Table Of Contents
What Are External Factors?
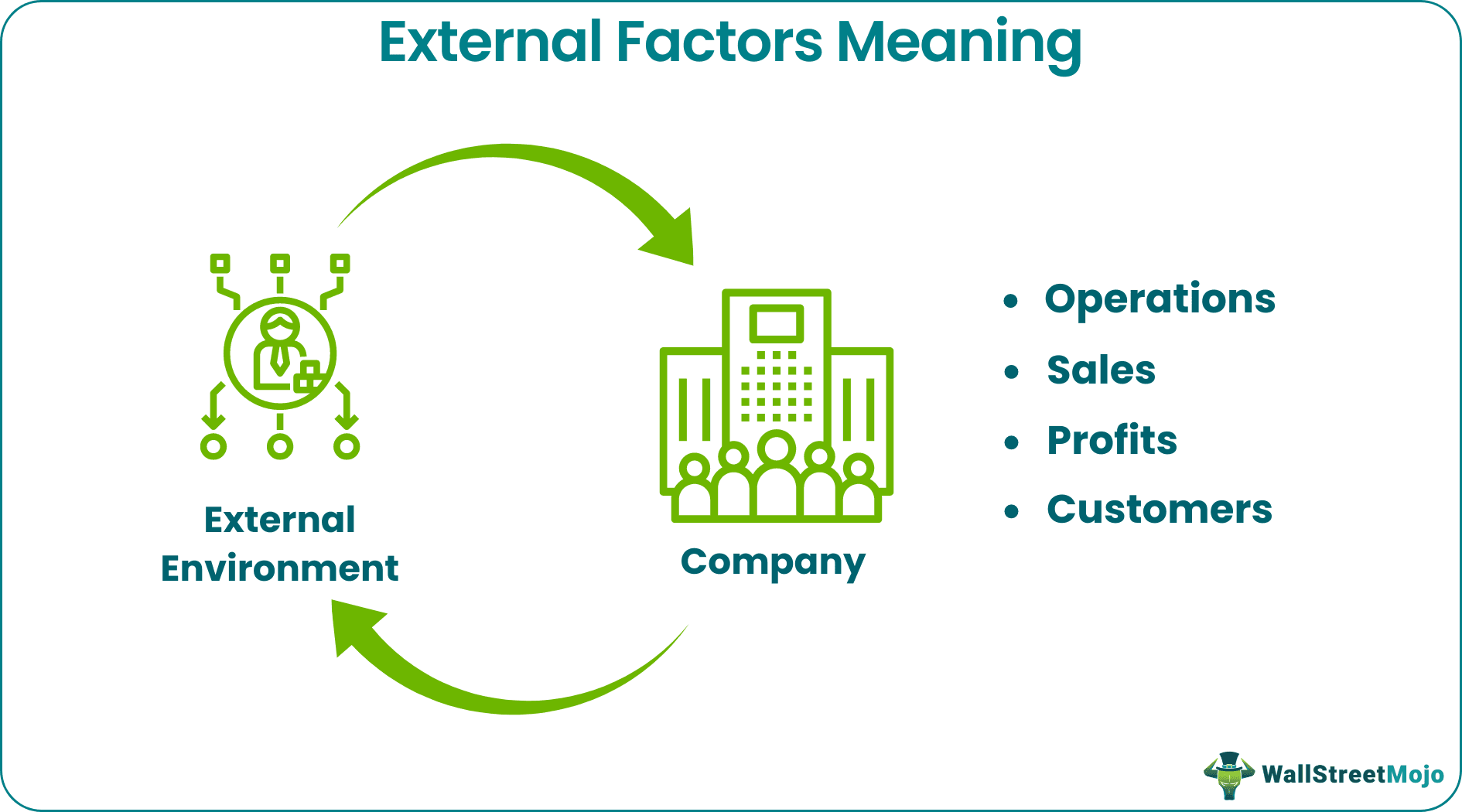
External factors of business environment refer to those factors outside the purview of the organization's control that can affect the business, its operations, profits, etc. These factors further impact the internal forces in an organization to a great extent. The effects can be positive or negative.
Though there are a wide variety of factors, some major ones include political, economic, environmental, social, technological, legal, and competitive. And, of course, sudden changes in customer preferences are another significant external factor. The best solution for businesses to deal with these factors is to manage their response.
Key Takeaways
- External factors are those forces that act from outside the organization and are out of its area of control but have an overall internal and external effect.
- If the effects of these factors are positive, the company should seek more benefits from them. On the other hand, if the effects are negative, the company should respond well to the consequences.
- In either case, a company should anticipate these situations and work well to manage them.
- External factors can be political, economic, social, technological, legal, environmental, and competitive.
External Factors In Business Explained
External factors affecting a business are a serious concern for companies. As a result, there is usually more emphasis and a higher probability of negative factors. But good or bad, a business needs to manage both. If a positive force is at play, the business should take advantage of this and develop it so that the company can benefit more from it.
If there is a negative factor, the company should be prepared for such an outcome and try to soften the blows. Negative factors can incur heavy damage to a firm, and while the company cannot avoid the consequences, it can reduce the damages or losses to a great extent.
One of the measures would be to keep track of all the possible things that could go wrong or work to a company's advantage. Major political, economic, social, and legal activities or events should be constantly watched, and when that event happens, employ the prepared plan.
Types
There is little consensus on what exactly constitutes external factors affecting a business. However, let's discuss the most common ones.
PESTLE analysis comprises the major external factors in an organization. PESTLE implies political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors.
- Political factors – With different types of governments across the globe, companies, especially multinational ones, are subject to political pressure. For example, political riots or coups in the country, unstable governance, elections, etc.
- Economic factors – This is probably one of the most important forces acting on an organization. It can be because businesses are a major part of economic operations and since there are many economic factors a business has to consider and manage simultaneously. Examples include supply-demand conditions, economic crises, financial issues like currency valuations, monetary and fiscal policies, etc.
- Social factors – These are those forces that affect a society wholly. Cultural factors play a huge role in influencing consumer preferences. For example, seasonality, festivals, or holidays are important social factors. Consumption and expenditure trends are other examples.
- Technological factors – Constant technological innovations in business and organizations are common. Companies should adopt these technologies to stay ahead or at least at par with competitors. For instance, one-touch payment systems, the use of AR in websites, etc.
- Legal factors – As the term suggests, these factors are related to the legal system of the companies' country. For example, new laws, amendments, minimum wages, taxation, working hours, restrictions, etc., can affect the business operations and profits.
- Environmental factors – Climate change and global warming are becoming major causes of environmental concern. With rising awareness, companies are required to exhibit a certain degree of responsibility towards the environment. When they fail to do so, the public realizes it, and the firm faces losses. Using renewable energy sources, reducing plastic usage, and active involvement in environmental programs are some examples.
- Competitive factors – Competitors are another major external force affecting a firm through its operations. If the competitor implements a low-pricing strategy or introduces a new innovative product, it could sweep away a firm's sales.
How External Factors Affect Business?
A company is a business entity constantly interacting with other units in an environment – suppliers, sellers, investors, employees, customers, government, competitors, and the general public. As a result, there is a constant flow of resources and capital. Within this, employees are the only units the firm can influence; however, not absolute. One example is the labor unions.
In a perpetual pipeline of participants, there is too much at stake for the company if a particular point presents some issue. These issues can be decreased sales, a fall in profits due to increased costs, a loss of customer base, stagnant growth, supply-side issues, etc. Of course, some positive factors can affect sales, costs, profits, operations, customers, production, etc.
Examples
Refer to the following examples to understand the external factors of the business environment better:
Example #1
EXP123 is a company involved in the export business. The company procures domestic goods and exports them to Asia. Recently, the company has faced many issues owing to external factors. First, the company's top markets were Russia and Ukraine, both amidst a war. Secondly, global inflation and fears of recession worldwide have led to a fall in importer confidence.
Example #2
Alibaba is a well-known Chinese e-commerce company. In July 2022, Chairman and Chief Executive Officer Daniel Zhang claimed that the last financial year, i.e., 2021, was when the company faced the most severe external environment. The factors stated include the country's political, technological, and social issues.
The COVID-19 pandemic, international geopolitical conflicts, and the expectations of China's internet sector have pushed the share price to 50%. In addition, the company faced a $2.7 billion fine from the government.
External Factors vs Internal Factors
External Factors
- By definition, these factors act from outside the firm and affect the business internally and externally.
- Beyond the firm's control.
- The best solution is to be prepared with a response and manage the consequences.
- Examples – change in government, inflation, new legislation, etc.
Internal Factors
- Internal factors act from within and inside an organization and have internal and external effects.
- Well within the company's hands and easier to control.
- The best solution is to avoid any negative forces and develop positive ones.
- Examples – change in management, employee policies, price rise, etc.
