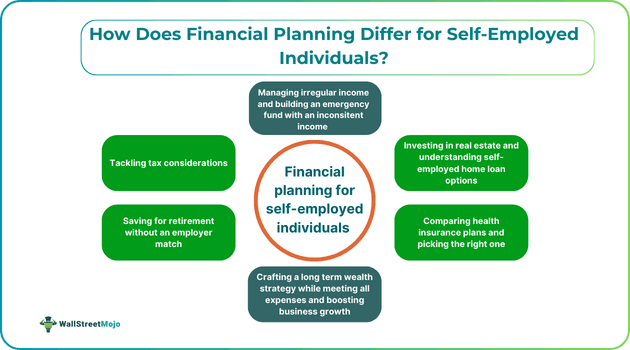
How Does Financial Planning Differ for Self-Employed Individuals?
Table of Contents
Introduction
Financial planning is a crucial topic and is mandatory for everyone. After all, losing control of your money can harm you at any age, and it takes a long time and courage to cover a loss. Financial planning is such an element of people’s lives that from the moment an individual starts going to college, they have to focus on it, managing their pocket money effectively to meet different expenses.
It becomes even more important from the moment individuals start earning from their first job and remains crucial till they finally retire. That said, in this article, we are not going to discuss financial planning for salaried employees. Instead, we are going to focus on self-employed individuals.
Let’s understand what it really means. The United States Internal Revenue Service (IRS) defines a self-employed individual who works as a sole proprietor or an independent contractor. If you are running your own business or are a partner with two or more people in business or trade, you are a self-employed individual. If you are a freelancer who works for a single employer or multiple clients, you still are considered a self-employed individual because they do not pay you as their on-roll employee. In a nutshell, when you are working for yourself and not for a company or an official employer with a legal job contract, you are a self-employed individual.
Now, because these individuals are not salaried employees, they have a totally different perspective with regard to earning and lifestyle. Hence, their financial planning also differs from salaried employees. Today, in this article, we are going to discuss in detail how financial planning for self-employed individuals differs from financial planning for salaried individuals.
How Does Financial Planning Differ For Self-Employed?
Here are some key pointers on how financial planning for a self-employed individual differs from other salaried employees:
#1 - Managing Irregular Income
When you are a salaried employee, you know your monthly income; you know how much will get credited to your bank account every month. This way, you get to plan your savings, investments, and other financial goals, but for a self-employed individual, there is no consistency in the income earned. There can be days with only one project and small earnings, and other days, there can be multiple clients, and substantial funds can flow right into their bank accounts. This highlights the key issue of not being able to know how much money they will be making, which, in turn, leads to less scope in retirement planning for freelancers. This is because they have no idea how much they are going to save, invest, or spend.
#2 - Tackling Tax Considerations
For salaried employees, most of the tax paperwork and documentation are already prepared and offered by their employers, such as salary slips, Form 16, and so on. This is where a sole proprietor or a freelancer struggles while filing their tax returns or producing any particular paperwork related to their taxation concerns and other legal procedures.
Additionally, there are comparatively fewer self-employed home loan options, which also tells us that if self-employed individuals are looking to buy a home as part of their financial planning, they may encounter some difficulties during the loan application process.
#3 - Investing In Real Estate And Understanding Self-Employed Home Loan Options
Banks like to give loans to assured clients and borrowers with stable incomes and good credit scores. Since a self-employed individual may lack a stable income, it becomes difficult to convince the banking personnel to sanction the loan amount. Additionally, it is often seen that self-employed individuals have trouble producing all the important documents, such as income tax returns, income proof, and business information, which makes it even more difficult when it comes to real estate investing. Even if banks are ready to lend a self-employed individual a home loan, the interest rate is higher because of the risk borne by them.
#4 - Saving for Retirement Without an Employer Match
Many workplaces’ retirement plans directly benefit a salaried employee because their employer matches their contribution and adds the same amount to their retirement fund. A simple example of this would be a 401(k). This means that the employer is also making a financial effort to shape their employees’ retirement, but again, a self-employed individual does not have this luxury. They have to build their retirement corpus on their own.
#5 - Health Insurance Planning
Health insurance planning for a sole proprietor or freelancer is also pretty much different from a salaried employee. We all know that almost all companies tend to offer medical insurance to their employees, along with other benefits to their workers. This facility is not available for self-employed individuals, which again makes financial planning for self-employed individuals tough. They have to do the entire research, compare insurance plans, and look for the most suitable policy they can choose per their income.
#6 - Building An Emergency Fund
When we are talking about financial planning for self-employed individuals, everything is interlinked with the income earned. A salaried employee can easily put aside a fixed portion of their monthly income and keep it safe as an emergency fund, but again, this is something a sole proprietor will fail to do.
While building such a fund is one of the most popular business finance tips, business owners often find it very hard to do so because of their irregular income sources. This underlines the basic problem that lies with self-employed individuals’ earnings: They cannot rely on their projects and work and, most of the time, operate without a cushion or risk tolerance.
#7 - Crafting A Long-Term Wealth Strategy
A simple example of a long-term wealth strategy is starting an SIP in mutual funds. It is the most popular investing strategy that most people tend to follow. They keep contributing a particular amount to mutual funds for the next ten to twenty years and enjoy the power of compounding.
However, again, the self-employed money management tips are different because of their irregular income and the various other expenses that they have to take care of on a daily basis. Even a small business requires daily operational capital. This indicates that it is challenging for a self-employed individual to craft a long-term wealth-creation strategy. Of course, some people earn substantial money by carrying out business, but then they have to use that money wisely to meet all expenses and boost growth. Hence, investing consistently for long-term wealth creation can be quite challenging.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, we can only tell you that financial planning for self-employed individuals often involves limited investing and saving practices. That said, with proper money management skills, you can build a plan that can help build wealth over time. Of course, your financial planning activities will definitely look very different from that of a salaried person, but who says it has to look similar? Every single individual has their own plan and vision when it comes to how they want to carve out their financial future.
Considering The CFA Instead?
When you embark on a professional journey, different milestones will come your way, and each one of them plays an important role in your career graph and learning curve. Comparing CPA vs CFA, we can easily say that CPA is a much more competitive choice, and it makes real sense to opt for CFA instead of CPA because of the requirements to fulfill. For instance, CFA demands only three exams to be passed, whereas CPA has four exams.
The CFA institute recommends 20 CPE credits each year, but when it comes to CPA, most states require an average of 40 credit points per year. With all these factors, you might find pursuing a CFA is a better decision instead of a CPA. That said, if you have the financial analyst certification and can accumulate the time, skills, and knowledge and qualify for the CPA criteria, you should definitely consider going for CPA. With this thought, we leave with our best wishes for your academic and professional career growth.