Table Of Contents
Financial Risk Definition
Financial risk refers to the types of risks and chances of losses associated with an investment. The analysts help assess this risk, thereby making it a parameter based on which investors can decide whether they can trust an organization with their money or they should skip investing in them.
In short, financial risk and return calculation allow the management of an organization improve measures to ensure better performance and the investors to make effective and valid investment decisions. The figure also assesses the capability of organizations to deal with financial obligations.
Key Takeaways
- Financial risk is the possibility that a company cannot repay the debt borrowed from a bank or financial institution.
- There are three main types of financial risk: credit risk, liquidity risk, and equity risk.
- There are various ways to measure financial risk for a company. One way is to examine how the market values the company, which provides insight into its position in the market.
Financial Risk Explained
Financial risk is calculated to find out the ability of a firm to be able to pay off the debt it has taken from the bank or financial institutions. When government reflects a higher financial risk, it shows the inability of the authorities to implement proper fiscal policies and repay their loans and debts. The same applies to the corporates as the risk calculation reflects their possibility to default on their financial liabilities.
When it comes to investors, they assess the financial risk associated with the business venture they are considering investing in. If the value they obtain is good to go, they stick to their decision to invest in the organization’s assets, or else they drop the idea. Hence, it plays an important role in helping individuals make efficient investment decisions. Though evaluating the chances of risk does not remove the risk associated with the investments, it, at least, lets one reduce the level and adopt some measures to manage it well for least loss or negative effect.
Types
There are mainly three types of Financial Risks. Let’s look at them below –
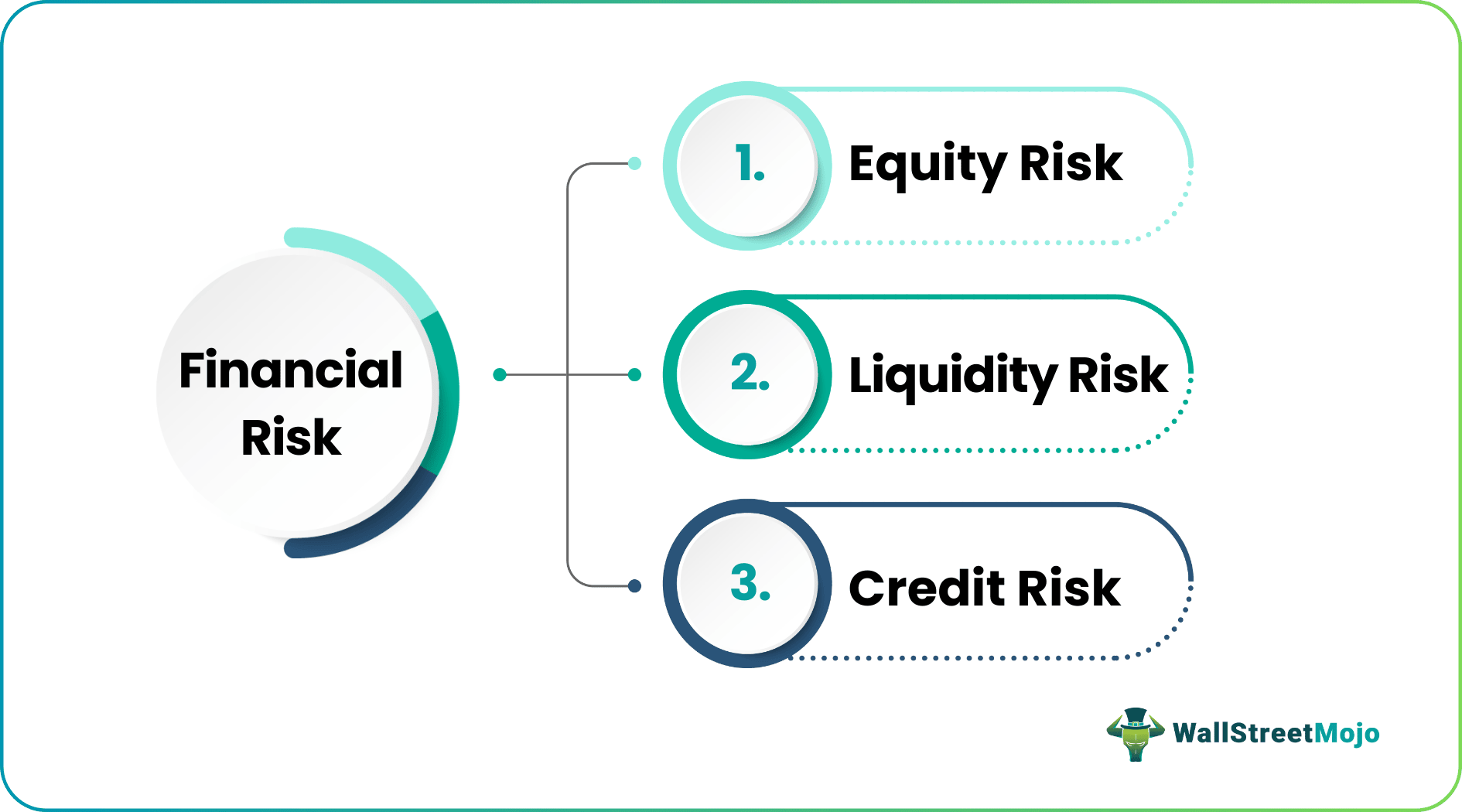
#1 - Credit risk:
It is the most common type of financial risk. If a firm takes a loan and isn’t able to pay it off, they have credit risk. Normally, firms that are about to default suffer from credit risk. The default isn’t a good idea because it can affect the firm's reputation, and it will also affect the banks or financial institutions. If, in any case, the firm would like to get a loan from the bank/financial institution, it would be too hard to convince them.
#2 - Liquidity risk:
It is another type of Financial risk. When a firm can’t sell an asset quickly, it is a liquidity risk for the firm. For example, if a firm buys an asset and then, shortly, it becomes obsolete, it would be pretty risky for the business. Because the business won't be able to sell it off, it wouldn't be able to keep the asset.
#3 - Equity risk:
Equity Risk is the third type of Financial Risk. When the market becomes volatile, it becomes difficult for the company to value its equity stocks. The market price often goes down, which isn't good news for the firm. This volatility of the equity stock market is called the equity risk, which comes with the firm's financial risk.
Sources/Causes
There are certain factors that lead to financial risk. Some of the financial risk sources include:
- Market Risk – When market fluctuations are observed, the values of the investments get affected adversely. This, in turn, leads to financial risk for entities as the investment amount declines in value, leading to losses for organizations.
- Inflation Risk – The hampered purchasing power is a sign of inflation risk. When the purchasing power of the common public decreases, it affects the performance of the business one invests in, which thereby becomes a negative instance for any business and its shareholders/investors.
- Interest Risk – This involves the fluctuations in the rate of interest, which affect the value of the securities, like fixed-income assets, including stocks, bonds, etc. The cause of interest fluctuations ranges from monetary policies being introduced to market sentiments.
Examples
Let us consider the following examples to understand the financial risk definition better:
Example #1
Let’s say that a firm wants to reduce financial risk, and at the same time, they want to take advantage of the financial leverage debt will provide. In this case, they should go for 70% of equity and only 30% of debt in their capital structure. Of course, this is hypothetical, and after looking at all factors, the decisions related to the capital structure should be made.
A firm should remember to reduce this type of risk to construct its capital structure by taking off too much burden from its shoulder. That means taking as much as loans as they can support themselves. If the firm goes for 60% debt and 40% equity, the financial risk for the firm would be much more than if the firm goes for 60% equity and 40% debt.
Example #2
Pepsi’s Debt to Equity ratio was around 0.50x in 2009-2010; however, Pepsi’s leverage has increased over the years and is currently at 3.38x. This situation is undesirable. But if a firm uses prudence to take debt, it can keep its risk at a minimum.

How To Measure?
Financial risk can be measured by all means. The firm should look at the market and see how the firm is being valued. The valuation is very important, which offers the firm an idea of where they stand in the market. At the same time, the firm can calculate the financial leverage and the degree of financial leverage. The firm can also use debt-equity ratio, interest coverage ratio, and other financial ratios to find out its level.
How To Manage?
Managing financial risks is a crucial affair. The effects of such risks can be destructive, hence having strategies to take care of them is recommended. Though these strategies do not eliminate the risks involved, they do help in mitigating them.
Once the risks are assessed and identified, strategies need to be implemented by entities, including measures to avoid risks or transfer risk to a third-party, etc. Though the risk management strategies may differ at individual and corporate levels, the objective is the same, i.e., to remain protected against the financial risks.

