Table Of Contents
What Is Fair Market Value?
Fair market value is generally taken as the price at which buyers and sellers are willing to exchange property where neither of the parties is under any obligation to buy or sell. Both have a reasonable awareness of the relevant facts and enter in their best interest without any pressure.
The fair market value (FMV) of assets is estimated to get the enterprise value of the businesses. To arrive at the same, companies must adjust the book value for inventory undervaluation, patents, goodwill, bad debts, and other necessary factors. The value in the open market also plays a role here.
Key Takeaways
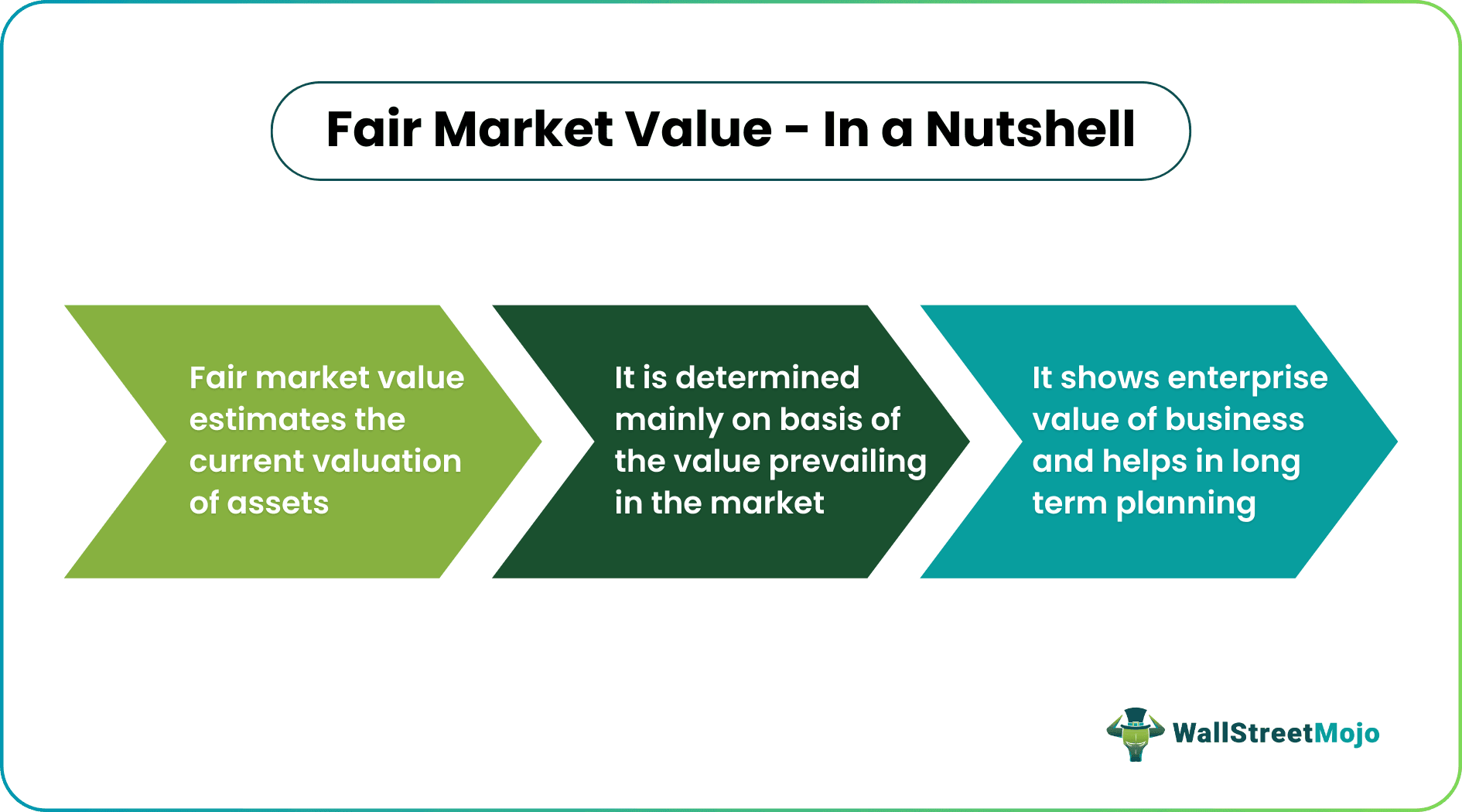
- A fair market value (FMV) is the price that a person who is fairly interested in purchasing a given asset would pay a person reasonably interested in selling it. In other words, it is the value the asset would normally fetch in the marketplace.
- The sale or purchase price of the involved items, sales of comparable properties, detailed replacement costs, and experts' opinions are all factors to be considered while determining FMV.
- The accounting of assets is estimated to get the enterprise value of the businesses. Therefore, it can help in acquisitions and mergers, and long-term planning.
Fair Market Value Explained
Fair market value is the price at which a buyer and seller exchange property when there is no obligation to purchase or sell. Here, both parties are aware of the relevant facts present. However, Arthur Anderson, an American holding company, gives a more elaborate fair market value definition. It states that FMV is the amount, price, highest price, most probable price, cash, or equivalent price at which properties would change hands or ownership might be justified by an investor, or willing buyers and sellers would exchange, would agree to exchange, have agreed to exchange, should agree to exchange, or may reasonably be expected to exchange, possibly with equity to both and both fully aware or knowing or at least basic knowledge of the relevant fact and not acting on compulsion.
Owners of companies (especially small companies) mostly possess knowledge about all facets of their business, even intricate details such as sales, marketing, personnel employed, and payroll. However, many may falter in knowing true, critical facts such as the worth of their companies when they put it on market. A business's fair market value is not just important when someone is about to sell it. They come in handy in long-term planning and taking corrective steps if necessary.
Fair Market Value - Video Explanation
Calculate Fair Market Value
The fair market value of the property and fair market value of stock determination is different from FMV calculation for business. The process is in-depth and time-consuming. The valuation grounds and premises determine the suitability of a valuation approach for establishing an asset's worth.
A valuer must examine the following major aspects when considering the appropriateness of a certain valuation strategy and method:
- The type of asset they are valuing
- Availability and reliability of adequate inputs or information;
- Thorough analysis of every valuation strategy and method's strengths and weaknesses; and
- The valuation approach/method chosen by the market participants (competitors).
Businesses should choose the valuation methodologies and procedures in such a way that they optimize the utilization of data. They can either use the income approach, asset approach, or market approach. Using only relevant observable inputs and avoiding unobservable inputs is the best approach. The pricing data gathered from an active market is a strong indicator of FMV.
Examples
Let us look at a few examples to gain a better idea of FMV.
Example #1
Ben wants to sell his house. He had bought that house in Denver for $40000 in 2000. The property belongs to a time when there were no facilities available. The housing area now has schools and hospitals nearby, and transportation facilities have also increased. More than two decades have passed, and development has surrounded the area, so it wouldn't be a smart decision to sell the house at $40000. It is essential to determine a rate. There is no readily available fair market value formula to calculate the property value. Therefore it is wise to look at the rates of similar houses in that particular neighborhood, but sometimes they may be less than the market value. The US has indices like the S&P/ Case- Shiller 20-City Composite Home Price Index, which periodically measures the value of residential real estate areas.
Denver is listed there, and Ben now can look at it and decide his sale price.
Example #2
Suppose Ben wants to sell an old vehicle or furniture. He considers factors such as desirability, utility, and scarcity here to determine the FMV. When the furniture is out of style or in poor condition, it will have little or no market value. On the other hand, if it is an antique or unique item, its value will be generally higher. He cannot determine it by the fair market value formula but only by considering a case-by-case basis.
When Fair Market Valuation is important?
Examples of other situations where fair market valuation is important are when one has to make arrangements for transferring shares to partners or their heirs through a buy-sell agreement funded by life insurance. This is so as to determine the buy-out price and support it with the necessary insurance. When the property or asset transfers to the heirs upon the death of an owner, the property's fair market value might have increased. The property acquisition may have taken time, and the purchase's market value could have increased. In such cases, the interest gathered by shares over the years may have grown, and the government shall estimate taxes and future capital gains along with the stock's fair market value.
Market comparisons are an effective technique to determine a company's critical fair market value. This is the most common method of determining the worth of a company. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) had released a revenue rule identifying certain criteria that can affect fair market value. The type of the business, the economic forecast, book value, earnings, dividends, goodwill, and recent prices paid for similar enterprises are all factors to consider while arriving at it.

