Table of Contents
What Are Financial Regulators?
Financial regulators are government agencies that regulate and oversee the functioning of the financial markets and the institutions involved in them. They monitor the health of the country's financial system, which is vital for its economic well-being.
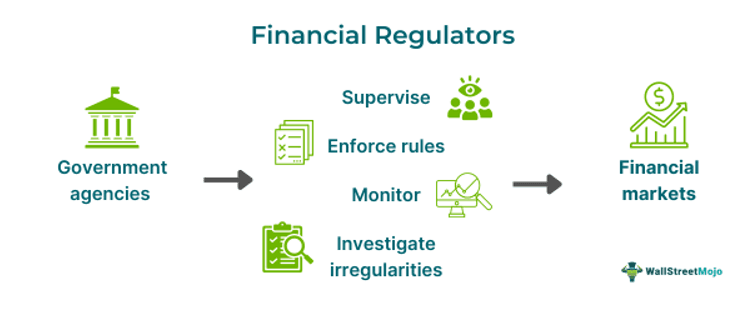
A well-functioning financial system is essential for the growth and development of a nation. These agencies enforce rules, monitor the institutions, and carry out investigations. The regulators frame policies with the primary goal of consumer protection, promotion of financial stability, and enhancing transparency within the financial sector.
Key Takeaways
- Financial regulators are government agencies that fulfill regulatory overseeing duties. They ensure market integrity, transparency, and stability.
- Various types of financial regulators oversee insurance, securities markets, banking services, and other sectors. Each country has its own regulatory bodies responsible for these areas.
- The role of financial regulators is important in an economy. Their functions include supervision, law enforcement, monitoring, and investigation regarding matters of financial markets.
- They are important as they promote fair competition, ensure stability, protect consumers, and support economic growth.
Financial Regulators Explained
Financial regulators are government agencies entrusted with the responsibility of regulating the financial markets and associated institutions. They ensure market transparency and fair practices while protecting consumers to maintain system stability. These agencies perform various functions, including supervision, law enforcement, monitoring, and investigations, to uphold the integrity of the financial system.
Moreover, these agencies supervise a country’s financial institutions, including banks, insurance companies, and credit unions. This ensures that the intuitions comply with the laws, rules, and regulations. They enforce laws and regulations, particularly regarding the functioning of institutions, fair practices, and the treatment of consumers. In addition, these agencies monitor the markets to detect abnormalities and promptly address any potential risks to prevent economic collapses. They conduct investigations on any mismanagement or violations of the laws and rules.
The types of financial regulators vary across countries, each governed by its own set of rules and regulations. In the U.S., the Federal Reserve oversees banks, while in the EU, the European Central Bank regulates the Eurozone, and in the UK, the Bank of England performs similar oversight. Regulators in the insurance field include the U.S.'s National Association of Insurance Commissioners and the U.K.'s Prudential Regulation Authority. There are different authorities for supervisory functions, such as the Comptroller of the Currency for the U.S. and the European banking authority in the U.K.
The Hargreaves Lansdown provides access to a range of investment products and services for UK investors.
Top Regulatory Agencies
The list of top US financial regulators includes:
#1 - The Federal Reserve System
The Federal Reserve System is the central bank of the U.S. established to provide a safe and stable financial system. It carries out the nation's monetary policies, rules, and regulations to improve the economy. This includes increasing employment opportunities and maintaining prices and interest rates.
#2 - Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation
The U.S. Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) is an independent government agency established to instill and maintain public confidence in the stability of the financial system. It insures deposits, supervises financial institutions, manages receiverships, and collaborates with large, complex financial institutions to enhance their resolvability.
#3 - The Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC)
The OCC is established to regulate federal savings associations and national banks. Its goal is to provide fair access to existing financial services and fair treatment for consumers. Additionally, the FDIC regulates charters and issues licenses for banks based on their activities and organizational structure, among other criteria.
#4 - The Securities and Exchange Commission
The Securities and Exchange Commission, or SEC, is the agency that regulates capital or securities markets. It aims to maintain fair, efficient markets that are orderly to protect investors and facilitate capital formation. The SEC also works hard to prevent market manipulation and protect consumers.
#5 - Other institutions
Important agencies such as the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau or the CFPB and the Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council are part of the supervisory system. U.S. financial regulators such as the Department of Justice, Financial Crimes Enforcement Network, and Federal Trade Commission also contribute to market functioning.
Examples
Let us look into some examples to understand the concept better.
Example #1
Let's imagine a scenario where a country called XYZ is experiencing bleeding stock markets. It realizes that the primary reason for the downfall was a large institution's illegal acquisition of inside information. The institution had access to information that wasn't otherwise available to others and had sold the shares before a key merger. The government, to regulate the market, has initiated action against such unfair practices through its financial market regulatory body.
Example #2
The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) regulates the U.S. securities market and recently charged Wayzata Investment Partners LLC. for a violation. The SEC had a pay-to-play regulatory rule for investment advisors that was violated. The firm had provided investment advice for compensation from a government entity. The SEC prohibits compensatory advisory services through pooled investment vehicles or directly to a government client. This restriction applies for two years following a campaign contribution made by the firm.
Importance
The importance and the role of financial regulators in an economy are given as follows:
#1 - Financial stability
Regulators monitor the country's financial system and identify and mitigate potential risks. They seek ways to prevent financial crises. The policies and rules are framed to build resistance in economic situations.
#2 - Promotes transparency and market integrity
The regulators implement regulations to prevent market manipulation, consumer exploitation, and unfair market practices. They also provide a level playing field and promote market efficiency.
#3 - Consumer and investor protection
Consumers and investors are active participants in the financial system, and protecting them becomes crucial for its health. Unfair practices can discourage them and slow economic growth.
#4 - Combating crimes
Regulatory bodies are established to combat crimes, especially financial crimes. These include money laundering, fraud, and illegally financed activities.
#5 - Promotes healthy competition
When the financial system operates transparently and protects consumers, it fosters healthy competition in the markets. This encourages innovation, which leads to the development of more technological advancements, products, and services.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.

