Table Of Contents
What Are Fixed Assets?
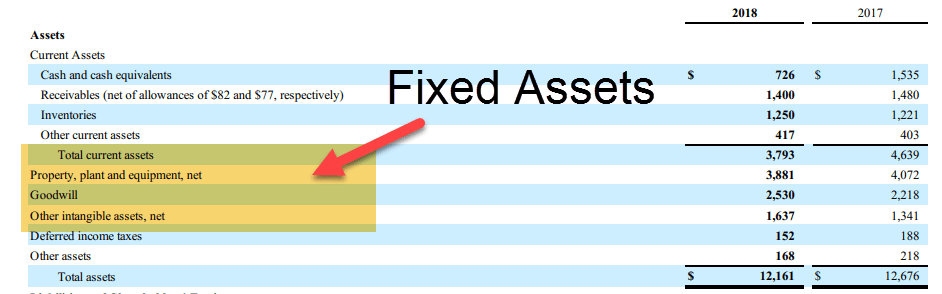
Fixed assets are used for business operations to generate income and are held for the long term. It is not expected to be converted into cash in the short term. Thus, these assets are not held for immediate resale and are intended to benefit the organization for more than one reporting period. Examples include plant and machinery, land and building, furniture, computer, copyright, and vehicles.
When these assets are sold, profit/loss on sale is calculated and recorded in the accounts books. While preparing a cash flow statement, a loss on the sale of assets is added to the net income to arrive at cash flow from operations (indirect method). Similarly, a profit on the sale of assets is deducted from income to get the cash flow from operations.
Fixed Assets Explained
Fixed assets are fixed, long-term assets owned by an individual or an organization. They are usually not easy to sell and are often confused with current assets such as bank accounts or cash.
Proceeds from the sale and purchase of assets are treated as cash cash flows from investing activity.
A change in net fixed assets’ market value is accounted for through a revaluation of fixed assets. In such a case, a reliable market value estimate is needed.
They are one of the most critical components of a business. Managing fixed assets is essential as their purchase involves significant cash outflows. Since the disposal of assets is not an easy task, considerable planning is required to purchase assets. Decisions, once taken, cannot be easily reversed. An organization also needs robust record-keeping system for accounting assets so that the decision-makers get vital information to make business decisions.
Types
Two major types comprise to make net fixed assets of an organization. Let us understand them with the help of the discussion below.
#1 - Tangible Assets
Tangible assets have a physical presence and can be touched, such as land and building, plant and machinery, vehicles, etc. Generally, it is easier to value tangible assets than intangible assets. This is because tangible assets are subject to depreciation, which reduces the asset's value over time.
#2 - Intangible Assets
Intangible Assets are assets with no physical presence and cannot be touched. These include goodwill, trademarks, patents, software, licenses, other forms of intellectual property, etc. Amortization happens in the case of intangible assets, which gradually write off the asset's initial cost.
List
Different companies can have different fixed assets based on their nature of business and their requirements. However, few of the most common ones found in fixed assets accounting are as mentioned below.
- Land
- Building
- Factories
- Machinery
- Vehicles
- Inventory
- Computer Hardware
- Softwares
- Office Supplies
- Office Equipment like Printers, Chairs, etc
- Natural Resources
- Patent
- Copyrights
- Franchisee
- Licenses
Examples
Let us understand fixed assets accounting and its intricate details with the help of a few examples.
Example #1
Downey is thinking of starting a business near the coast of Gujarat. First, he starts a firm with the name of 3M and registers it with the relevant authorities. Then, he purchases the below asset to start the firm using the loan proceeds; you must account for the fixed assets in the books of account and discuss why they fall in each category.

Solution:
Fixed assets are those purchased and held by the firm for more than one accounting period or more than 12 months. Let's test whether the above equipment passes the test?

Hence, the total cost to be accounted for will be 58,050,000 in books of account.
Example #2
Fun and foods, a leading company that sells hamburgers, is now considering an expansion plan. It has considered Italy the next country where it would like to establish its footprints. It also plans to set up an administrative team where they would require a computer, laptop, computer accessories, and Cisco phones for those employees working for corporate. You are required to discuss whether these Cisco phones, computer accessories, computers, and laptops will fall within the definition of fixed assets?
Solution:
The definition of fixed assets states any asset that the firm purchases for more than one accounting period or administrative purposes or rental to others. In this case, we are not given any period of information. Still, however, it is mentioned that this equipment will be used for the administrative team, and hence the purpose will be for administrative purposes. Furthermore, this equipment will be used for more than one accounting period since its planning to expand business in Italy, and further, a new corporate office is also opened. Therefore, from the above discussion, equipment will fall within the purview of the fixed asset definition.
However, the computer accessories need to be scrutinized, whether the same are separable or inseparable assets, as the accounting for the same is done differently. 0If they are inseparable, they will be included in the cost to the computer, or if they are separable, they will be recorded as a different asset in the books of account.
Example #3
Asha builders are on the verge of completing the construction of buildings at the remote site, which they started five years ago. However, those buildings are not ready to use, but 80% of the flats have been sold out. Asha, the owner of Asha builder, is unsure how she should account for buildings in her books of account as this was her new business. So she has approached an accountant to help her decide how these buildings cost and sell should be recorded in books of accounts.
Solution:
Asha is in the field of a construction business, where the normal course of business is to sell the buildings at a price more than what it took to make and purchase the raw materials. Further, it took more than five years for them to complete the project. So, let's consider a definition of fixed assets. It states that an asset is intended to use for more than one accounting period or more than 12 months or administrative purposes. Here, the first criteria are met where the assets were in possession for more than five years. So, whether this should be included?
Well, the answer to the above question is No. The reason is buildings, on normal occasions, take more time to complete, and it is the business of Asha builders to sell them, and they don't intend to use them. So, these criteria of using those constructed buildings fail to meet and hence cannot be accounted for as fixed assets in the books of accounts. So, instead, the selling pricing is less cost price, and all the costs will be treated as normal income in the revenue statement, and the balance will be profit. However, one needs to follow what accounting standards on revenue state how to account for revenue, cost, and profit; for example, there is a cost of completion method that one can use.
Example #4
General motor transport services are in the business of transporting goods from one place to another. They owned 12 trucks, six small tempos, and five rented (on operating lease for five years) trucks. Discuss how these assets will be recorded in the books of account of general motor transport services, whether as fixed assets or will be recorded in revenue statements?
Solution:
The criteria for recording assets as fixed assets that are purchased and:
- Intention to use for more than one accounting period or 12 months
- Use for administrative purposes.
Here, these vehicles are used by them, and since it's their business and hence they would be using them for more than one accounting period else, they won't be able to do business since replacing them every year will be too costly for them. The second thing here is that the rest of the five tracks are rented (operating lease) and are not purchased; hence, they will not be recorded as fixed assets. However, 12 trucks and six small tempos will be recorded as fixed assets.
Advantages
For an organization, its net fixed assets play a vital role not just in its overall net worth but also in its daily activities. Let us understand their advantages through the explanation below.
- It helps in generating income. For instance, in a manufacturing unit, goods are to be produced. Fixed assets in the form of machinery help in producing those goods. If goods are not produced, the business will not be able to sell those goods, and the organization's purpose won't be fulfilled. Similarly, such assets in the form of delivery trucks help sell the goods.
- The depreciation on assets is spread over the useful life of the asset. Hence, the expense burden is spread over several years.
- Investors and creditors use information about assets to determine a company's financial health. They then decide whether to invest/lend also, depending on the financial ratios calculated from the financial statements.
- If an organization wants to take loans, assets can act as security for the loan. Thus, it enables a business to take loans.
- It assumes more importance in capital-intensive industries, such as manufacturing units.
Disadvantages
To understand any concept, it is vital to understand both extremes of opinions. Hence, let us also discuss the disadvantages found in fixed assets accounting through the discussion below.
- Generally, they are bulky. Hence, moving many fixed assets like plants and machinery from one place to another is challenging.
- It can not be easily converted into cash. For instance, if a new car is bought, it would fetch generally lower than the purchase price immediately once it moves outside the car showroom. It generally takes a significant time to be disposed of. For instance, selling land requires numerous negotiations with buyers and many legal formalities.
- A big enterprise has thousands of assets. Tracking and recording them is a cumbersome process.
- Generally, It requires significant investment and cash outflows when they are purchased.


