Table Of Contents
Finance Lease Definition
Finance lease refers to the lease where the finance company legally owns the asset during the lease's tenure. Still, all the risk and reward associated with the asset are transferred to the lessee by the lessor and at the end of the lease term the lessee also gets the ownership of the asset.
In the process, the leasing company buys the asset and offers another party the right to use it for an agreed period. A finance lease (also called a capital lease) substantially transfers all the risks and rewards of asset ownership to the lessee. It is often used to buy leased assets for a major part of its economic life.
How Does A Finance Lease Work?
Finance lease is an appropriate mode of finance for those who cannot raise funds through debt. The finance lease grants the right to use the asset. A company must carefully decide whether it wants to enter finance lease agreements after considering them. This is all the more important as a finance lease involves a substantial transfer of risks to the lessee along with the rewards that they are subject to receive during the lease period. Generally, firms in a higher tax bracket would like to classify leases as finance.
After every period when the lease payment is made, there is a reduction in the balance payment to be made as given in the amortization schedule. As the finance lease is a long-term financial involvement, itimpacts the lessee’s financial statements. They influence assets, liabilities, interest, and depreciation.
Leasing parties are calculative when deciding on the charges that other party must pay for the asset. A finance lease can either be fully amortized or follow regular rental payments based on the balloon rental procedure. However, whichever be the case, the amount must meet the worth of the property.
As a result, when thoroughly amortized, the value of the property is written off to zero after the hire period. On the other hand, when rents are paid until the lease period is over, the total amount paid must meet the expected value of the asset over that period.
When the lease agreement is prepared, it includes the names of the parties involved identified as a lessor and lessee, the details of the leased property, the total price of the asset and its economic life, the rate of interest applicable along with the payment plan, and penalties that may apply in certain situations.
Criteria
The basic criteria to classify a finance lease (also known as a capital lease under US GAAP) is where the lessor remains the legal owner of the asset throughout the lease period. Still, all the risks and rewards related to leased assets are transferred to the lessee. The, i.e., the lessee records a liability and an asset related to leasing in its balance sheets; legal ownership of leased assets transfers from the lessor to the lessee after the end of the lease.
However, there is a little contradiction under IFRS and US GAAP in classifying a lease as a finance lease.
IFRS: The above basic criteria classify a lease as a finance lease under IFRS jurisdiction.
GAAP: if the lease agreement fulfills at least one of the following four conditions, then such lease is categorized like a finance lease under US GAAP:
- The legal ownership of the leased asset transfers from the lessor to the lessee at the end of the lease;
- The lessee is allowed to purchase the leased asset at a lower price than the fair value of the leased asset.
- The lease term is more than 75% of the leased asset’s useful life.
- The present value of lease rentals is equal to or greater than the asset's fair market value.
Lease vs Rent - Explained in Video
Accounting
Let us have a look at how the journal entries for a finance lease are made:
#1 - In the Books of Lessee
- At the inception of the lease agreement, Lessee will record the fair value (present value of min lease payments) of the asset on lease at both the asset and liability sides of the balance sheet.

- Distribute the payments of periodic lease rentals (paid) into two parts
- Finance expenses or interest cost (expenses in the income statement) and
- Reduction in outstanding liability.

- Journal entry for depreciation is passed.

#2 - In the Books of Lessor
- Lessor, at the inception of lease record, lease receivable at an amount equal to net investment value in lease. The net investment value is calculated by discounting the minimum lease payments at the implicit interest rate.

- Distribute the cash received as periodic lease rentals into two parts
- Finance or interest income and
- Reduction in lease receivable.

Examples
Let us consider the following instances to understand what is finance lease and how it works:
Example 1
Suppose Mary, a baker, has set up a store where she bakes personalized cakes and pastries. Gradually her efforts get recognized and orders start being placed in bulk. As a result, she decides to have a place where she has more equipment placed for more baking. However, she is unsure if the increase in demand was a permanent one or just for some time. So, she plans to lease a plant and not purchase it.
She connects with one of her friends’ friend John, looking for a tenant for a suitable unit. They sign a agreement of one year, after which they decide to go for renewal if the change in the business leads were a permanent one.
Example 2
Jet Aviation Ltd, an Indian airline company, requires passenger planes. Jet enters into a legal lease agreement with Boeing (an American-based plane manufacturing company) to lease out airplanes. Boeing supplies planes to Jet on January 1, 2019, on a 5-year term against which Jet will pay an annual lease rental of $500,000 at the end of each year. Assume the implicit rate of interest is 10%
The useful life of the plane is six years. Jet has the option to buy the planes at the termination of the lease period.
Journalize the necessary accounting in the books of both the lessor (Boeing) and the lessee (Jet Aviation).
#1 - Examine whether lease meets finance lease criteria
- The lease is allowed to purchase the leased asset at the end of the lease period.
- The lease term is 83.33% (5/6), which is more than 75% of the leased asset’s useful life.
#. The lease satisfies most of the conditions; hence it is classified as a finance lease.
#2 - Calculation of present value (PV) of min finance lease payments
The formula of PV,
PV = P *
Given:
- annual lease rents (P) = $500,000 and
- Implicit rate of interest (i) = 10%
- Period (n) = 5 years

#3 - Calculation of Depreciation
- PV of plane = $1,895,393
- Useful life = 6 years

#4 - Accounting in the books of Boeing (Lessor)
i) Record lease receivable against the asset leased out at an amount equal to net investment value in lease.

ii) Distribute the cash received as periodic lease rentals into two parts
- Finance or interest income and
- Reduction in lease receivable.

Note: the debited value of lease receivables will reduce the principal amount of $1,895,393 by $450,000. The remaining principal value of $1,445,393 will also reduce the next year's financial income.
#5 - Accounting in the books of Jet (Lessee)
i) Record the asset's fair value on lease at both asset and liability sides of the balance sheet.

ii) Distribute the payments of periodic lease rentals (paid) into two parts
- Finance expenses or interest cost (expenses in the income statement) and
- Reduction in outstanding liability.

iii) The entry for depreciation is passed.

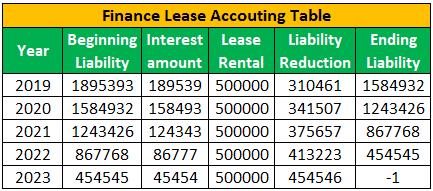
#6 - Accounting Table Calculation for Finance Lease
The table presents the calculation of the finance lease for a five years lease period. The table is helpful for the accountant to journalize the annual entry and tally the entered figures.

Advantages and Disadvantages
The process of finance leasing is advantageous to both the parties involved, i.e., the one who is leasing it and another that is accepting the asset on lease. It allows the latter to use a property against a specific charge, thereby serving the purpose it wants it for. In turn, the lease amount is paid to the actual owner that becomes their regular income. The best part is that the ownership remains in the hands of the original owner and they are the ultimate authority.
However, there are a few restrictions that one must be aware of when opting for finance leasing. Listed below are the merits and demerits of the process to help one be aware of all the aspects related to it. Let us have a quick look below:
Benefits
- A finance lease is an important source of medium and long-term financing of assets.
- Finance lease grants rights to the lessee to use an asset.
- Lease financing is generally cheaper than all other forms of financing.
- The finance lease arrangement helps spread the lease payments over several years. Hence, there is no burden of a lump-sum payment for asset purchases.
- The lessee can claim depreciation on the asset leased. This reduces the tax liability of the lessee as depreciation is an expense charged to the Profit and Loss Account.
- In general, the finance lease recognizes expenses earlier than the operating lease. Charging interest expense also gives a tax benefit.
- Lessee gets some technical assistance about the asset from the lessor.
- Even if there is a subsequent rise in the asset's price, the lessee has to pay the fixed payments originally agreed upon.
- The lessee has the right to purchase the asset at the end of the lease period, generally at a bargain price.
Limitations
- The responsibility for the maintenance of the asset lies with the lessee. Hence, the lessee has to incur some maintenance expenses.
- The financial lease involves a substantial transfer of risks to the lessee. Hence, the risks are significantly borne by the lessee.
- The finance lease is non-cancellable by the lessee. Hence, the lessee is bound by its decision.
- If the lessee decides not to purchase the asset, he will not become the asset owner.
- The lessee controls the asset even though he is not the asset owner during the finance lease. Since he is not the owner, he may not exercise due care of the asset.
- Entering into a finance lease involves a lot of documentation and other formalities.
Finance Lease vs Operating Lease
When it comes to leasing, there are two types of leases that are most common. One is finance lease and another is the operating lease. These two differ in various aspects, which one must know of to understand which is more suitable for them. Let us have a look at the difference between finance lease and operating lease below:
- While finance lease is a long-term affair, operating lease is for a shorter-term.
- The ownership of the finance lease moves to the lessee even if the asset is fully paid for. On the other hand, the ownership remains with the lessor in operating lease.
- The former has better tax advantages. Lessee here enjoy tax-deductible expenses, including depreciation and financing. On the contrary, the operating lease only offers rent deduction facility for the lessee.
- Finance lease keeps buying the leased property open for lessee, while the operating counterpart does not allow the lessee to own the property.