Table Of Contents
What Are Financial Systems?
A financial system is an economic arrangement wherein financial institutions facilitate the transfer of funds and assets between borrowers, lenders, and investors. Its goal is to efficiently distribute economic resources to promote economic growth and generate a return on investment (ROI) for market participants.
The market participants may include investment banks, stock exchanges, insurance companies, individual investors, and other institutions. It functions at corporate, national, and international levels and is governed by various rules dictating the eligibility of participants and the use of funds for different purposes. Aside from financial institutions, financial markets, financial assets, and financial services are the components of the financial system.
Key Takeaways
- A financial system consists of individuals like borrowers and lenders and institutions like banks, stock exchanges, and insurance companies actively involved in the funds and assets transfer.
- It gives investors the ability to grow their wealth and assets, thus contributing to economic development.
- It serves different purposes in an economy, such as working as payment systems, providing savings options, bringing liquidity to financial markets, and protecting investors from unexpected financial risks.
- A specific set of rules drafted under different government policies is required for a stable financial system operating at corporate, national, and international levels.
Explanation
In any functional economy, economic resources are limited, with individuals having unlimited wants and desires. This problem, referred to as scarcity, is one of the significant drivers of an economy. However, it challenges an economy in determining when, where, to whom to distribute its resources. Consequently, it resulted in a financial system structure capable of efficiently allocating economic resources to stimulate growth. Also, it allows participants to benefit by:
- Providing a way of making payments (banks)
- Giving participants a way of earning interest in the form of time value (investment institutions)
- Protecting them against financial risks (insurance)
- Collecting and distributing financial information (credit agencies)
- Governing regulations to maintain stability (central banks and governments)
- Maintaining liquidity and converting investments into cash (banks and financial institutions)
Financial institutions are at the core of the financial system, giving individuals the ability to save and invest whenever and wherever they want. Investors put their money in these institutions, which offer them a reward for saving and use it to lend to borrowers. The borrowers can use these funds to build goods and services or fund other projects. All this activity helps promote economic growth – either by creating additional jobs or generating a profit and contributing back to the economy.
The money or funds flow from the lender to the borrower in one of two ways:
- Market-Based
- Centrally Planned
In a market-based economy, borrowers, lenders, and investors can obtain funds by trading securities, such as stocks and bonds in the financial markets. The law of supply and demand will determine the price of these securities. With a centrally planned economy, governing authority or central planner makes the investment decisions. In most instances, there will be a mix of both types of economies.
The Hargreaves Lansdown provides access to a range of investment products and services for UK investors.
Components of Financial Systems
There are several financial system components to ensure a smooth transition of funds between lenders, borrowers, and investors.
- Financial Institutions
- Financial Markets
- Tradable or Financial Instruments
- Financial Services
- Currency (Money)
#1 - Financial Institutions
Financial institutions act as intermediaries between the lender and the borrower when providing financial services. These include:
- Banks (Central, Retail, and Commercial)
- Insurance Companies
- Investment Companies
- Brokerage Firms
#2 - Financial Markets
These are places where the exchange of assets occurs with borrowers and lenders, such as stocks, bonds, derivatives, and commodities.
Financial markets help businesses to grow and expand by allowing investors to contribute capital. Investors invest in company stock with the expectation of it producing a return in the future. As the business makes a profit, it can then pass on the surplus to the investors.
#3 - Financial Instruments
Tradable or financial instruments enable individuals to trade within the financial markets. These can include cash, shares of stock (representing ownership), bonds, options, and futures.
#4 - Financial Services
Financial services provide investors a way of managing assets and offer protection against systemic risk. These also ensure individuals have the appropriate amount of capital in the most efficient investments to promote growth. Banks, insurance companies, and investment services would be considered financial services.
#5 - Currency (Money)
A currency is a form of payment to exchange products, services, and investments and holds value to society.
Examples
Financial systems are an essential part of an economy, and without them, the flow of funds would cease to exist. It keeps evolving considering the regional or global economic situations.
An example of this is the G20’s virtual summit held in March 2020, discussing the role and significance of the global approach to the financial crisis caused by the coronavirus pandemic. The center of discussion was the ability of the global financial system to operate effectively and efficiently. Financial markets have mitigated systemic risk due to the improved financial market infrastructures, systemically important financial market utilities, risk management standards, and centralized clearing houses.
Here is another example to understand its importance in everyday life.
Business Loans
- When a business requires capital to fund new projects or develop new technology, it applies for a business loan. There are several options to get it done, such as getting a line of credit or an installment loan.
- To qualify for the loan, the lender looks at several business components like its credit score or balance sheet to determine the systemic risk of giving out the loan.
- The financial institution (bank) then allocates the necessary funds to the business. The business can use the money to fund a future project to generate additional income.
- The bank then requires the business to make payments towards the loan, including interests for its time value.
Functions of Financial Systems
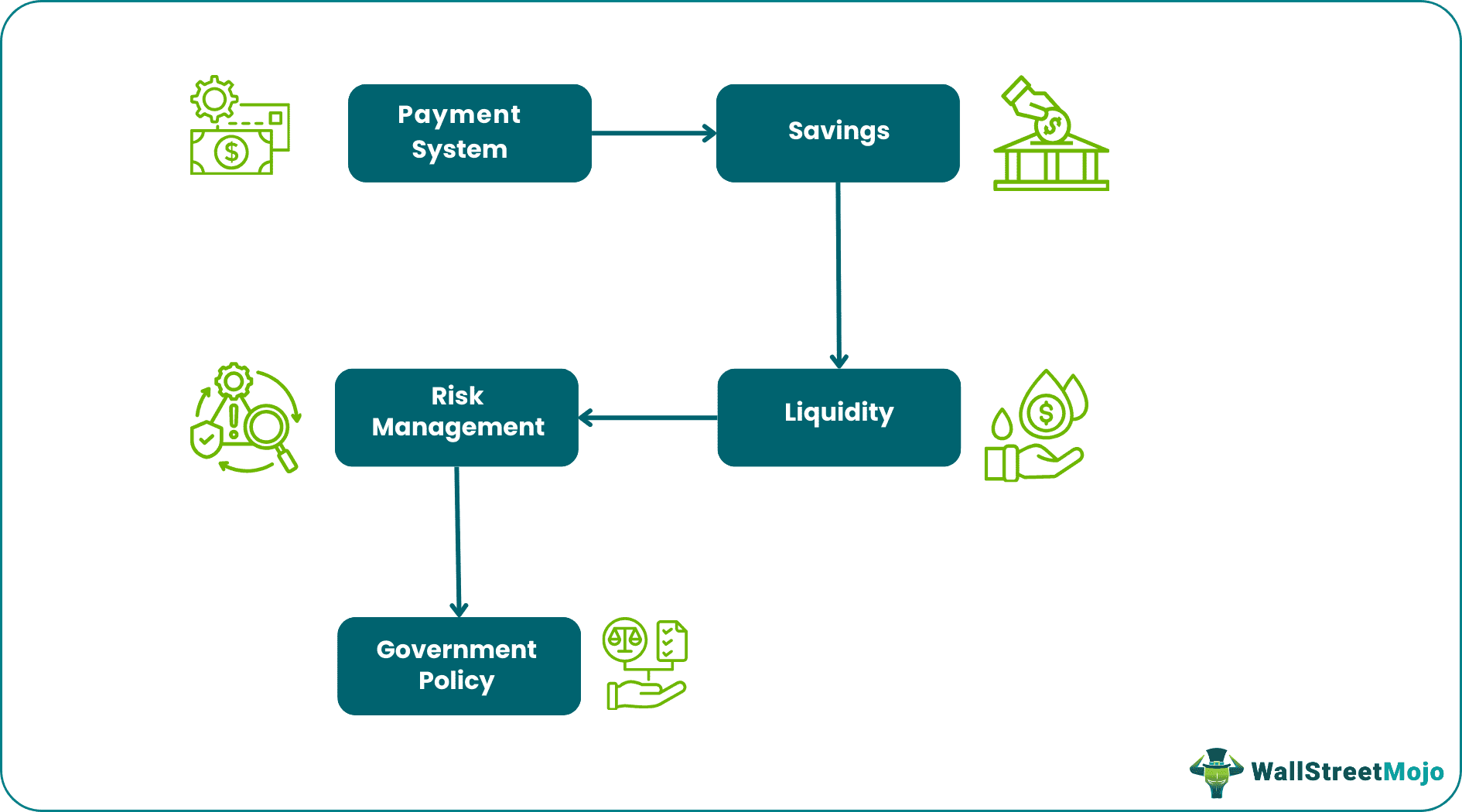
A financial system allows its participants to prosper and reap the benefits. It also helps in borrowing and lending when needed. In simpler words, it will circulate the funds to different parts of an economy. Here are some of the financial system functions:

- Payment System - An efficient payment system allows businesses and merchants to collect money in exchange for their products or services. Payments can be made with cash, checks, credit cards, and even cryptocurrency in certain instances.
- Savings - Public savings allow individuals and businesses to invest in a range of investments and see them grow over time. Borrowers can use them to fund new projects and increase future cash flow, and investors get a return on investment in return.
- Liquidity - The financial markets give investors the ability to reduce the systemic risk by providing liquidity. It thus allows for easy buying and selling of assets when needed.
- Risk Management - It protects investors from various financial risks through insurances and other types of contracts.
- Government Policy - Governments attempt to stabilize or regulate an economy by implementing specific policies to deal with inflation, unemployment, and interest rates.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.

