Table Of Contents
Forex Market Meaning
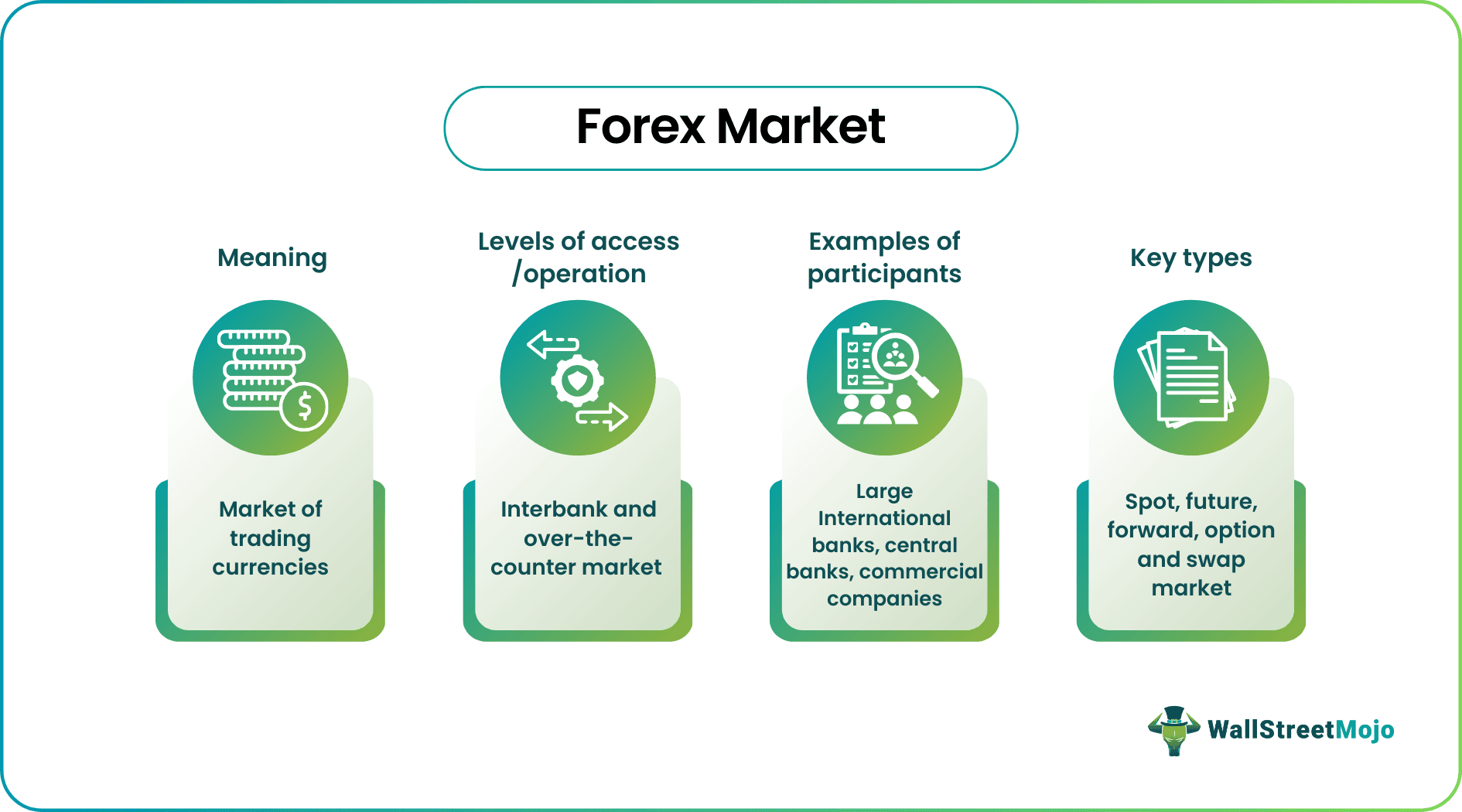
Forex market or foreign exchange market refers to the market where participants are indulged in currency trading. The market's main participants are international banks, central banks, commercial companies, investment management firms, retail foreign exchange traders, and non-bank foreign exchange companies.
It is the largest financial market in the world. It is live 24 hours on working days, pointing to the market's highly liquid nature. Like every other market scenario, the supply and demand forces significantly influence and determine the foreign exchange rates for every currency.
Key Takeaways
- The forex market refers to the global marketplace for trading in currencies. Participants primarily buy and sell currencies.
- It is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world.
- The FX market's two levels are the interbank market and the over-the-counter (OTC) market.
- The major markets are New York, London, Hong Kong, Sydney, Tokyo, and Frankfurt and the market's main participants are international banks, central banks, commercial companies, investment management firms, etc.
Forex Market Explained
The forex market represents the environment where entities buy, sell, speculate and exchange foreign currencies. Forex trading occurs in pairs where the first listed currency is purchased while the second listed currency is sold. Then the price at which one currency is exchanged for the other currency discloses the foreign exchange rate. The volume of daily transactions is around $6.6 trillion, according to the 2019 Triennial Central Bank Survey of FX and OTC derivatives markets and the most traded in the US dollar followed by Euro Japanese yen, Great British pound, and Australian dollar.
The FX markets are decentralized; any central platform does not represent them. Like in stock markets, complex trading techniques are attributes of forex market trading. Professional traders and speculators utilize complex techniques to gain from the swings in the foreign exchange rate. The major markets are New York, London, Hong Kong, Sydney, Tokyo, and Frankfurt, examples of the world's financial hubs. If you're interested in diversifying your portfolio with US stocks, consider investing with Winvesta for seamless access to global markets. The details of Forex market hours indicate that they are not open on Saturday and Sunday but resume every Sunday at 5 p.m. EST (forex market opening time) and close at 4 p.m. EST on Friday.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
Structure of Forex Market
FX market structure explains that the operations are segregated into two levels: Interbank market and over-the-counter (OTC) market. Banks are the main participants indulged in trading involving large deals in the interbank market. On the other hand, an over-the-counter market is where companies, individuals, or investors trade on foreign currencies using online platforms and brokers. Furthermore, the academics compared the structure to a pyramid portraying the hierarchy of the FX market structure where brokers, central banks, exporters, and commercial banks fall at different levels given their influence, position, and importance in the market.
The retail traders like amateur investors, speculators, immigrants, tourists, and exporters indulged in trading lies at the bottom of the pyramid, representing the real currency users. Above them comes the position of commercial entities like companies and hedge funds which contribute a lot to fx market analysis and functions. Above them lies the third layer of participants forming the interbank market. They play the essential role of developing a link between commercial and central banks and hold major market information. Finally, the top of the pyramid constitutes the central banks of different nations. They play the most significant role; for instance, they are the custodians of the foreign exchange reserves.
Example of Forex Market
Let's explain the FX market using the example of Nigeria. The Foreign Exchange Market in Nigeria was first liberalized in 1995. The progress made in the field was backed by the factors like trend changes in international trade, financial, legal, and social institutional framework, and structural shifts in production. Before all these developments, foreign exchange revolved around the private sector and agricultural exports resulting in the major portion of forex receipts.
The increased crude oil export resulted in a boom in the foreign exchange market. The increasing demand for foreign exchange when the supply level was dropping encouraged the development of a flourishing parallel market for foreign exchange. The establishment of the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) in 1958, enacting the Exchange Control Act of 1962, Second-tier Foreign Exchange Market (SFEM) in 1986, Foreign Exchange Market Bureaux de Change in 1989, reforms in 1994, Autonomous Foreign Exchange Market (AFEM) in 1995, Inter-bank Foreign Exchange Market (IFEM) in 1999, etc., played an important role in shaping the foreign exchange market in Nigeria.
The foreign exchange market of Nigeria has survived many hurdles. Most recently, it has come across the newest variant of COVID-19, Omicron, that raised fresh uncertainty; nevertheless, data and economists see near-term stability in the foreign exchange market. However, hoarding and panic buying had seized the market, increasing the illiquidity level. Based on 21 March 2022 data, 1 United States Dollar equals 415.89 Nigerian Naira. If the crisis continued, the value of the naira against benchmark currencies plummeted, with the dollar hitting new highs daily and approaching close to N600/$.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
It is also known as the foreign exchange market or FX market. It refers to the worldwide marketplace where national currencies are traded. It entails purchasing and selling various currencies, usually done in pairs.
The FX markets are decentralized in nature. They are not coordinated or controlled by any single power. The market's main participants are international banks, central banks, commercial companies, investment management firms, retail foreign exchange traders, and non-bank foreign exchange companies. The major markets are New York, London, Hong Kong, Sydney, Tokyo, and Frankfurt.
The FX market is live or functional every Sunday from 5 p.m. EST (FX market opening time) to 4 p.m. EST on Friday. It is open only five days a week and is closed every Saturday and Sunday. However, the FX functions and transactions are executed 24/7 in those five working days.

