Table Of Contents
Financial Crisis Meaning
A financial crisis or economic crisis refers to the sudden loss in the value of numerous monetary assets like realty and stocks. It causes a loss in the paper wealth but does not essentially bring major economic modifications. Moreover, its prominent instances are the great depression in 1929 and the global financial crisis of 2008.
It also entails the indebtedness of firms and customers, along with financial institutions encountering cash deficit problems. Additionally, the financial crisis inquiry commission is formed to investigate the causes of the latest economic crisis in the US.
Key Takeaways
- A financial crisis infers a dramatic disruption in the financial market mostly connected with liquidation between defaulters and brokers and plummeting asset values.
- An inquiry commission is developed to scrutinize the global and domestic reasons for any economic crisis in the US.
- Its timeline follows the credit crisis (1772), the great depression (1929), the OPEC price shock (1973), the Asian crisis (1997), and the global economic crisis (2008).
- The economic crisis causes include liquidity, leverage, and subsidies and taxes.
Financial Crisis Explained
The financial crisis is tough to forecast because it can be triggered by a comparatively minor event or sequence of little events and thus an inquiry commission is developed for the same. Generally, distinct economic crises have different natures and degrees of seriousness but are accompanied by common conditions such as extensive credit squeezes.
It rarely occurs but with relative consistency, often leading to a critical period of complete economic downturn. Usually, an economic contraction succeeding the crisis decreases the country’s gross domestic product (GDP) more than only a recession. Although it induces great losses for investors, the economic crisis also forces regulatory authorities to introduce methods for market efficiency. The collateralized debt obligations and poor lending standards are among its major causes. Moreover, the financial crisis inquiry commission assists ordinary citizens in comprehending the economic crisis and its reasons.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
Financial Crisis Timeline
To clarify, let’s go through the economic crisis timeline:
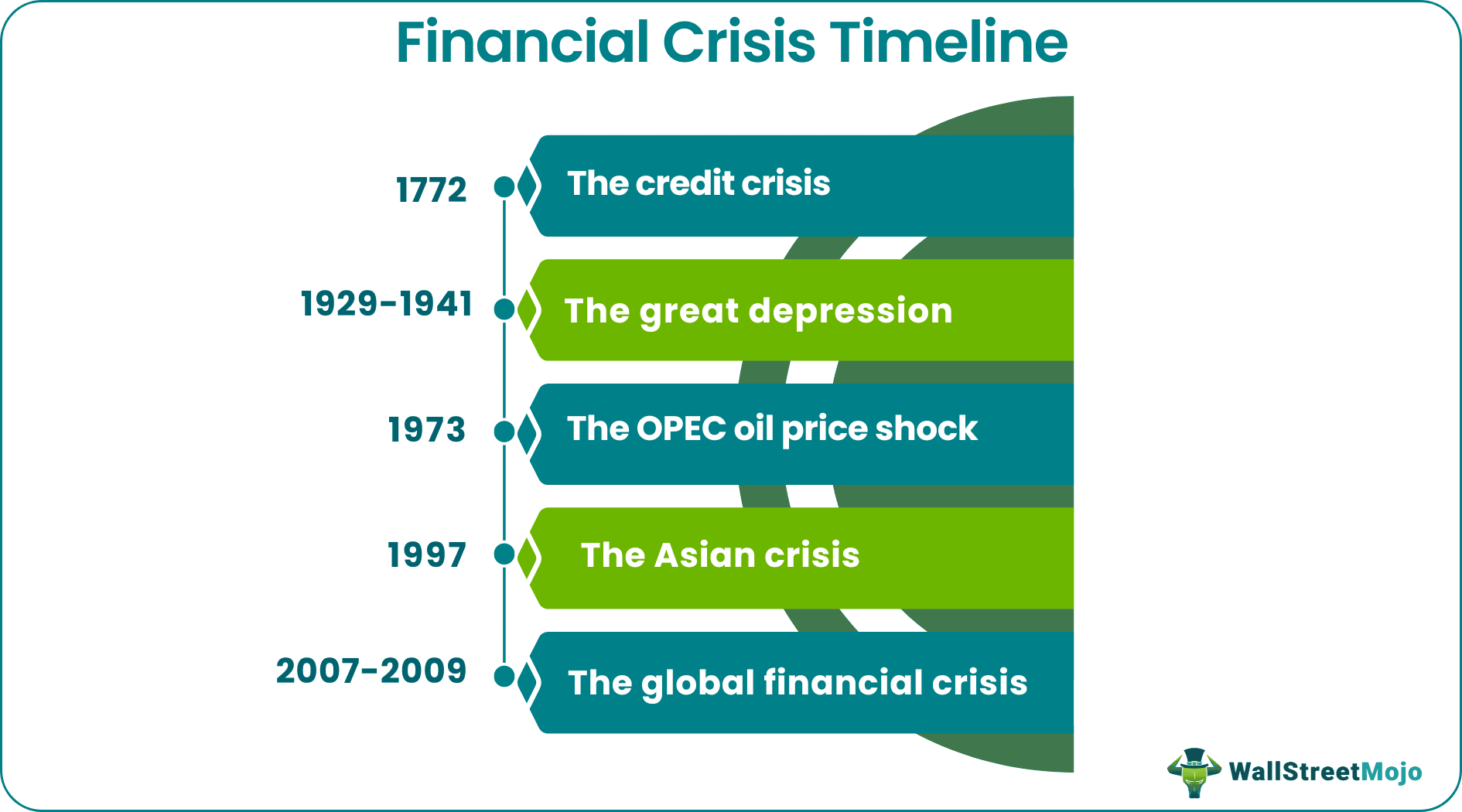
1. 1772: The Credit Crisis
Originating in London, the economic crisis instantly expanded to the remaining parts of Europe. One of the British banking house partners escaped to France to avoid the debt settlement on 8 June 1772. So, creditors began demanding immediate cash withdrawals, allegedly leading to bank runs and Boston Tea Party protests.
2. 1929-1941: The Great Depression
This was the deepest and longest crisis in the history of the US, lasting over a decade (ended in 1941). Subsequently, industrial production and marriage rates decreased, unemployment surged, and the downturn spread worldwide. Contrary to popular belief, some US Federal policies damaged the economy, resulting in this severe downturn.
3. 1973: The Organization of The Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) Oil Price Shock
The organization of Arab petroleum exporting countries (OAPEC) imposed an oil embargo on the US as a penalty for supporting Israel. In January 1974, this prevented US oil imports from partaking in OAPEC countries and almost quadrupled the rates from $2.90 to $11.65 (per barrel). It stayed the same even after the embargo was formally lifted.
4. 1997: The Asian Crisis
On 2 July 1997, Thailand experienced currency devaluation corresponding to the US dollar. Thus, Thailand’s equity, property markets, and currency weakened, wreaking havoc through East Asia. The Philippines, Indonesia, and Malaysia also underwent a currency crisis, with Indonesia facing an extremely dramatic political and economic crisis.
5. 2007-2009: The Global Financial Crisis
It implicates the duration of absolute distress in international banking systems and financial markets between 2007 and 2009. A contraction in the US housing industry accelerated the global financial crisis spreading from the US to other geographical locations. Resultantly, US house rates decreased, and mortgagors missed reimbursements.
Examples
For better understanding, here are a few examples.
Example #1
Some critical economic crises include,
- The credit crisis (1772)
- The great depression (1929-1941)
- The OPEC oil shock (October 1973-January 1974)
- The Asian financial crisis (July 1997-December 1998)
- The great financial crisis (December 2007-June, 2009)
Example #2
Contrary to the administration’s belief, Russia may encounter a financial crisis in the not-so-distant future. The headline inflationary trend is the highest in 20 years (since 2002). The month-by-month consumer price expansion has also decreased extensively by 6% from March (7.6%) to April (1.6%).
According to the statistics reported on 17 May 2022, the ruble registered an all-time reduction of 150 on March 7, trading at only over 62 to the dollar. However, economic indicators have considerably improved, and the country has managed to avert defaulting on the global currency debt, by now.
Financial Crisis Causes
That is to say, here are the major causes of a financial crisis:
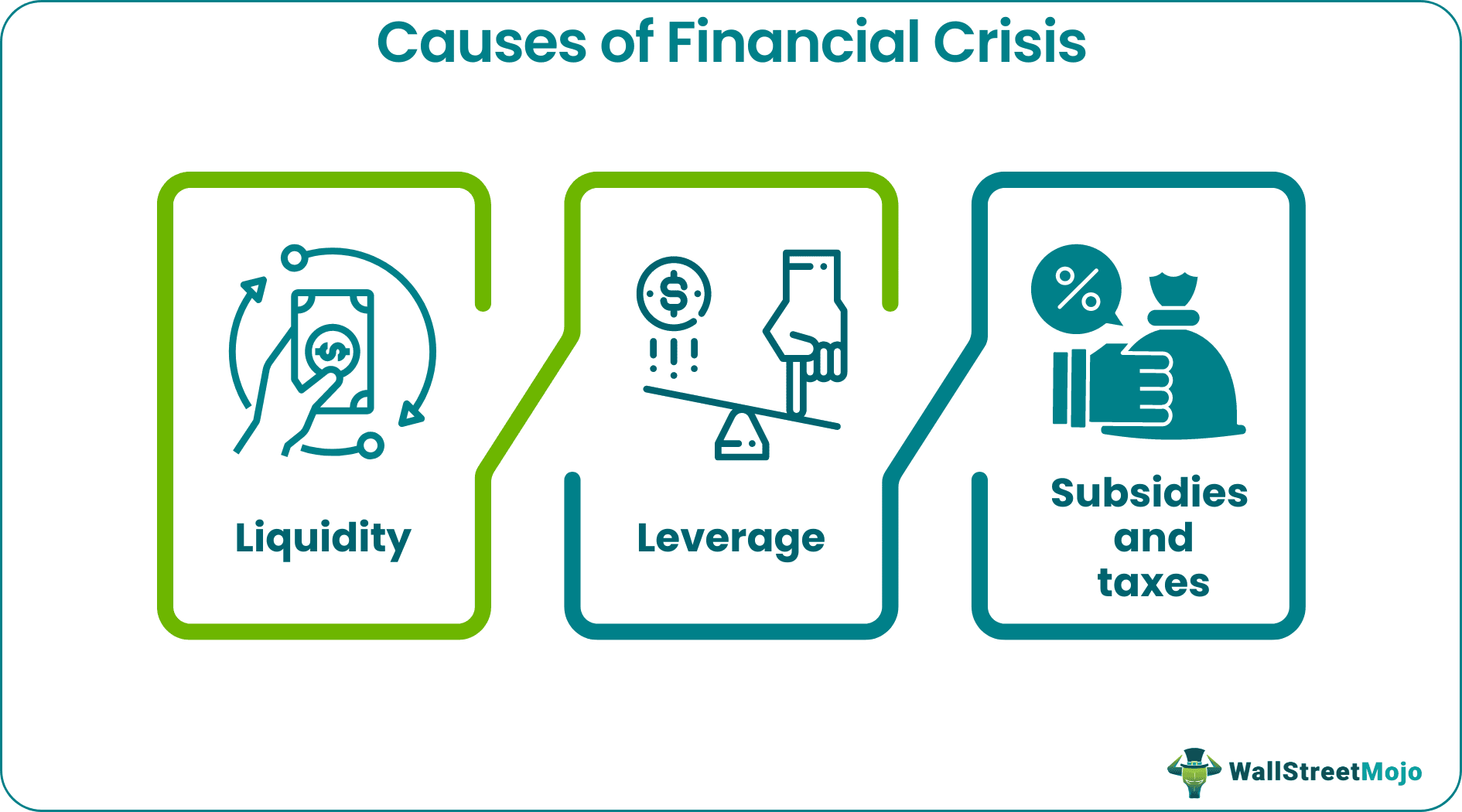
1. Liquidity
Liquidity mismatches are among the crucial reasons behind downturns like the financial crisis in 2008. Through accounting gimmicks, misinterpretation among investors regarding their actual liquidity position brings about such economic contractions.
2. Leverage
Extra leverage certainly triggers an economic crisis as hazardous hidden leverage is instituted in the structured securities. It does not have any transparent accounting, and hence, its limitation is difficult and beyond the capacity of regulators and the expertise of legislators.
3. Subsidies And Taxes
Though covered by legislators, short-term speculation and the advantageous taxation of carried interest is ridiculous. Therefore, taxes like financial transaction tax are required to sustain system resiliency and facilitate actual long-term investment.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A financial crisis denotes specifically extreme disturbance in the economic system causing price or value decrement in financial assets and bankruptcy. Moreover, the famous examples of financial crises include the credit crisis, the great depression, the OPEC oil shock, and the great financial crisis.
The depletion of US house rates culminating in 2006-2007 was the major catalyst to the global financial crisis in 2008. Resultantly, borrowers missed debt repayments causing unrest in the fiscal system in both the US and other nations. In addition, the monetary failure of the American financial company Lehman Brothers brought panic to financial markets.
Currently, Sri Lanka faces a severe financial crisis with an extreme shortage of necessities like medicines, food, water, and electricity. If not handled properly, this crisis may expand to other countries and result in economic collapse. That is why the government must capitalize on the available resources, and other nations must also offer financial assistance to Sri Lanka.

