Table of Contents
What Is Financial Exposure?
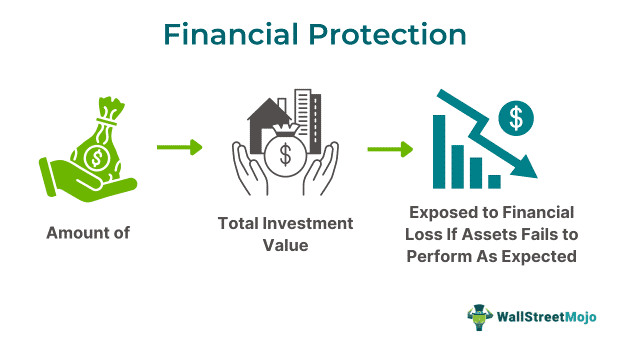
Financial exposure refers to the percentage or amount of invested funds that is at stake if the investment loses value or asset prices fall. Thus, it gauges the potential investment risk of a security or asset, which is crucial for devising appropriate risk mitigation strategies.
Even banks are exposed to potential uncertainties involved in personal loans, unsecured loans, business loans, foreign exchange fluctuations, devaluation, and revaluation. Nevertheless, investors emphasize analyzing and minimizing the financial exposure of their portfolio, which comprises stocks, bonds, derivatives, and other assets, to ensure maximum returns, proper capital allocation, and wealth preservation over the period.
Key Takeaways
- Financial exposure is the portion of investment value that is vulnerable to absolute financial loss if the investment moves negatively.
- Investors or institutions often make efforts to minimize their exposure to financial uncertainties to derive maximum returns, preserve their capital, and ensure proper asset allocation.
- The different types of exposure in finance are currency, interest rate, market, credit, and country exposures.
- Some of the proven strategies adopted by financial institutions, investors, and other organizations to reduce their financial exposure are diversification, hedging, portfolio optimization, and insurance.
Financial Exposure Explained
Financial exposure refers to the sum of the overall investment amount that the investor tends to lose if the assets don't perform in the desired manner. Investors and portfolio managers often seek to curtail the investment's exposure to financial risk. Tracking such risk is essential for ensuring that the investor doesn't lose all or most of their capital, properly allocating the funds across different investment options with varying risk-return potential, and making informed investment decisions for wealth maximization.
Moving forward, let us have a glance at the different trigger points of such an exposure in the financial markets:
- The primary factors are international economic conditions, including Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth rates, monetary policy decisions, inflation, and the geopolitical scenario.
- The other is market volatility, i.e., interest rate changes, asset price movements, economic conditions, and so on.
- Next are the legal and regulatory compliance requirements, standards, and frameworks.
- Lastly, the changes in industry trends, competitive scenarios, and market conditions also contribute to such risk exposures.
However, investors must know the various limitations of analyzing such exposures. The foremost concern is finding reliable, timely, complete, and accurate information on asset performance in a dynamic financial market. However, artificial intelligence and technological advancements have made access to such information easy. Further, understanding complex arrangements of financial instruments requires expertise.
Types
The investors, including retail and institutional investors, are exposed to different kinds of potential risk in finance as discussed below:
- Credit Exposure: Banks, bondholders, debt security investors, and other lenders are susceptible to default or non-payment risk when the borrower fails to reimburse the loan for any reason. Such risk can be mitigated through the analysis of the borrower's creditworthiness and collateral quality.
- Market Exposure: Stock market investors and traders often encounter uncertainties and potential loss of asset value due to market volatility. Some of these factors include asset price fluctuation, interest rate changes, economic conditions, and market movements.
- Interest Rate Exposure: These are the vulnerabilities that arise from changes in interest rates of fixed-income securities like bonds. They can impact the borrowing cost, debt-servicing cost, and overall returns of these assets. Financial institutions, loan providers, and bondholders usually face such risk.
- Currency Exposure is the potential risk faced by foreign exchange investors, international traders, or other players engaged in any type of financial activity that involves foreign currencies due to fluctuations in exchange rates. Such an exposure can affect the revenues, expenses, assets, and liabilities of these parties.
- Country or Sovereign Exposure: Such risk is generally present when trade or investment is made in other nations. It involves the uncertainties associated with the change in economic conditions, government policies, political conditions, legal and regulatory environment, and other sovereign factors prevailing in the respective country.
Examples
To have a comprehensive understanding, let us go through the following examples:
Example #1
Suppose a high net-worth investor, Clinch, has invested $10 million in different asset classes. His portfolio manager, Clara, has diversified the funds across different domestic and international assets and ensures regular portfolio optimization to reduce the overall financial exposure risk of the investments. She makes sure that the net financial exposure of the portfolio is limited to 30% without compromising the investment returns. She has included a mix of different mutual funds, equities, real estate, bonds, ETFs, commodities, and other assets for proper diversification of the invested money.
One of these adjustments was made when $50,000 was invested in small-cap stocks that offered a 100% return over a period of 5 years. Clara sold half of these stocks to recover the initial investment value and reinvested the amount in new potential small-cap stocks.
Example #2
As per an article published on November 22, 2023, the U.S. dollar weakened due to falling interest rates and increased speculation about potential Federal Reserve rate cuts. However, the Japanese yen bucked this trend, hitting a 33-year low against the dollar even after the usual greenback decline. The reason for this downfall was the Bank of Japan's decision to stick with ultra-low interest rates, although inflation had surged to the highest level over the decades.
As a result, the Invesco CurrencyShares Japanese Yen Trust (FXY) showed a 12% fall in 2023, though it secured investments worth $76 million. Further, the weakening of the yen influenced the Japanese equity ETFs, such as the iShares MSCI Japan ETF (EWJ), which was up 13.8% but couldn't match the 30% gain of the MSCI Japan Index in yen. Hence, it is an example of how the yen's weakening has eroded nearly half of EWJ's gains for U.S. investors.
Nevertheless, currency-hedged ETFs have performed better in this scenario. The iShares Currency Hedged MSCI Japan ETF (HEWJ) is up by approximately 34%, and the WisdomTree Japan Hedged Equity ETF (DXJ) has shown a surge of nearly 40%. Generally, currency-hedged ETFs perform well when the dollar is strong and underperform when the dollar weakens.
How To Reduce?
Retail and institutional investors should constantly monitor their financial exposure risk to make sensible strategic decisions for its mitigation. Given below are some of the effective strategies for limiting such exposure in finance:
- Diversification: One of the best ways to decrease potential risk is to allocate funds across different asset classes, markets, and investment products with diverse risk and return profiles. A well-diversified portfolio contains a balanced mix of real estate, equities, bonds, and other assets.
- Hedging: Organizations, investors, and traders often use hedging through options and futures to reduce their exposure to fluctuations in currency exchange rates, commodity prices, stock prices, etc., for instance, using exchange-traded funds or derivatives.
- Portfolio Optimization: One method is to adjust the investment portfolio based on the risk tolerance level, asset allocation strategy, and return expectations.
- Insurance: It is an arrangement that allows businesses, institutions, and investors to transfer or share their investment or other risks with insurance providers to obtain financial security against the underlying potential losses involved in such assets.
