Table Of Contents
What Are Excess Reserves?
Excess Reserves refer to the amount kept or deposited with the principal or central regulatory authority (in India, Reserve Bank of India) over and above the statutory requirements. If reserves are positive, it simply means that the bank has kept the amount in reserves more than the statutory requirement and vice versa. In the case of zero value, there is no deficit or surplus reserves balance kept.
Sometimes it is seen that the regulating bank pays interest on the amount extra deposited in the reserve account to encourage the banks to deposit their extra cash balance in the reserve account as it is very necessary for the overall growth of the economy to maintain the cash and funds of the economy properly.
Key Takeaways
- Excess reserves are funds that a bank retains or deposits with the central regulatory authority above and beyond the required statutory reserve requirements.
- A positive excess reserve occurs when a bank holds more than the required reserve amount, while a negative excess reserve occurs when a bank holds less than the required reserve amount.
- No surplus or deficit reserve balance is maintained when there is zero value.
- Banks with surplus reserves are better equipped to handle unexpected losses or significant cash demands, and they can address liquidity issues when cash supply is scarce.
Excess Reserves Explained
Excess reserve refers to the fund that is available in a bank or any financial institution that exceeds the minimum reserve that is required to be kept as per the law. Such reserves can be considered as a safety fund or a buffer that protects the institution against any unexpected fund withdrawal due to any unforeseen contingency.
Every bank has to hold a fixed sum of money as a reserve that they deposit with the central bank of the country where it operates. If the bank has any excess reserve, then the fund is used for lending, making investments or keeping as a safety provision.
Excess reserves in the banking system signifies that the financial institution is strong enough to meet its obligations and other day to day expenses. It signifies good financial health. However, on the other hand it also tell us that the fund is lying idle and not being used for any productive investment purpose, which means it is missing opportunities.
Sometimes banks and financial institutions tend to hold extra reserve as a measure to protect themselves as a precaution, in case there is any economic downturn or contingency that cannot be predicted beforehand. This helps them to absorb losses and also brings a stability to the financial system.
The Hargreaves Lansdown provides access to a range of investment products and services for UK investors.
Formula
Let us look at the formula that is used to calculate excess reserves.
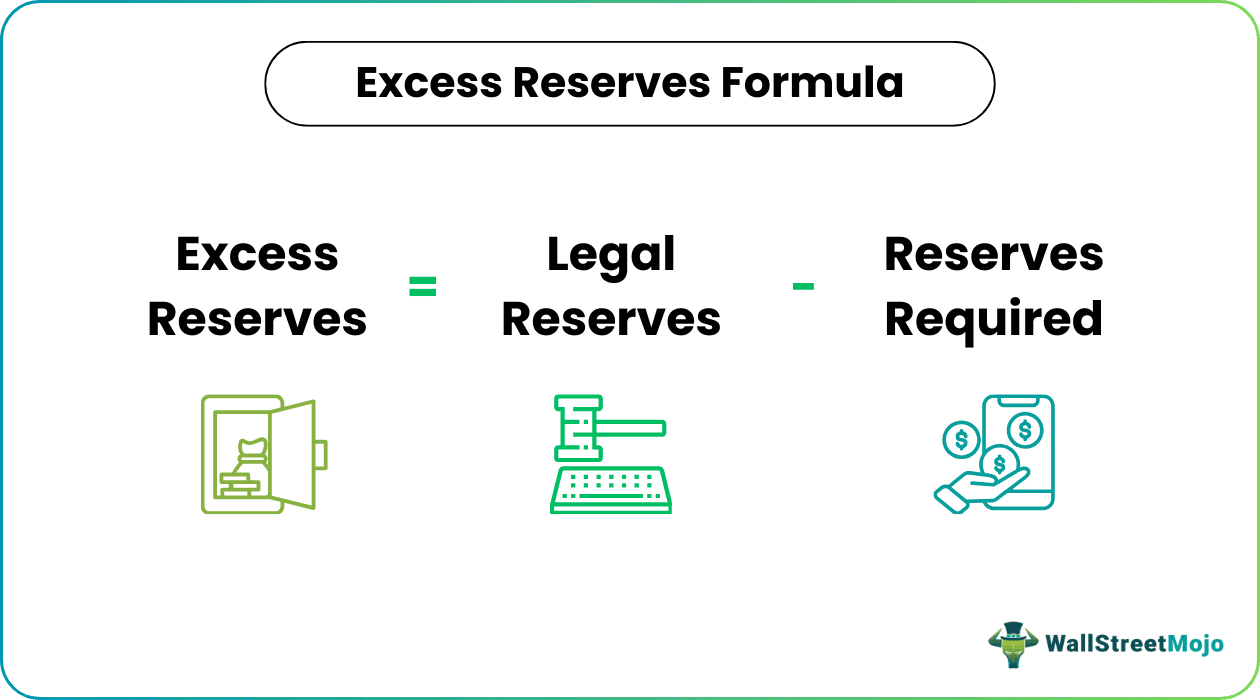
Excess Reserves Formula = Legal Reserves (Amount Deposited) – Reserves Required
How To Calculate?
Follow the below-given steps to check how to find excess reserves.
Calculate the amount required to be maintained per statutory requirements (reserves required). To calculate the minimum required to be maintained, the use of the below-given formula gives us the required results:
Minimum Requirement = Rate of Minimum Requirement * Total amount on which the rate applies
- Identify the amount kept or maintained by the bank in the reserves account with statutory authority (legal reserve). Take a total of all amounts deposited during the year in the reserve account maintained with the regulatory authority.
Calculate the difference between legal reserves calculated in step 2 above and reserves required computed in step 1 above. Mathematically represented as:
Excess Reserves = Legal Reserves (Amount Deposited) u2013 Reserves Required
Examples
Let us look at some examples to understand the concept better.
Example #1
The statutory guidelines for the bank are: Bank should maintain a minimum of 20(twenty) percent of their demand deposits with central regulating authority (let us say ABC Bank). Now, Bank P has demand deposits of $50,000,000 and has maintained $11,000,000 with ABC Bank. Now, by applying the above steps, we can calculate excess reserves as follows:
Solution
Given:
- Legal Reserves = $11,000,000
- Minimum reserve percentage = 20% of demand deposits
- Demand Deposits = $50,000,000

Calculation of Reserves Required

Statutory Requirement (Reserves Required) = Demand Deposits * 20%
- =50000000*20%
- Reserves Required =10000000
Calculation of the excess reserves can be done as follow –

- =11000000 - 10000000

Example #2
Bank PQR has deposited $35000 in reserves account and has total deposits of $75000. The reserves bank should maintain 150 percent of its deposits all the time. The rate of interest given by the regulatory bank on extra deposits is 3% per annum. We have to find out from the below-given options which option is the correct one regarding interest earned on excess reserves: a) $470 b) $675 c) $815 d) $715.
Solution
Given:
- Legal Reserves = $1000
- Minimum reserve percentage = 150% of deposits
- Deposits = $500

Calculation of Reserves Required

Statutory Requirement (Reserves Required) = Demand Deposits * 20%
- =500*150%
- = 750

- =1000 - 750

Example #3
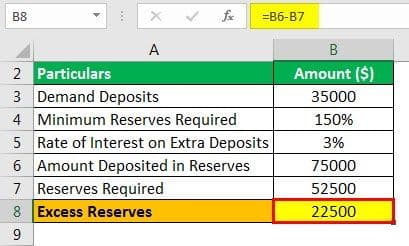
Let us see how to find excess reserves along with another example. Bank PQR has deposited $35000 in reserves account and has total deposits of $75000. The reserves bank should maintain 150 percent of its deposits all the time. The rate of interest given by the regulatory bank on extra deposits is 3% per annum. We have to find out from the below-given options which option is the correct one regarding interest earned on excess reserves: a) $470 b) $675 c) $815 d) $715.
Solution
Given:
- Legal Reserves = $75000
- Minimum reserve percentage = 150% of deposits
- Deposits = $35000

Calculation of Reserves Required

Statutory Requirement (Reserves Required) = Demand Deposits * 20%
- = $3500*150%
- = $52500
Calculation of the excess reserves can be done as follow –

- = $75000 - $52500

Interest Income on Extra Deposits

Interest Income on Extra Deposits = Excess Reserves * Rate of Interest.
- = $22500*3%
- = $675
Advantages
Let us try to understand the importance of excess reserves equation.
- Those banks who have maintained excess reserves are more secure in sudden loss or a situation of heavy cash demand.
- The excess reserves equation resolve the liquidity issues of the bank in the situation when there is a shortage in the supply of cash.
- If there are excess reserves in the banking system, they may deposit the same with the regulatory bank. They can earn interest thereupon if the same is above the minimum requirement. For example, if Bank A must maintain $500 as minimum reserves and has deposited $750 in the reserve account, the statutory bank pays them interest over $250 for the period they were deposited.
Disadvantages
It is also important to analyse the disadvantages of this type of reserve.
- Holding reserves which are in excess of the statutory requirement signifies that the money is lying idle, which is a negative situation. The fund could have been used for some productive investment or giving out as loans.
- It can be derived from the above point that the hoarded fund is not being lent out to borrowers. Interest earned from loan is the main source of income for any bank or financial institution. If that is not done then it is a waste of resource.
- The opportunity cost of holding the money is the return earned from investments which is likely to be much higher that the return from holding the excess reserve.
- In case of inflation, the value of the money held as reserve falls because it is not invested and thus the money is not multiplied to match the current value.
- The rules and regulation may become strict so that it becomes compulsory to abide by certain laws in case the banks hold a large amount of fund.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.