Table Of Contents
What is Expanded Accounting Equation?
Expanded Accounting Equation refers to the expanded version of the basic accounting equation for the particular corporation / sole proprietor, giving detailed information about financial transactions of the corporation, such as assets, liabilities, share capital, income, expenses, and withdrawals.
The Expanded Accounting equation is generally different for varying forms of businesses. The equation differs slightly in the case of a proprietary concern, partnership firm, and corporation.
For a proprietary concern, the equation will be:
Assets = Owner’s Capital – Drawings + Liabilities + Income – Expenses
For a partnership firm, the equation will be:
Assets = Partner’s Capital – Distributions + Liabilities + Income – Expenses
For a corporation, the equation will be:
Assets = Stockholder Equity + Retained Earnings
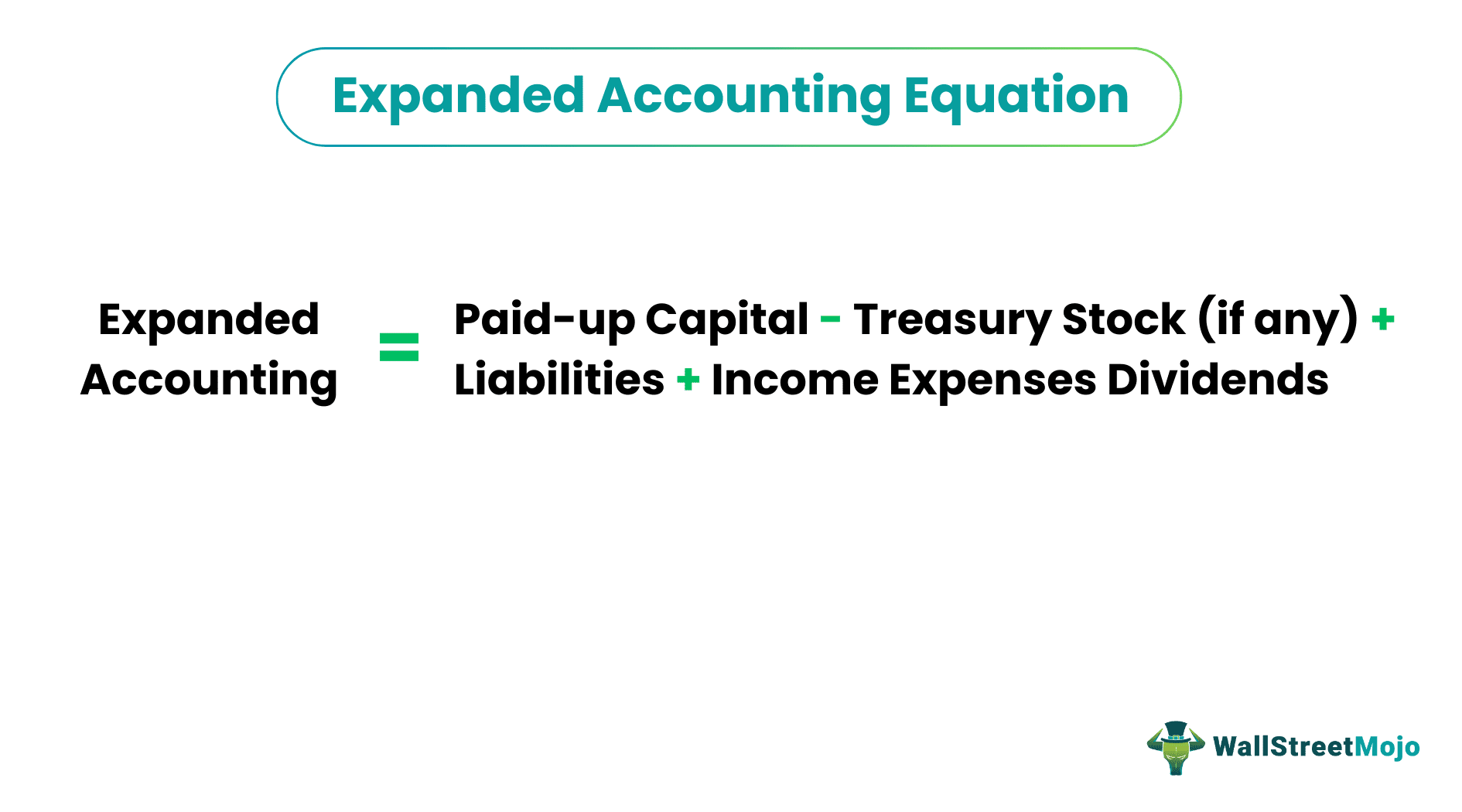
Expanded Accounting Equation = Paid-up Capital – Treasury Stock (if any) + Liabilities + Income – Expenses - Dividends
- Stockholders Equity is the sum of the Paid-up capital of the organization reduced by Treasury stock. TTreasury stock means the amount of equity stock in which the organization had earlier issues but repurchased/reacquired subsequently.
- Retained Earnings are arrived at by reducing the expenses and dividends from the revenue.
Example of Expanded Accounting Equation
Let us take the example of Foods & Drugs Inc. The Company was incorporated on 1 June 2019 with a paid-up capital consisting of 1000 shares having a value of $50. During the first quarter of its operations, the company has entered into the following transactions:
| Date | Transaction |
|---|---|
| 1-Jun | Capital introduced - $ 50,000 |
| 6-Jun | Paid $10,000 for purchase of furniture and computers. |
| 15-Jun | Paid $ 5,000 towards purchase of machinery and equipment. Paid $ 1,000 towards purchase of raw materials |
| 22-Jun | Incurred expenditure towards advertising and marketing amounting to $200 |
| 30-Jun | Paid salaries to its employees - $13,000 |
| 30-Jun | Paid Rent and telephone bills - $15,000 |
| 13-Jul | Earned revenue through sale of products worth $ $ 35,000 |
| 18-Jul | Made payments towards petty cash and bills for $ 1,500 |
| 31-Jul | Paid salaries to its employees - $13,000 |
| 31-Jul | Paid Rent and telephone bills - $13,500 |
| 05-Aug | Received $28,000 as an advance from suppliers for future orders |
| 26-Aug | Purchased raw materials costing $5,000 on credit |
| 31-Aug | Paid salaries to its employees - $13,000 |
| 31-Aug | Paid Rent and telephone bills - $17,000 |
| 31-Aug | Paid $1,000 as dividend |
| 31-Aug | Miscellaneous expenses paid $3,000 |
Solution
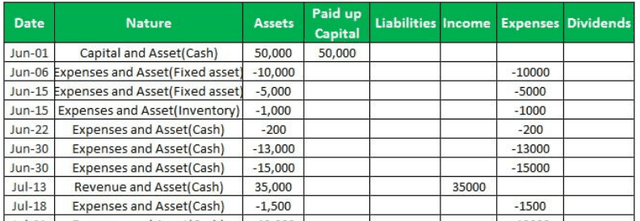
Below table provides the segregation of the aforementioned details under specific heads:

- Assets = Paid-up Capital – Treasury Stock (if any) + Liabilities + Income – Expenses - Dividends
- Assets = 50000 – 0 + 0 + 63000 – (-110200) – (-1000)
- = 1800
Relevance and Use
It is an important concept from the accounting point of view because it provides a picture of the organization's financial well-being. The accounting equation includes information from the balance sheet and provides information about the income-expenditure statement.
As seen in the example above, the net result of the expanded accounting equation is such that the corporation's assets are equal to the net impact of stockholder equity, liabilities, and net earnings. A balanced equation also ensures that the whole accounting process has been followed properly. It further helps strengthen the fact that all the debit and credit entries about all transactions entered during the period have been considered.
It shows the effect of every transaction taking place and how it affects the corporation's liabilities. Further, it also elaborates on the detailed aspects of any increase in cash flows on account of revenue earned or any decrease in cash flows on expenses incurred for running the operations.
Organizations use the equation to understand a holistic and descriptive financial statement picture. It can be used for deep diving into the organization's financial transactions, thereby also in the detailed analysis of the financial statements.
Professionals use it to understand the effectiveness of the accounting policies followed by the organization.