The differences between these concepts are given as follows:
Table of Contents
What Are Eurodollar Futures?
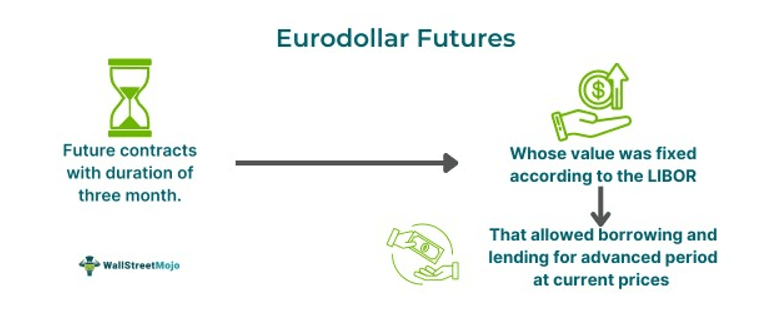
Eurodollar futures contracts are known for being cash-settled whose price fluctuates in proportion to the LIBOR (London Interbank Offered Rate) interest rate. Eurodollar futures allow businesses and banks to secure an interest rate today for money they want to lend or borrow in the future.
In essence, the contract price reflects the LIBOR's anticipated value at the time of settlement. If the user has exposure to the U.S. dollar, these products are an excellent risk-management tool. Eurodollar futures contracts are employed by a wide range of entities, including banks, commercial businesses, proprietary trading organizations, hedge funds and individuals.
Key Takeaways
- CME eurodollar futures are interest rate-based contracts used by businesses and banks to secure future borrowing rates.
- The Eurodollar time deposit instrument, with a principal value of one million U.S. dollars, has a three-month maturity period and allows the seller to transfer the cash position upon expiry.
- Their advantages: high liquidity, trustworthiness, and flexibility.
- CME Group has converted open interest into SOFR contracts, allowed traders to hedge using Eurodollar futures until their expiry dates, leveraging gains to offset potential losses if SOFR rates increase.
Eurodollar Futures Explained
The Eurodollar futures contract is a contract that is interest rate-based. These are three-month contracts ON a $1 million Eurodollar deposit. CME (Chicago Mercantile Exchange) began offering cash-settled futures contracts in 1981, and it is the first cash-settled futures contract. Its operations happen during both the American and Asian trading hours. Anyone with a futures brokerage account can use the instrument.
Eurodollar time deposit is the instrument's underlying asset, and its principal value is one million U.S. dollars. They have a fixed maturity period of three months. On the expiry of the contract, the seller has the option of transferring the cash position instead of delivering the underlying asset. Eurodollar futures are often employed to hedge fixed-income obligations, particularly fixed-income derivatives. The CME supports trading in complete strips known as bundles.
They are popular with market participants such as businesses and banks. This is due to their ability to lock in current interest rates on a future borrowing fund. This enables businesses to settle international transactions, invest extra funds, and extend short-term loans, and fund exports and imports. Banks employ these securities to hedge against anticipated FOREX risks while trading fixed-income derivatives. This is because the U.S. dollar's liquidity enables them to finance dollar-denominated loans without incurring exchange risks.
Examples
Let us look into a few examples to understand the concept better
Example #1 - Hypothetical
Imagine Dan, an individual investor with a keen interest in understanding financial markets. Recently, he stumbled upon an intriguing financial instrument known as Eurodollar futures. Curious to learn more, Dan delves into the mechanics of these futures contracts. CME eurodollar futures are traded using a price index, which determines their value. The index is calculated by subtracting the interest rate of the futures contract from 100. For instance, if the interest rate is set at 5%, the index price would be $95 (100 - 5 = 95). Excited by this concept, Dan realizes that he can ascertain the interest rate by examining the quoted value of a futures contract. For example, if a futures contract is quoted at $91.50, Dan understands that the associated interest rate is 8.5%.
Example #2 - Real-life example
CME Group, the world's leading derivatives marketplace, proposed the conversion of Eurodollar futures and options open interest into corresponding SOFR (Secured Overnight Financing Rate) contracts on April 14, 2023, under the company's fallbacks plan. Eurodollar futures and options contracts expiring before June 30, 2023, continued trading until their expiry. The proposed conversion date helped clients complete their operational work early in the transition process and aligned with recently published industry timelines for over-the-counter interest rate swaps.
In August, CME Group reported a record average daily volume that equaled 2.5 million contracts and a record open interest of 19 million contracts for SOFR futures and options contracts. SOFR options experienced record volume and open interest in August, while SOFR futures had record open interest during the same period.
Prior to the final conversion under fallbacks, liquid standard and reduced-tick Inter-Commodity Spread (ICS) instruments were available to facilitate the voluntary conversion of Eurodollar open interest via the SED Spread for futures and the L.S. Spread for options. CME Group had planned to add SOFR options to its portfolio margining solution for cleared products in December 2022, subject to regulatory approval. SOFR futures and options had broad participation from global banks, hedge funds, asset managers, principal trading firms, and other traders.
Advantages And Disadvantages
Some of the advantages and disadvantages of the concept are given as follows:
Advantages
- High liquidity: One of the major advantages of the instrument is that it is highly liquid. the Eurodollar futures chart have been positive and it had surpassed crude oil futures. The liquidity it has shown over the years attracts investors, especially those who are looking for instruments with open interest rates and notable daily trading volume that similarly change other points.
- Trustworthy: The instruments are tied to LIBOR and it has been over four decades after launch. All through the years they have given a stable performance. This garnered the trust of many investors and thus is a reliable choice.
- Versatile: The Eurodollar future provides flexibility through a variety of derivatives. This provides users with a variety of choices which they may choose according to their preferences.
Disadvantages
- Geopolitical unrest: Geopolitical elements such as trade conflicts and tariff impositions have the potential to disrupt global trade and impact the import-export activities of businesses. Similarly, a decline in economic activity may result in reduced demand for these instruments and the Eurodollar futures chart may show negative signs. This is because many rely on Eurodollar futures to hedge against interest rate fluctuations, and reduced demand will consequently drive down their prices. these may contribute to the shift in eurodollar futures curve.
- Impact of upcoming news events: The instruments depend on the Federal Reserve policy trajectory, and hence, any decisions or news regarding meetings of the Fed creates uproar. The volatility may cause a shift in eurodollar futures curve, a price increase or decrease.
- Not beginner friendly: Trading the Eurodollar financial futures contract demands a comprehensive grasp of concepts. They may include knowledge of yield curves, adjustments, and convexity biases etc. These may be complex for a beginner to understand.
Eurodollar futures vs FRA
| Points | Eurodollar futures | FRA |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Concept | US dollar time deposits held in banks outside the United States, traded as futures. | A Forward Rate Agreement (FRA) is a forward contract based on interest rates, primarily in U.S. dollar contracts, favored by major banks. |
| 2. Functioning | Eurodollar futures, cash-settled contracts, fluctuate with LIBOR interest rates, determined by the three-month LIBOR at expiration. | FRAs, acquired through investment banks, involve cash-settled agreements where payouts depend on future interest rates like three-month ICE LIBOR. Parties agree on interest rates for hypothetical deposits set to begin on future dates. |
| 3. Essence | Eurodollar futures prices reflect FRAs in the market, allowing arbitrage opportunities when prices misalign. | Investment banks obtain customizable FRAs, managing risks through Eurodollar futures. |
