Table of Contents
What Is The Financial Reporting Framework?
The financial reporting framework in accounts describes the conceptual objective of financial reporting's general purpose. It assists the IASB in developing and revising IFRS based on consistent concepts. Assistance is necessary to help people develop consistent accounting policies.
In such a derivatives contract, the seller holds an unlimited risk while the buyer's risk is limited. Exercising the contract if it seems profitable helps traders take advantage of a short position while limiting risk during commodities futures trade. Moreover, the buyer pays a premium to the commodities options contract seller for taking the additional risk.
Key Takeaways
- A financial reporting framework is a standard rule-making process that helps record and report financial data.
- It helps ensure transparency, consistency, and comparability in reporting financial statements, which helps stakeholders understand the company's financial health.
- The two most common frameworks are IFRA and GAAP.
- The key factors to consider in preparation are transparency, comprehensiveness, relevance, consistency, comparability, and true and fair view provision. A strong framework helps companies comply with rules and facilitate investment decisions.
Financial Reporting Framework Explained
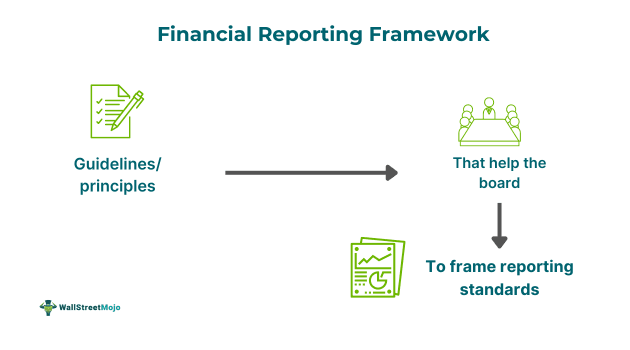
The financial reporting framework (FRF) consists of the guidelines, principles, and standards that are to be followed in recording or reporting financial data. These rules help professionals who prepare standards of accounting to develop them in a manner that can be applicable globally. This is critical because these guidelines help the reporting process to be transparent. It ensures that the recording reflects the true and fair view of the business's operations and its financial health.
Financial reports are particularly useful for existing and potential investors. They are also helpful to lenders, creditors, and interested third parties. These reports provide the financial information required for making informed decisions. These guidance principles are also responsible for assisting companies to develop accounting policies where International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) standards do not apply. It helps stakeholders understand what standard suits them better in such transactions.
The framework sets out certain characteristics for financial reporting. They are objectives, qualitative characteristics, description of reporting entity, definition of assets, liability, income, expense, and equity. Additionally, measurement bases, concepts on presentation and disclosure, and concepts relating to capital and its maintenance are also included. The framework also includes the criteria for including such definitions and concepts and guidance on the DE recognition of the same.
Types
There are two common types of FRF they are as follows:
- As per the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
- As per the generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP)
As per the IFRS
The reporting guidelines are based on comparability, faithful representation, and relevance. These principles are built for consistency, comprehensiveness, and transparency.
As per the GAAP
As per GAAP, the reporting framework's objective is to offer details on claims and resources through financial data. It aims to give investors details on assessing potential cash flows and information on credit decisions and investment choices.
Factors To Consider
Below are some of the factors that can be considered for the development of a financial reporting framework.
- Transparency: Frameworks shall be transparent, accurately present financial statements, and reveal the true state of economic events. Transparency shall include timely, full, and fair disclosure and representation.
- Comprehensiveness: The framework built shall be based on standard principles and shall be in such a manner that it is universally applicable. It shall be inclusive of all transactions. It includes those in existence and those that arise in the future.
- Consistent Financial Reporting Framework: Frameworks shall imply equal treatment and consistency in measuring different types of transactions. Consistency refers to the constant nature of treatment across locations, periods, and industries. A consistent FRF does not mean there should be rigid standards but flexible ones to ensure fair treatment of transactions that are specifically alike.
- Relevance: The standards drafted shall be based on the relevant rules. The information provided through reporting shall reveal credit and resource allocation information. It shall give interested parties an opportunity to make decisions on evaluating future, present, and past transactions on prospective cash flows.
- True And Fair View: The framework shall encourage businesses to reveal information that gives a true and fair view of the business.
- Comparability: The frameworks shall be drafted so that the measurements involved and the results derived are comparable. They shall make metrics comparable with similar businesses.
Importance
Below are some of the points that highlight the importance of building an applicable financial reporting framework:
- They help in complying with the regulations laid out by supervisory bodies.
- This framework ensures consistency in financial reporting practices and helps in effective comparisons between organizations.
- Following a financial framework helps stakeholders make better investment choices and credit decisions by offering valuable information regarding lending, investments, etc.
- It provides details that help assess cash flows.
- Companies that follow a financial framework find it easier to attract investment capital by making their financial information credible and reliable.
- Financial frameworks also help organizations comply with legal requirements and regulatory standards, minimizing the risk of non-compliance penalties.
- It provides details on the business's claims and resources. The net flow information gives an insight into the company's economic resources and claims applicable to its liabilities.

