availability of suitable acquisition targets, the cost of building or acquiring new capabilities, and the risks and benefits of the strategy.
The threat of forward integration is in Business-to-Business (B2B) connections. For example, it happens if a manufacturer is pressured to sell directly to a consumer or retailer. Therefore, such threats typically apply to companies operating in industries with significant power asymmetry between upstream and downstream firms.
The impact of forward integration depends on various factors. However, the potential impact of these integrations includes increased control, cost savings, competitive advantage, disruptive influence, resource requirements.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to forwarding Integration and its definition. Here we discuss how forward integration works, along with examples (Amazon-Whole Foods acquisition) and integration strategies. Also, we discuss their advantages and disadvantages. You can learn more about Corporate finance from the following articles –
