Table Of Contents
What Is Foreign Corporation?
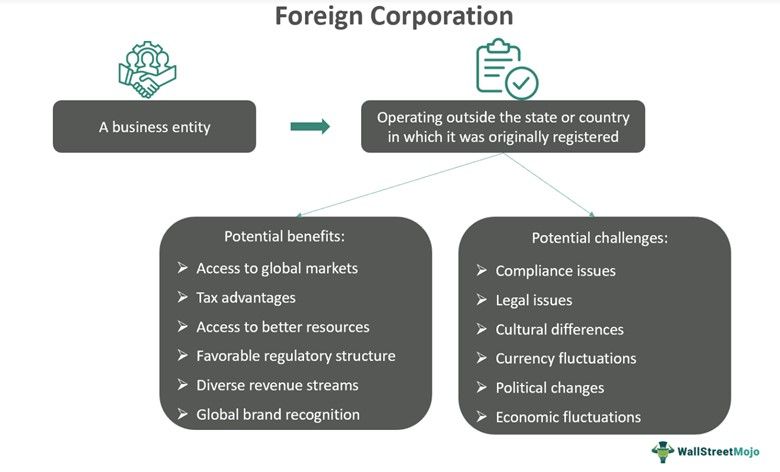
A Foreign Corporation is a business entity that is incorporated under the laws of a country or state other than where it conducts its operations. It aims to expand its operations into new markets, increase its customer base, and generate additional revenue and profits.
These corporations contribute to the economic growth of the countries in which they operate by creating jobs, investing in infrastructure, and stimulating the local economy through increased demand for goods and services. Additionally, it promotes trade and investment between countries by facilitating cross-border transactions, promoting exports, and creating global supply chains.
Key Takeaways
- A foreign corporation is a company that is incorporated in one country but operates outside the country in which it was registered.
- It is an organized business entity that operates under the laws of a foreign country, and it can engage in various business activities.
- It must be noted that such companies are required to register with local authorities and comply with local regulations pertaining to the region or country in which they operate.
- Foreign corporations that have securities traded in the United States may be subject to certain requirements under the US securities laws, including the Securities Act of 1933 and the Securities Exchange Act of 1934.
Foreign Corporation Explained
A foreign corporation is a business entity that is incorporated in one country or state but conducts its operations in another country or state. For example, a company based in the United States may choose to establish a subsidiary or branch office in another country, such as China or Germany. This subsidiary or branch would be considered a foreign corporation because it is incorporated in the United States but operates in a foreign country.
Foreign corporations can operate in a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, retail, technology, and finance. They may enter a new market by establishing a subsidiary or branch, acquiring an existing business, or forming a joint venture with a local company.
The process of establishing a foreign corporation typically involves the following steps:
- Research and Planning: The first step in establishing a foreign corporation is to research the target market, including the legal and regulatory environment, the competitive landscape, and the cultural and economic factors that may impact the business. This will help the corporation to develop a sound business plan and identify any potential risks or challenges.
- Entity Formation: Once the target market has been identified, the foreign corporation must establish a legal entity in the country where it wishes to operate. This typically involves registering the corporation with the local government and obtaining any necessary licenses and permits. Depending on the country, the corporation may need to appoint a registered agent to act as its representative.
- Tax and Accounting Compliance: Foreign corporations must comply with the tax and accounting requirements of the country where they operate. This may involve registering for taxes, obtaining a tax identification number, and filing regular tax returns. The corporation may also need to establish a local bank account and comply with local accounting standards.
- Employment and Labor Laws: Foreign corporations must comply with the employment and labor laws of the country where they operate. This may involve obtaining work permits for foreign employees, complying with local labor standards, and adhering to any regulations related to hiring, termination, and compensation.
- Marketing and Sales: Once the corporation has established a legal presence in the target market, it can begin marketing and selling its products or services. This may involve developing a local sales team, partnering with local distributors or retailers, and adapting its marketing strategy to meet the needs and preferences of the local market.
As an extension of the above discussion, let us also briefly understand the concept of a Controlled Foreign Corporation (CFC). A CFC refers to a business entity incorporated outside the US but is controlled by US shareholders. Both shareholding and voting rights play a key role in determining the status of a corporation in this context. The foreign corporation tax rules in the US are ascertained based on the composition of a corporation and how it is connected with the US.
SEC Requirements
SEC stands for Securities and Exchange Commission, which is a US government agency in charge of regulating stock markets in the US, enforcing relevant laws, and protecting investors. After the Stock Market Crash of 1929 and the Great Depression that followed, the need to have a strong regulatory body was felt, and the SEC was established in 1934.
The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) requirements in the context of foreign corporations can vary depending on the nature of their operations and the extent of their involvement in the US securities market.
If a foreign corporation wishes to offer securities in the United States or have its securities listed on a US stock exchange, it must comply with SEC regulations. This includes filing registration statements with the SEC, which contain information about the corporation's business, financials, and other relevant data.
Foreign corporations may also be subject to additional regulations such as the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA) and the Patriot Act. The FCPA prohibits companies from making illegal payments or bribes to foreign officials to obtain or retain business, while the Patriot Act aims to prevent money laundering and terrorist financing.
In addition, foreign corporations may be required to appoint a US-based registered agent for service of process, maintain books and records in the United States, and comply with state-level securities laws.
Overall, foreign corporations seeking to operate in the US market should carefully review and comply with all applicable SEC regulations and other relevant laws and regulations to avoid legal and financial penalties.
Examples
Let us study some examples to understand the concept better.
Example #1
Toyota Motor Corporation, a Japanese multinational automotive manufacturer, operates as a foreign corporation in the United States. Toyota is headquartered in Toyota City, Aichi Prefecture, Japan, and operates worldwide, including in the United States.
Toyota has a significant presence in the US, with production facilities and offices across the country. The company has a large US workforce and is a major employer in many states. Toyota is also listed on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and is subject to SEC regulations and other US laws and regulations. The company increased its investment in the US further to the tune of $383 million to grow its business in vehicle electrification, according to an April 2022 news report.
As a foreign corporation operating in the US, Toyota must comply with various legal and regulatory requirements, including those related to securities, employment, taxes, and environmental regulations. The company is also subject to US trade policies, such as tariffs and trade agreements, which can have a significant impact on its operations and financial performance.
Example #2
Suppose Solis Health Pharmaceuticals, a pharmaceutical company headquartered in Germany, develops and manufactures medications for various health conditions. Solis Health Pharmaceuticals wishes to expand its market and increase its global presence, including in the United States. To achieve this, the company decided to establish a subsidiary in the US, Zephyr Pharmaceuticals Inc., which will sell its products and conduct research and development activities.
As a foreign corporation operating in the US, Zephyr Pharmaceuticals Inc. must comply with various legal and regulatory requirements. For example, the company will need to register with the SEC if it plans to offer securities to the public or list its securities on a US stock exchange. The company will also need to comply with US patent and trademark laws to protect its intellectual property.
Zephyr Pharmaceuticals Inc. will also need to comply with US labor laws and regulations, including those related to employment contracts, worker safety, and non-discrimination. Additionally, the company will need to comply with US environmental regulations related to the production and disposal of pharmaceuticals.
