Table Of Contents
What Are Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG)?
Fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) are non-durable consumer goods that sell like hotcakes as they usually come with a low price and high usability. Their examples include toothpaste, ready-to-make food, soap, cookie, notebook, chocolate, etc.
These products are usually stacked up on the shelves of the supermarkets like Walmart. Less durability, high demand, and low price are some FMCG traits that enable them to be sold off quickly. A strong distribution channel plays a crucial role in the FMCG industry as it ensures that the products are delivered to the stores on time. However, an expensive supply chain will also add to the cost. As such, global brands try to find ways to source resources locally.
Key Takeaways
- Fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) are non-durable by nature. They have a huge demand and are affordable for most everyone.
- The FMCG examples include processed foods, beverages, cosmetics, toiletries, health products, consumer electronics, etc.
- Less durability, high demand, and low price are some FMCG traits that enable them to be sold off quickly from the shelves of the stores. Sometimes, they are also called consumer packaged goods or CPG, as many are packaged goods.
- Proper planning, innovation, localization, diversification, and investment are reasons behind many FMCG brands’ success. Some popular FMCG brands are Nestle, Coca-Cola, P&G. The distribution channel is an important aspect of product delivery.
How Does FMCG Work?
The FMCG sector’s popularity is far-reaching. The fast-moving consumer goods industry provides affordable solutions to everyday problems, from packaged daily necessities that can be easily grabbed from a store to ready-to-make food. For example, hostel students prefer packaged food like instant noodles as it does not require elaborate cooking. In addition, packaged food helps individuals who live alone and cannot arrange home-cooked meals. Likewise, the fast-moving consumer goods companies industry has been helping consumers by providing medicines, masks, cosmetics, personal care, and hygiene products.
In 2017, the value of the Global FMCG market size was $10,020.0 billion, with its 2025 growth projections being $ 15,361.8 billion. Asia is one of the largest markets for these products. Many studies have found that FMCG brands have succeeded in using innovation, localization, value-oriented products, better customer targeting, and product diversification.
For example, this Mckinsey study explains how Wrigley chewing gum quickly became a fast-growing product in China, acquiring over $2 billion using products designed especially for Chinese consumers. It further explains how FMCG giant Nestle reduced prices by 30% in its ready-to-drink coffee segment in China to provide more value-oriented products.
For example, Nestle offered discounted coffee in China by saving on the cost of using a local supply base in Yunnan. Consequently, its sourcing became 99 % Chinese.
Moreover, the distribution model is divided into two parts, one part is direct, and another part is indirect. In the direct state, the transaction occurs between the manufacturers and clients without the interference of the third party. In the indirect state, the manufacturers sell the product through a distribution channel to their clients.
Characteristics
Here are some characteristics that differentiate them from other types of consumer goods. Let us study them in details.
- They are always in high demand and consumers frequently purchase them. So the retailers or sellers need to keep a good stock of such goods.
- Due to high demand, they have high sales and are a good source of revenue.
- The prices of these goods are relatively low as compared to any other type of goods. Thus, consumers can easily afford them.
- They have a short shelf life, meaning the sellers cannot keep them in stock for many days because they lose their freshness or get spoilt.
- The fast-moving consumer goods companies have a huge customer base. Almost all the people of a place will buy such products since most of them are of daily use and are important in our day to day living.
- This category of products have a tendency to create brand loyalty. People who buy a particular brand of a product will prefer to stick to that brand every time they purchase that product. So they need a lot of advertising and product differentiation continuously.
- They are available through a variety of channels like small and big shops, supermarkets, online retailers, etc.
- People often prefer to stock them up so that they are available when needed, even if the consumer is not able to purchase them immediately. Thus, this triggers impulse buying.
- Many of them experience a seasonal demand which may lead to fluctuations in the inventory turnover.
- Since they are in high demand, the distribution needs a very good and strong supply chain system and robust distribution system.
- Branding and packaging plays an important role in this industry. The fast-moving consumer goods brands helps in differentiating the products and thereby influence consumer choices. Attractive and useful packaging can catch consumer’s attention.
Thus, depending on the above characteristics, the producers and the retailers fix prices so that they are able to earn maximum revenue as well as concentrate on expanding the customer base.
List Of Fast Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG)
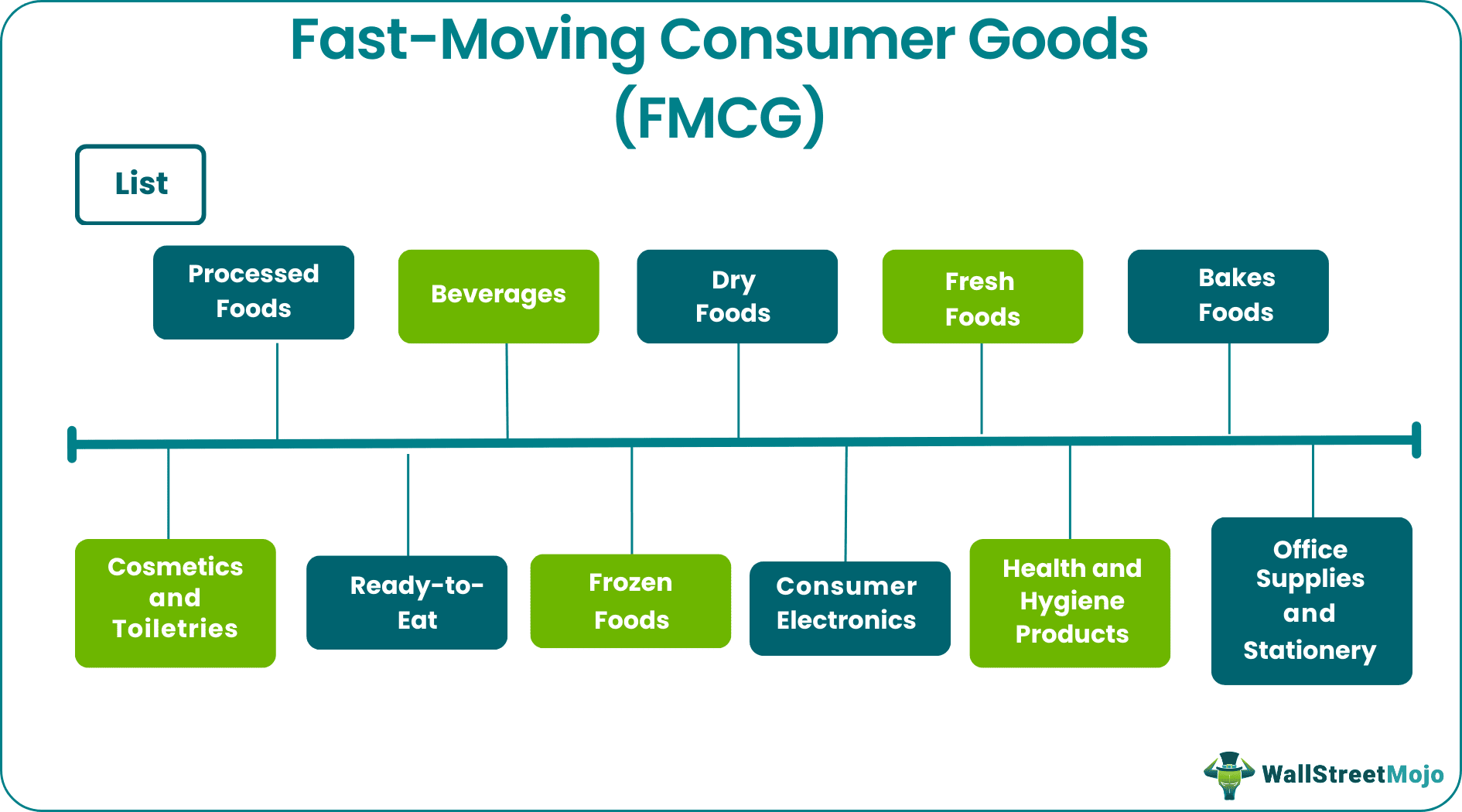
The fast-moving consumer goods are bought on a need basis and sold frequently. Therefore, the classification of the FMCG industry is done primarily by product type. Some of the types are listed below.
#1 - Processed Foods
They come in a package. Some serve as a cooking ingredient; some are ready-to-eat food, while some have nutritional value. For example, tinned vegetables, cereals, flavored yogurt, cheese, tofu, canned beans, etc. Almost all kinds of food are processed. Some of them contain artificial flavors and preservatives to increase their shelf life.
Almost all kinds of food undergo some form of processing. For example, even a can of fresh diced tomatoes undergoes cleaning, dicing, and packaging. Also, sometimes vitamins are added to dairy products to boost their nutritional levels.
#2 - Beverages
This category includes fruit juice, drinking water, cold drink, shake, and soft drink. For example, you grab a can of packaged orange juice on your way to work.
#3 - Dry Foods
Examples of dry foods are sugar, powdered milk, tea, rice, flour, etc. Had they not been available as packaged food, people would have had to head to a factory or a farmer’s cottage to purchase a bag of rice.
#4 - Fresh Foods
Fruits and vegetables are examples of fresh foods, but they are perishable by nature, making them less durable.
#5 - Bakes Foods
Different types of cookies, biscuits, packaged cakes, doughnuts, muffins, etc., come under this category. The fast-moving consumer goods companies keep coming up with innovative varieties of baked goods to entice customers. However, the products also come with a shelf life, and if they are not consumed by then, they become unfit for consumption.
#6 - Cosmetics and Toiletries
This category includes different skin moisturizers, facial makeup, hair colors, beautifying products, deodorants, etc. Examples of toiletries include soap, toothpaste, razors, shaving creams, etc.
#7 - Ready-to-Eat
They are ready to eat food and need to be consumed immediately. Examples include snacks, noodles, soups, etc.
#8 - Frozen Foods
Ice creams, sausages, etc., belong to this category.
#9 - Consumer Electronics
Electronic equipment is typically used in everyday life. Examples of this category include memory cards, headphones, laptops, etc.
#10 - Health and Hygiene Products
This includes different medicines, surgical masks, hospital gowns, tampons, etc.
#11 - Office Supplies and Stationery
They are the items that are regularly used for performing office work. The list of items includes a stapler, eraser, marker, highlighter, fountain, pen, sticky notes, folder, etc.
Examples
Let’s focus on some leading companies and fast-moving consumer goods brands:-
#1 - Procter and Gamble (P&G)
In 1837, William Procter and James Gamble founded the company in Cincinnati, Ohio. It is one of the giant multinational consumer goods companies. They sell different beauty, personal care, health products, etc. P&G’s market cap is $326.64 billion. The brand is present in approximately 180 countries and territories.
#2 - Nestle SA
The Swiss company was founded in 1866 in Switzerland. It has its presence in almost 190 countries. It has a market cap of over $304.1 billion. Nestle boasts different product lines such as beverages, coffee, cereals, snacks, baby food, dairy, chocolates, pet food, food service, etc. Fast-moving consumer goods saw major profit during the frenzy food stocking phase of the Covid-19 lockdown, with Nestle outperforming many competitors.
#3 - PepsiCo
The popular company was founded in 1965 in the United States, and it has its presence in many countries. The wide range of foods and beverages is appreciated by many. The market cap of the brand is $199.18 billion. Post pandemic, the company also saw massive profit with the increased buying of packaged foods.
Many channels were disrupted, leading to losses in the aftermath of the pandemic. At the same time, the companies had to buckle up to meet the increased demands of consumer goods due to panic buying. Another challenge for the FMCG industry has been the changing consumer preference toward healthier alternatives. Moreover, the e-commerce boom has forced companies to offer their products using online platforms. Also, more and more consumers are turning price-sensitive. All these challenges have hurdled the growth of the sector.
Objectives
These kinds of products have the objectives that will help them succeed in gaining market share and retaining them, resulting in huge sale and revenue.
- The main objective is to boost revenue and sales. This will ensure profitability and help them to expand their product range and reach out to a broader market.
- Another important objective is to make the consumer know the existence of a particular type of product in the market that has useful features as well as affordable. This is called brand awareness. A positive brand image is essential to remain competitive in the market.
- It is important to reach out to the maximum market with limited cost. If the production and distribution process is not cost efficient, then the goods cannot sustain for long.
- The companies selling such goods always try to expand the market through identification of consumer needs, taste and preferences. Therefore, innovation is a continuous process which brings improvement. However, it also leads to customer base expansion and satisfaction.
- The fast-moving consumer goods industry also have the responsibility of maintaining a balance in the environment through use of ecofriendly and biodegradable materials in the manufacturing process, reduce waste, carbon emission and ensure resources are utilized up to the level they are needed.
- Product differentiation and prices are also some of the objectives of fast-moving consumer goods industry. They ensure that they continue to remain a part of the market and keep the loyal customer base intact in order to increase profitability and competitive advantage.
FMCG Vs Consumer Packaged Goods (CPG)
Both the terms refer to the goods that are highly in demand in the market, but have their own featires that differentiate them from each other. Let us study the differences as given below:
- The former is a type of CPG. So they are those packaged goods that are sold very frequently and have a relatively low price. But the latter is a broader rand of products which include the former and some others which may vary in their consumption frequency and prices.
- From the above point it can be derived that the former is fast moving goods, whereas the latter is both fast and slow moving goods.
- The former needs very frequent replenishment of stock from the seller’s side whereas the latter includes goods that may or may not ned frequent replenishment.
- The former is a low product. Therefore, consumers do not take much time to decide whether they will purchase them or not. But in case of the latter, the consumers may sometimes take long time to make purchase decision because they are often priced higher.
- The former is found in any type of convenience store, supermarkets, small shops, ect, but the latter is usually found in speciality store and require a special distribution channel for better distribution.
Thus, the above points clearly explain the various differences between the two types of goods available in the market.
